Abstract
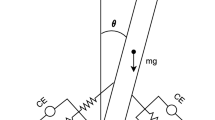
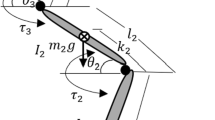
Maintenance of upright stance is one of the basic requirements in human daily life. Stance postural control is achieved based on multisensory inputs such as visual, vestibular and proprioceptive somatosensory inputs. In this paper, we proposed a stance postural control model including a neural controller with feed-forward inputs (muscle stiffness regulation) and sensory feedback of vestibular and proprioceptive somatosensory sensation. Through the optimization, variables of neural controller were designed to keep a musculoskeletal model standing during a 5 s forward dynamics simulation. From the results, we found that when both vestibular and proprioceptive somatosensory sensory input are available, low muscle stiffness is enough to maintain the balance of a musculoskeletal model in a stance posture. However, when vestibular sensory input get lost, higher muscle stiffness will be desired to keep the musculoskeletal model standing.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Hwang, S., Agada, P., Kiemel, T., Jeka, J.J.: Dynamic reweighting of three modalities for sensor fusion. PloS one 9(1) (2014)
Peterka, R.: Sensorimotor integration in human postural control. J. Neurophys. 88(3), 1097–1118 (2002)
Chiba, R., Ogawa, H., Takakusaki, K., Asama, H., Ota, J.: Muscle activities changing model by difference in sensory inputs on human posture control. In: Intelligent Autonomous Systems 12, pp. 479–491. Springer (2013)
Masani, K., Vette, A.H., Popovic, M.R.: Controlling balance during quiet standing: proportional and derivative controller generates preceding motor command to body sway position observed in experiments. Gait & posture 23(2), 164–172 (2006)
Asai, Y., Tasaka, Y., Nomura, K., Nomura, T., Casadio, M., Morasso, P.: A model of postural control in quiet standing: robust compensation of delay-induced instability using intermittent activation of feedback control. PLoS One 4(7), e6169–e6169 (2009)
van der Kooij, H., Jacobs, R., Koopman, B., Grootenboer, H.: A multisensory integration model of human stance control. Biol. Cybern. 80(5), 299–308 (1999)
Jo, S., Massaquoi, S.G.: A model of cerebellum stabilized and scheduled hybrid long-loop control of upright balance. Biol. Cybern. 91(3), 188–202 (2004)
Jiang, P., Chiba, R., Takakusaki, K., Ota, J.: Stance postural control of a musculoskeletal model able to compensate neurological time delay. In: 2014 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Biomimetics (ROBIO), pp. 1130–1135, Dec 2014
Jiang, P., Chiba, R., Takakusaki, K., Ota, J.: Generation of biped stance motion in consideration of neurological time delay through forward dynamics simulation. In: 2015 International Symposium on Micro-NanoMechatronics and Human Science, pp. 205–208, Nov 2015
Au, C.: Gait 2392 and 2354 models (2013)
Hicks, J.: Simulation-based design to prevent ankle injuries (2014)
Millard, M., Uchida, T., Seth, A., Delp, S.L.: Flexing computational muscle: modeling and simulation of musculotendon dynamics. J. Biomech. Eng. 135(2), 021005 (2013)
Masani, K., Popovic, M.R., Nakazawa, K., Kouzaki, M., Nozaki, D.: Importance of body sway velocity information in controlling ankle extensor activities during quiet stance. J. Neurophys. 90(6), 3774–3782 (2003)
Dorn, T.W., Wang, J.M., Hicks, J.L., Delp, S.L.: Predictive simulation generates human adaptations during loaded and inclined walking. PLoS ONE 10(4), e0121407, Apr 2015
Winters, J.M.: An improved muscle-reflex actuator for use in large-scale neuromusculoskeletal models. Ann. Biomed. Eng. 23(4), 359–374 (1995)
Jacobs, D.A.: First-order activation dynamics (2015)
Mergner, T.: A neurological view on reactive human stance control. Ann. Rev. Control 34(2), 177–198 (2010)
Lockhart, D.B., Ting, L.H.: Optimal sensorimotor transformations for balance. Nature Neurosci. 10(10), 1329–1336 (2007)
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by JSPS KAKENHI Grant Number 26120004 and 26120006.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2017 Springer International Publishing AG
About this paper
Cite this paper
Jiang, P., Shirafuji, S., Chiba, R., Takakusaki, K., Ota, J. (2017). Proposal of a Stance Postural Control Model with Vestibular and Proprioceptive Somatosensory Sensory Input. In: Chen, W., Hosoda, K., Menegatti, E., Shimizu, M., Wang, H. (eds) Intelligent Autonomous Systems 14. IAS 2016. Advances in Intelligent Systems and Computing, vol 531. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-48036-7_4
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-48036-7_4
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-319-48035-0
Online ISBN: 978-3-319-48036-7
eBook Packages: EngineeringEngineering (R0)