Abstract
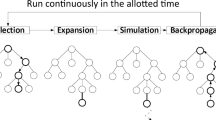
Monte-Carlo Tree Search (MCTS) is a popular technique for playing multi-player games. In this paper, we propose a new method to bias the playout policy of MCTS. The idea is to prune the decisions which seem “bad” (according to the previous iterations of the algorithm) before computing each playout. Thus, the method evaluates the estimated “good” moves more precisely. We have tested our improvement for the game of Havannah and compared it to several classic improvements. Our method outperforms the classic version of MCTS (with the RAVE improvement) and the different playout policies of MCTS that we have experimented.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arneson, B., Hayward, R., Henderson, P.: Monte-Carlo tree search in hex. IEEE Trans. Comput. Intell. AI Games 2(4), 251–258 (2010)
Baier, H., Drake, P.: The power of forgetting: improving the last-good-reply policy in Monte-Carlo go. IEEE Trans. Comput. Intell. AI Games 2(4), 303–309 (2010)
Bertsimas, D., Griffith, J., Gupta, V., Kochenderfer, M.J., Mišić, V., Moss, R.: A comparison of Monte-Carlo tree search and mathematical optimization for large scale dynamic resource allocation (2014). arXiv:1405.5498
Browne, C., Powley, E., Whitehouse, D., Lucas, S., Cowling, P., Rohlfshagen, P., Tavener, S., Perez, D., Samothrakis, S., Colton, S.: A survey of Monte-Carlo tree search methods. IEEE Trans. Comput. Intell. AI Games 4(1), 1–43 (2012)
Cazenave, T.: Monte-Carlo kakuro. In: Herik, H.J., Spronck, P. (eds.) ACG 2009. LNCS, vol. 6048, pp. 45–54. Springer, Heidelberg (2010). doi:10.1007/978-3-642-12993-3_5
Chaslot, G., Saito, J., Bouzy, B., Uiterwijk, J., Herik, H.: Monte-Carlo strategies for computer go. In: Proceedings of the 18th BeNeLux Conference on Artificial Intelligence, pp. 83–91, Namur, Belgium (2006)
Coulom, R.: Efficient selectivity and backup operators in Monte-Carlo tree search. In: Herik, H.J., Ciancarini, P., Donkers, H.H.L.M.J. (eds.) CG 2006. LNCS, vol. 4630, pp. 72–83. Springer, Heidelberg (2007). doi:10.1007/978-3-540-75538-8_7
Drake, P.: The last-good-reply policy for Monte-Carlo go. Int. Comput. Games Assoc. J. 32(4), 221–227 (2009)
Edelkamp, S., Tang, Z.: Monte-Carlo tree search for the multiple sequence alignment problem. In: Eighth Annual Symposium on Combinatorial Search (2015)
Ewalds, T.: Playing and Solving Havannah. Master’s thesis, University of Alberta (2012)
Finnsson, H., Björnsson, Y.: Simulation-based approach to general game playing. In: Proceedings of the 23rd National Conference on Artificial Intelligence, AAAI 2008, vol. 1, pp. 259–264. AAAI Press (2008)
Gelly, S., Silver, D.: Combining online and offline knowledge in UCT. In: Proceedings of the 24th International Conference on Machine Learning, pp. 273–280. ACM (2007)
Gelly, S., Silver, D.: Monte-Carlo tree search and rapid action value estimation in computer go. Artif. Intell. 175(11), 1856–1875 (2011)
Guo, X., Singh, S., Lee, H., Lewis, R.L., Wang, X.: Deep learning for real-time atari game play using offline Monte-Carlo tree search planning. In: Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, pp. 3338–3346 (2014)
Heinrich, J., Silver, D.: Self-play Monte-Carlo tree search in computer poker. In: Workshops at the Twenty-Eighth AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence (2014)
Herik, H.J., Kuipers, J., Vermaseren, J.A.M., Plaat, A.: Investigations with Monte Carlo tree search for finding better multivariate horner schemes. In: Filipe, J., Fred, A. (eds.) ICAART 2013. CCIS, vol. 449, pp. 3–20. Springer, Heidelberg (2014). doi:10.1007/978-3-662-44440-5_1
Hoock, J., Lee, C., Rimmel, A., Teytaud, F., Wang, M., Teytaud, O.: Intelligent agents for the game of go. IEEE Comput. Intell. Mag. 5(4), 28–42 (2010)
