Abstract
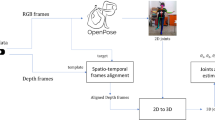
Human action recognition is an important topic and it has been widely applied in human-computer interaction. This work aims at human pose recognition based on RGB-D camera data streams for patients in a supine position (for example, with limb movement disorders), where bed backgrounds are misinterpreted as part of the human body. The target human limb poses include both upper and lower limbs’ movements. A novel framework for human limb movement recognition in a supine position is investigated and developed. The main steps include human region locating, limb detection and segmentation, limb labeling and limb movement tracking. Based on the tracking information on human bones by the RGB-D camera, human body region detection is executed according to the depth information. Further, this system is able to solve the problem of the human limb label confusions for left and right limbs due to their occlusion cases. Our proposed tracking algorithm achieves accurate positioning of the human body, and it provides reliable mid-level data for tracking human limbs. Experiment results show that four human limbs in supine positions are able to be located successfully. It is valuable and promising in the field of medical rehabilitation.
This work is supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 61103062, 61472357, 61571063), the NPU Foundation for Fundamental Research (No. JC201249), Scientific Research Foundation for Returned Scholars, Ministry of Education of China (2013), and the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities under the grant 2015QNA5005.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Yao, Y., et al.: Real-time hand gesture recognition using RGB-D sensor. In: CVPR (2014)
Shi, J., et al.: A real-time bimanual 3D interaction method based on bare-hand tracking. In: ACM Multimedia (2011)
Kyriazis, N., et al.: Efficient model-based 3D tracking of hand articulations using kinect. In: BMVC (2011)
Tang, H., et al.: Hand’s skin detection based on ellipse clustering. In: ISCSCT (2008)
Jun, W., et al.: A 3D fingertips detecting and tracking algorithm based on the sliding window. In: ACM Multimedia (2014)
Chang, Y.J., et al.: A Kinect-based system for physical rehabilitation: a pilot study for young adults with motor disabilities. Res. Dev. Disabil. 32(6), 2566–2570 (2011)
Lange, B., et al.: Development and evaluation of low cost game-based balance rehabilitation tool using the Microsoft kinect sensor. In: EMBC (2011)
Da Gama, A., et al.: Improving motor rehabilitation process through a natural interaction based system using kinect sensor. In: 3DUIC (2012)
Naccache, N.J., et al.: An investigation into the skeletonization approach of Hilditch. Pattern Recognit. 17(3), 279–284 (1984)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2016 Springer International Publishing AG
About this paper
Cite this paper
Wu, J. et al. (2016). RGB-D Camera based Human Limb Movement Recognition and Tracking in Supine Positions. In: Chen, E., Gong, Y., Tie, Y. (eds) Advances in Multimedia Information Processing - PCM 2016. PCM 2016. Lecture Notes in Computer Science(), vol 9917. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-48896-7_70
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-48896-7_70
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-319-48895-0
Online ISBN: 978-3-319-48896-7
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)