Abstract
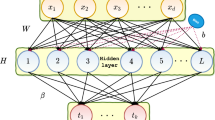
Extreme Learning Machine (ELM) or Randomized Neural Network (RNN) is a feedforward neural network where the network weights between the input and the hidden layer are not learned; they are assigned from some probability distribution. The weights between the hidden layer and the output targets are learnt. Neural networks are believed to mimic the human brain; it is well known that the brain is a redundant network. In this work we propose to explicitly model the redundancy of the human brain. We model redundancy as linear dependency of link weights; this leads to a low-rank model of the output (hidden layer to target) network. This is solved by imposing a nuclear norm penalty. The proposed technique is compared with the basic ELM and the Sparse ELM. Results on benchmark datasets, show that our method outperforms both of them.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Paul, S., Boutsidis, C., Magdon-Ismail, M., Drinea, P.: Random projections for linear support vector machines. ACM Trans. Knowl. Disc. Data 8(4) (2014). Article 22
Shi, Q., Shen, C., Hill, R., van den Hengel. A.: Is margin preserved after random projection? In: ICML (2012)
Huang, G.-B., Zhu, Q.-Y., Siew, C.-K.: Extreme learning machine: theory and applications. Neurocomputing 70, 489–501 (2006)
Scardapane, S., Comminiello, D., Scarpiniti, M., Uncini, A.: Online sequential extreme learning machine with kernels. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst. 26(9), 2214–2220 (2015)
Zhou, Y., Peng, J., Chen, C.L.P.: Extreme learning machine with composite kernels for hyperspectral image classification. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sen. 8(6), 2351–2360 (2015)
LeCun, Y.: Optimal Brain Damage. In: NIPS (1990)
Thom, M., Palm, G.: Sparse activity and sparse connectivity in supervised learning. J. Mach. Learn. Res. 14, 1091–1143 (2013)
Gripon, V.: Sparse neural networks with large learning diversity. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst. 22(7), 1087–1096 (2011)
Glorot, X., Bordes, A., Bengio, Y.: Deep sparse rectifer neural networks. In: AISTATS 2011 (2011)
Bai, Z., Huang, G.-B., Wang, D., Wang, H., Westover, M.B.: Sparse extreme learning machine for classification. IEEE Trans. Cybern. 44(10), 1858–1870 (2014)
Gogna, A., Majumdar, A.: Matrix completion incorporating auxiliary information for recommender system design. Expert Syst. Appl. 42(5), 5789–5799 (2015)
Majumdar, A., Ward, R.K.: Increasing energy efficiency in sensor networks: blue noise sampling and non-convex matrix completion. Int. J. Sens. Netw. 9(3/4), 158–169 (2011)
Jindal, A., Psounis, K.: Modeling spatially correlated data in sensor networks. ACM Trans. Sensor Netw. 2(4), 466–499 (2006)
Pal, P., Vaidyanathan, P.P.: A grid-less approach to underdetermined direction of arrival estimation via low rank matrix denoising. IEEE Sign. Proces. Lett. 21(6), 737–741 (2014)
Gogna, A., Shukla, A., Majumdar, A.: Matrix Recovery using Split Bregman. In: International Conference on Pattern Recognition (2014)
Majumdar, A., Ward, R.K.: Some empirical advances in matrix completion. Sign. Process. 91(5), 1334–1338 (2011)
Chartrand, R.: Nonconvex splitting for regularized low-rank + sparse decomposition. IEEE Trans. Sig. Process. 60, 5810–5819 (2012)
Wright, J., Yang, A., Ganesh, A., Sastry, S., Ma, Y.: Robust face recognition via sparse representation. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 31(2), 210–227 (2009)
http://www.iro.umontreal.ca/~lisa/twiki/bin/view.cgi/Public/MnistVariations
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2016 Springer International Publishing AG
About this paper
Cite this paper
Gogna, A., Majumdar, A. (2016). Nuclear Norm Regularized Randomized Neural Network. In: Hirose, A., Ozawa, S., Doya, K., Ikeda, K., Lee, M., Liu, D. (eds) Neural Information Processing. ICONIP 2016. Lecture Notes in Computer Science(), vol 9948. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-46672-9_17
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-46672-9_17
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-319-46671-2
Online ISBN: 978-3-319-46672-9
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)