Kocsis, L., Szepesvári, C.: Bandit based Monte-Carlo planning. In: Fürnkranz, J., Scheffer, T., Spiliopoulou, M. (eds.) ECML 2006. LNCS (LNAI), vol. 4212, pp. 282–293. Springer, Heidelberg (2006). doi:10.1007/11871842_29
Lanctot, M., Saffidine, A., Veness, J., Archibald, C., Winands, M.: Monte Carlo*-minimax search. In: Proceedings of the Twenty-Third International Joint Conference on Artificial Intelligence, pp. 580–586. AAAI Press (2013)
Lorentz, R.: Improving Monte-Carlo tree search in Havannah. In: Computers and Games 2010, pp. 105–115 (2010)
Lorentz, R.J.: Amazons discover Monte-Carlo. In: Herik, H.J., Xu, X., Ma, Z., Winands, M.H.M. (eds.) CG 2008. LNCS, vol. 5131, pp. 13–24. Springer, Heidelberg (2008). doi:10.1007/978-3-540-87608-3_2
Mazyad, A., Teytaud, F., Fonlupt, C.: Monte-Carlo Tree Search for the “mr jack” board game. J. Soft Comput. Artif. Intell. Appl. (IJSCAI) 4(1) (2015)
Powley, E.J., Whitehouse, D., Cowling, P.I.: Bandits all the way down: UCB1 as a simulation policy in Monte-Carlo tree search. In: CIG, pp. 81–88. IEEE (2013)
Rimmel, A., Teytaud, F.: Multiple overlapping tiles for contextual Monte Carlo tree search. In: Chio, C., Cagnoni, S., Cotta, C., Ebner, M., Ekárt, A., Esparcia-Alcazar, A.I., Goh, C.-K., Merelo, J.J., Neri, F., Preuß, M., Togelius, J., Yannakakis, G.N. (eds.) EvoApplications 2010. LNCS, vol. 6024, pp. 201–210. Springer, Heidelberg (2010). doi:10.1007/978-3-642-12239-2_21
Rimmel, A., Teytaud, F., Teytaud, O.: Biasing Monte-Carlo simulations through RAVE values. In: Herik, H.J., Iida, H., Plaat, A. (eds.) CG 2010. LNCS, vol. 6515, pp. 59–68. Springer, Heidelberg (2011). doi:10.1007/978-3-642-17928-0_6
Schmittberger, R.: New Rules for Classic Games. Wiley, New York (1992)
Stankiewicz, J.A., Winands, M.H.M., Uiterwijk, J.W.H.M.: Monte-Carlo tree search enhancements for havannah. In: Herik, H.J., Plaat, A. (eds.) ACG 2011. LNCS, vol. 7168, pp. 60–71. Springer, Heidelberg (2012). doi:10.1007/978-3-642-31866-5_6
Tak, M.J., Winands, M.H., Björnsson, Y.: N-grams and the last-good-reply policy applied in general game playing. IEEE Trans. Comput. Intell. AI Games 4(2), 73–83 (2012)
Taralla, D.: Learning Artificial Intelligence in Large-Scale Video Games. Ph.D. thesis, University of Liège (2015)
Teytaud, F., Teytaud, O.: Creating an upper-confidence-tree program for havannah. In: Herik, H.J., Spronck, P. (eds.) ACG 2009. LNCS, vol. 6048, pp. 65–74. Springer, Heidelberg (2010). doi:10.1007/978-3-642-12993-3_7
Wilisowski, Ł., Dreżewski, R.: The application of co-evolutionary genetic programming and TD(1) reinforcement learning in large-scale strategy game VCMI. In: Jezic, G., Howlett, R.J., Jain, L.C. (eds.) Agent and Multi-Agent Systems: Technologies and Applications. SIST, vol. 38, pp. 81–93. Springer, Heidelberg (2015). doi:10.1007/978-3-319-19728-9_7
Acknowledgements
Experiments presented in this paper were carried out using the CALCULCO computing platform, supported by SCOSI/ULCO (Service Commun du Système d’Information de l’Université du Littoral Côte d’Opale).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2016 Springer International Publishing AG
About this paper
Cite this paper
Duguépéroux, J., Mazyad, A., Teytaud, F., Dehos, J. (2016). Pruning Playouts in Monte-Carlo Tree Search for the Game of Havannah. In: Plaat, A., Kosters, W., van den Herik, J. (eds) Computers and Games. CG 2016. Lecture Notes in Computer Science(), vol 10068. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-50935-8_5
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-50935-8_5
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-319-50934-1
Online ISBN: 978-3-319-50935-8
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)