Abstract
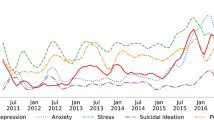
Student resilience and emotional wellbeing are essential for both academic and social development. Earlier studies on tracking students’ happiness in academia showed that many of them struggle with mental health issues. For example, a 2015 study at the University of California Berkeley found that 47 % of graduate students suffer from depression, following a 2005 study that showed 10 % had considered suicide. This is the first large-scale study that uses signals from social media to evaluate students’ emotional wellbeing in academia. This work presents fine-grained emotion and opinion analysis of 79,329 tweets produced by students from 44 universities. The goal of this study is to qualitatively evaluate and compare emotions and sentiments emanating from students’ communications across different academic discourse types and across universities in the U.S. We first build novel predictive models to categorize academic discourse types generated by students into personal, social, and general categories. We then apply emotion and sentiment classification models to annotate each tweet with six Ekman’s emotions – joy, fear, sadness, disgust, anger, and surprise and three opinion types – positive, negative, and neutral. We found that emotions and opinions expressed by students vary across discourse types and universities, and correlate with survey-based data on student satisfaction, happiness and stress. Moreover, our results provide novel insights on how students use social media to share academic information, emotions, and opinions that would pertain to students academic performance and emotional well-being.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
Notes
- 1.
EmoTag Project: http://nil.fdi.ucm.es/index.php?q=node/186.
- 2.
- 3.
Google+ API –https://developers.google.com/+/web/api/rest/.
- 4.
Twitter API – https://dev.twitter.com/rest/public.
- 5.
Freebase – https://www.freebase.com/.
- 6.
- 7.
- 8.
Pretrained models were released during NAACL Tutorial on Social Media Predictive analytics: http://naacl.org/naacl-hlt-2015/tutorial-social-media.html.
- 9.
- 10.
- 11.
- 12.
- 13.
We found that correlations with Forbes university ranking are not significant.
- 14.
UC Berkeley report: http://ga.berkeley.edu/wellbeingreport/.
References
Benson, V., Morgan, S., Filippaios, F.: Social career management: social media and employability skills gap. Comput. Hum. Behav. 30, 519–525 (2014)
Chang, L., Krosnick, J.A.: National surveys via RDD telephone interviewing versus the internet comparing sample representativeness and response quality. Public Opin. Q. 73(4), 641–678 (2009)
Correa, T., Hinsley, A.W., De Zuniga, H.G.: Who interacts on the web? The intersection of users personality and social media use. Comput. Hum. Behav. 26(2), 247–253 (2010)
Desmet, P.M.: Designing emotion (2002)
Ekman, P.: An argument for basic emotions. Cogn. Emot. 6(3–4), 169–200 (1992)
Grosseck, G., Bran, R., Tiru, L.: Dear teacher, what should I write on my wall? A case study on academic uses of Facebook. Procedia Soc. Behav. Sci. 15, 1425–1430 (2011)
Han, K., Volkova, S., Corley, C.D.: Understanding roles of social media in academic engagement and satisfaction for graduate students. In: Proceedings of the ACM CHI Conference on Human Factors in Computing Systems, pp. 1215–1221. ACM (2016)
Jacobsen, W.C., Forste, R.: The wired generation: academic and social outcomes of electronic media use among university students. Cyberpsychol. Behav. Soc. Netw. 14(5), 275–280 (2011)
Junco, R., Heiberger, G., Loken, E.: The effect of Twitter on college student engagement and grades. J. Comput. Assist. Learn. 27(2), 119–132 (2011)
Knight, C.G., Kaye, L.K.: To tweet or not to tweet? A comparison of academics and students usage of Twitter in academic contexts. Innovations Educ. Teach. Int. pp. 1–11 (2014)
Kosinski, M., Stillwell, D., Graepel, T.: Private traits and attributes are predictable from digital records of human behavior. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 110, 5802–5805 (2013)
Lampos, V., Aletras, N., Preoţiuc-Pietro, D., Cohn, T.: Predicting and characterizing user impact on Twitter. In: Proceedings of the 14th Conference of the European Chapter of the Association for Computational Linguistics (EACL), pp. 405–413 (2014)
