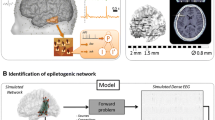
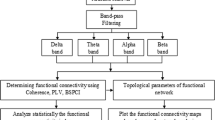
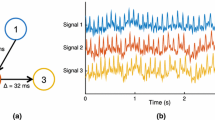
Abstract
Epilepsy is one of the most common brain disorders and affect people of all ages. Resective surgery is currently the most effective overall treatment for patients whose seizures cannot be controlled by medications. Seizure spread network with secondary epileptogenesis are thought to be responsible for a substantial portion of surgical failures. However, there is still considerable risk of surgical failures for lacking of priori knowledge. Cortico-cortical evoked potentials (CCEP) offer the possibility of understanding connectivity within seizure spread networks to know how seizure evolves in the brain as it measures directly the intracranial electric signals. This study is one of the first works to investigate effective seizure spread network modeling using CCEP signals. The previous unsupervised brain network connectivity problem was converted into a classical supervised sparse representation problem for the first time. In particular, we developed an effective network modeling framework using sparse representation of over-determined features extracted from extensively designed experiments to predict real seizure spread network for each individual patient. The experimental results on five patients achieved prediction accuracy of about 70 %, which indicates that it is possible to predict seizure spread network from stimulated CCEP networks. The developed CCEP signal analysis and network modeling approaches are promising to understand network mechanisms of epileptogenesis and have a potential to render clinicians better epilepsy surgical decisions in the future.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Barabási, A.L., Albert, R.: Emergence of scaling in random networks. Science 286(5439), 509–512 (1999)
Bullmore, E., Sporns, O.: Complex brain networks: graph theoretical analysis of structural and functional systems. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 10(3), 186–198 (2009)
Deco, G., Tononi, G., Boly, M., Kringelbach, M.L.: Rethinking segregation and integration: contributions of whole-brain modelling. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 16(7), 430–439 (2015)
Delorme, A., Makeig, S.: EEGLAB: an open source toolbox for analysis of single-trial EEG dynamics including independent component analysis. J. Neurosci. Methods 134(1), 9–21 (2004)
Donoho, D.L., Tsaig, Y.: Fast solution of-norm minimization problems when the solution may be sparse. IEEE Trans. Inf. Theory 54(11), 4789–4812 (2008)
Enatsu, R., Piao, Z., OConnor, T., Horning, K., Mosher, J., Burgess, R., Bingaman, W., Nair, D.: Cortical excitability varies upon ictal onset patterns in neocortical epilepsy: a cortico-cortical evoked potential study. Clin. Neurophysiol. 123(2), 252–260 (2012)
Friston, K.J.: Functional and effective connectivity: a review. Brain Connect. 1(1), 13–36 (2011)
Guan, Z.H., Liu, F., Li, J., Wang, Y.W.: Chaotification of complex networks with impulsive control. Chaos: Interdisc. J. Nonlinear Sci. 22(2), 023137 (2012)
Snead, O.C.: Basic mechanisms of generalized absence seizures. Annals. Neurol. 37(2), 146–157 (1995)
Jefferys, J.G.: Advances in understanding basic mechanisms of epilepsy and seizures. Seizure 19(10), 638–646 (2010)
Keller, C.J., Honey, C.J., Entz, L., Bickel, S., Groppe, D.M., Toth, E., Ulbert, I., Lado, F.A., Mehta, A.D.: Corticocortical evoked potentials reveal projectors and integrators in human brain networks. J. Neurosci. 34(27), 9152–9163 (2014)
Keller, C.J., Honey, C.J., Mégevand, P., Entz, L., Ulbert, I., Mehta, A.D.: Mapping human brain networks with cortico-cortical evoked potentials. Phil. Trans. R. Soc. B 369(1653), 20130528 (2014)