Li, J., Ritter, A., Hovy, E.: Weakly supervised user profile extraction from Twitter. In: Proceedings of ACL (2014)
Mikolov, T., Chen, K., Corrado, G., Dean, J.: Efficient estimation of word representations in vector space. arXiv preprint arXiv:1301.3781 (2013)
Mohammad, S.M., Kiritchenko, S.: Using hashtags to capture fine emotion categories from tweets. Comput. Intell. 31, 301–326 (2014)
Nakov, P., Rosenthal, S., Kozareva, Z., Stoyanov, V., Ritter, A., Wilson, T.: Semeval-2013 task 2: sentiment analysis in Twitter. In: Proceedings of SemEval, pp. 312–320 (2013)
O’Connor, B., Balasubramanyan, R., Routledge, B.R., Smith, N.A.: From tweets to polls: linking text sentiment to public opinion time series. In: Proceedings of ICWSM, pp. 122–129 (2010)
Pak, A., Paroubek, P.: Twitter as a corpus for sentiment analysis and opinion mining. In: Proceedings of LREC (2010)
Pang, B., Lee, L.: Opinion mining and sentiment analysis. Found. Trends IR 2(1–2), 1–135 (2008)
Pang, B., Lee, L., Vaithyanathan, S.: Thumbs up? Sentiment classification using machine learning techniques. In: Proceedings of EMNLP, pp. 79–86 (2002)
Pedregosa, F., Varoquaux, G., Gramfort, A., Michel, V., Thirion, B., Grisel, O., Blondel, M., Prettenhofer, P., Weiss, R., Dubourg, V., Vanderplas, J., Passos, A., Cournapeau, D., Brucher, M., Perrot, M., Duchesnay, E.: Scikit-learn: machine learning in Python. J. Mach. Learn. Res. 12, 2825–2830 (2011)
Pennington, J., Socher, R., Manning, C.D.: Glove: global vectors for word representation. In: Proceedings of EMNLP, vol. 14, pp. 1532–1543 (2014)
Perrin, A.: Social media usage: 2005–2015 (2015)
Priem, J., Costello, K.L.: How and why scholars cite on Twitter. Proc. Am. Soc. Inf. Sci. Technol. 47(1), 1–4 (2010)
Qadir, A., Riloff, E.: Bootstrapped learning of emotion hashtags# hashtags4you. In: Proceedings of WASSA (2013)
Roberts, K., Roach, M.A., Johnson, J., Guthrie, J., Harabagiu, S.M.: Empatweet: annotating and detecting emotions on Twitter. In: Proceedings of LREC (2012)
Roblyer, M.D., McDaniel, M., Webb, M., Herman, J., Witty, J.V.: Findings on Facebook in higher education: a comparison of college faculty and student uses and perceptions of social networking sites. Internet High. Educ. 13(3), 134–140 (2010)
Salathé, M., Khandelwal, S.: Assessing vaccination sentiments with online social media: implications for infectious disease dynamics and control. PLoS Comput. Biol. 7(10), e1002199 (2011)
Strapparava, C., Mihalcea, R.: Semeval-2007 task 14: affective text. In: Proceedings of SemEval, pp. 70–74 (2007)
Veletsianos, G.: Higher education scholars’ participation and practices on Twitter. J. Comput. Assist. Learn. 28(4), 336–349 (2012)
Volkova, S., Yoram, B.: On predicting sociodemographic traits and emotions from communications in social networks and their implications to online self-disclosure. Cyberpsychol. Behav. Soc. Netw. 18(12), 726–736 (2015)
Volkova, S., Bachrach, Y., Armstrong, M., Sharma, V.: Inferring latent user properties from texts published in social media (demo). In: Proceedings of AAAI (2015)
Wang, W., Chen, L., Thirunarayan, L., Sheth, A.P.: Harnessing Twitter big data for automatic emotion identification. In: Proceedings of SocialCom, pp. 587–592 (2012)
Zheng, S., Han, K., Rosson, M.B., Carroll, J.: The role of social media in MOOCs: how to use social media to enhance student retention. In: Proceedings of the ACM Conference on Learning@ Scale, pp. 419–428. ACM (2016)
Zhu, X., Kiritchenko, S., Mohammad, S.M.: NRC-Canada-2014: recent improvements in the sentiment analysis of tweets. In: Proceedings of SemEval (2014)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2016 Springer International Publishing AG
About this paper
Cite this paper
Volkova, S., Han, K., Corley, C. (2016). Using Social Media to Measure Student Wellbeing: A Large-Scale Study of Emotional Response in Academic Discourse. In: Spiro, E., Ahn, YY. (eds) Social Informatics. SocInfo 2016. Lecture Notes in Computer Science(), vol 10046. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-47880-7_32
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-47880-7_32
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-319-47879-1
Online ISBN: 978-3-319-47880-7
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)