Kim, D.W., Kim, H.K., Lee, S.K., Chu, K., Chung, C.K.: Extent of neocortical resection and surgical outcome of epilepsy: intracranial EEG analysis. Epilepsia 51(6), 1010–1017 (2010)
Kreuz, T.: Measures of neuronal signal synchrony. Scholarpedia 6(12), 11922 (2011). (Revision 152249)
Lega, B., Dionisio, S., Flanigan, P., Bingaman, W., Najm, I., Nair, D., Gonzalez-Martinez, J.: Cortico-cortical evoked potentials for sites of early versus late seizure spread in stereoelectroencephalography. Epilepsy Res. 115, 17–29 (2015)
Letzen, J.E., Craggs, J.G., Perlstein, W.M., Price, D.D., Robinson, M.E.: Functional connectivity of the default mode network and its association with pain networks in irritable bowel patients assessed via lidocaine treatment. J. Pain 14(10), 1077–1087 (2013)
Liu, J., Ji, S., Ye, J., et al.: SLEP: sparse learning with efficient projections. Ariz. State Univ. 6, 491 (2009)
Nathan, S.S., Sinha, S.R., Gordon, B., Lesser, R.P., Thakor, N.V.: Determination of current density distributions generated by electrical stimulation of the human cerebral cortex. Electroencephalogr. Clin. Neurophysiol. 86(3), 183–192 (1993)
Newman, M.E.: The structure and function of complex networks. SIAM Rev. 45(2), 167–256 (2003)
Otti, A., Guendel, H., Henningsen, P., Zimmer, C., Noll-Hussong, M.: Functional network connectivity of pain-related resting state networks in somatoform pain disorder: an exploratory fMRI study. J. Psychiatry Neurosci.: JPN 38(1), 57 (2013)
Sporns, O.: Structure and function of complex brain networks. Dialogues Clin. Neurosci. 15(3), 247–262 (2013)
Sporns, O., Tononi, G., Kötter, R.: The human connectome: a structural description of the human brain. PLoS Comput. Biol. 1(4), e42 (2005)
Uddin, L.Q., Clare Kelly, A., Biswal, B.B., Xavier Castellanos, F., Milham, M.P.: Functional connectivity of default mode network components: correlation, anticorrelation, and causality. Hum. Brain Mapp. 30(2), 625–637 (2009)
Vecchio, F., Miraglia, F., Curcio, G., Della Marca, G., Vollono, C., Mazzucchi, E., Bramanti, P., Rossini, P.M.: Cortical connectivity in fronto-temporal focal epilepsy from EEG analysis: a study via graph theory. Clin. Neurophysiol. 126(6), 1108–1116 (2015)
Wang, H., Fan, W., Yu, P.S., Han, J.: Mining concept-drifting data streams using ensemble classifiers. In: Proceedings of the Ninth ACM SIGKDD International Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Data Mining, pp. 226–235. ACM (2003)
Watts, D.J., Strogatz, S.H.: Collective dynamics of small-world networks. Nature 393(6684), 440–442 (1998)
Wright, S.J., Nowak, R.D., Figueiredo, M.A.: Sparse reconstruction by separable approximation. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 57(7), 2479–2493 (2009)
Yaffe, R.B., Borger, P., Megevand, P., Groppe, D.M., Kramer, M.A., Chu, C.J., Santaniello, S., Meisel, C., Mehta, A.D., Sarma, S.V.: Physiology of functional and effective networks in epilepsy. Clin. Neurophysiol. 126(2), 227–236 (2015)
Ye, J., Liu, J.: Sparse methods for biomedical data. ACM SIGKDD Explor. Newsl. 14(1), 4–15 (2012)
Zhou, J., Seeley, W.W.: Network dysfunction in Alzheimers disease and frontotemporal dementia: implications for psychiatry. Biol. Psychiatry 75(7), 565–573 (2014)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2016 Springer International Publishing AG
About this paper
Cite this paper
Liu, F., Xiang, W., Wang, S., Lega, B. (2016). Prediction of Seizure Spread Network via Sparse Representations of Overcomplete Dictionaries. In: Ascoli, G., Hawrylycz, M., Ali, H., Khazanchi, D., Shi, Y. (eds) Brain Informatics and Health. BIH 2016. Lecture Notes in Computer Science(), vol 9919. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-47103-7_26
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-47103-7_26
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-319-47102-0
Online ISBN: 978-3-319-47103-7
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)