Abstract
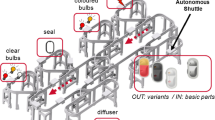
In this paper we introduce a novel application of model checking to find optimal planning solutions for a flow production system. Originally controlled by a multiagent system, the production system consists of autonomous products and asynchronous production stations with limited space for waiting products. In this work, we present two different approaches of application of the Spin model checker to optimize throughput in the given production system. Instead of mapping the multiagent system directly, we model the production line itself as a set of communicating processes. Each communication channel between two processes represents a one-way monorail connection from one station to another. Experiments show that both approaches derive valid and optimized plans with several thousands of steps using constrained branch-and-bound. However, experiments also indicate individual advantages of both approaches.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Armando, A., Mantovani, J., Platania, L.: Bounded model checking of software using SMT solvers instead of SAT solvers. In: Valmari, A. (ed.) SPIN 2006. LNCS, vol. 3925, pp. 146–162. Springer, Heidelberg (2006). doi:10.1007/11691617_9
Bhat, U.: Finite capacity assembly-like queues. Queueing Syst. 1, 85–101 (1986)
Biere, A., Cimatti, A., Clarke, E., Zhu, Y.: Symbolic model checking without BDDs. In: Cleaveland, W.R. (ed.) TACAS 1999. LNCS, vol. 1579, pp. 193–207. Springer, Heidelberg (1999). doi:10.1007/3-540-49059-0_14
Bošnački, D., Dams, D.: Integrating real time into spin: a prototype implementation. In: Budkowski, S., Cavalli, A., Najm, E. (eds.) FORTE/PSTV, vol. 6, pp. 423–438. Springer, New York (1998)
Bracht, U., Geckler, D., Wenzel, S.: Digitale Fabrik: Methoden und Praxisbeispiele. Springer, Heidelberg (2011)
Brinksma, E., Mader, A.: Verification and optimization of a PLC control schedule. In: Havelund, K., Penix, J., Visser, W. (eds.) SPIN 2000. LNCS, vol. 1885, pp. 73–92. Springer, Heidelberg (2000). doi:10.1007/10722468_5
Bürckert, H.J., Fischer, K., Vierke, G.: Holonic transport scheduling with teletruck. Appl. Artif. Intell. 14(7), 697–725 (2000)
Burman, M.: New results in flow line analysis. Ph.D. thesis, Massachusetts Institute of Technology (1995)
Cimatti, A., Giunchiglia, E., Giunchiglia, F., Traverso, P.: Planning via model checking: a decision procedure for AR. In: Steel, S., Alami, R. (eds.) ECP 1997. LNCS, vol. 1348, pp. 130–142. Springer, Heidelberg (1997). doi:10.1007/3-540-63912-8_81
Cimatti, A., Roveri, M., Traverso, P.: Automatic OBDD-based generation of universal plans in non-deterministic domains. In: AAAI, pp. 875–881 (1998)
Clarke, E., Grumberg, O., Peled, D.: Model Checking. MIT Press, Cambridge (2000)
Dorer, K., Calisti, M.: An adaptive solution to dynamic transport optimization. In: AAMAS, pp. 45–51. ACM (2005)
Edelkamp, S., Lafuente, A.L., Leue, S.: Directed explicit model checking with HSF-SPIN. In: Dwyer, M. (ed.) SPIN 2001. LNCS, vol. 2057, pp. 57–79. Springer, Heidelberg (2001). doi:10.1007/3-540-45139-0_5
Edelkamp, S., Reffel, F.: OBDDs in heuristic search. In: Herzog, O., Günter, A. (eds.) KI 1998. LNCS, vol. 1504, pp. 81–92. Springer, Heidelberg (1998). doi:10.1007/BFb0095430
Edelkamp, S., Sulewski, D.: Flash-efficient LTL model checking with minimal counterexamples. In: SEFM, pp. 73–82 (2008)
Edelkamp, S., Greulich, C.: Using SPIN for the optimized scheduling of discrete event systems in manufacturing. In: Bošnački, D., Wijs, A. (eds.) SPIN 2016. LNCS, vol. 9641, pp. 57–77. Springer, Heidelberg (2016). doi:10.1007/978-3-319-32582-8_4
Fischer, K., Müller, J.R.P., Pischel, M.: Cooperative transportation scheduling: an application domain for DAI. Appl. Artif. Intell. 10(1), 1–34 (1996)
Fox, M., Long, D.: The detection and exploration of symmetry in planning problems. In: IJCAI, pp. 956–961 (1999)
Fujimoto, R.: Parallel and Distributed Simulation Systems. Wiley, Hoboken (2000)
Ganji, F., Morales Kluge, E., Scholz-Reiter, B.: Bringing agents into application: intelligent products in autonomous logistics. In: Schill, K., Scholz-Reiter, B., Frommberger, L. (eds.) Artificial Intelligence and Logistics (AiLog) - Workshop at ECAI 2010, pp. 37–42 (2010)
Gerth, R., Peled, D., Vardi, M., Wolper, P.: Simple on-the-fly automatic verification of linear temporal logic. In: PSTV, pp. 3–18. Chapman & Hall (1995)
Giunchiglia, F., Traverso, P.: Planning as model checking. In: Biundo, S., Fox, M. (eds.) ECP 1999. LNCS (LNAI), vol. 1809, pp. 1–20. Springer, Heidelberg (2000). doi:10.1007/10720246_1
Godefroid, P.: Using partial orders to improve automatic verification methods. In: Clarke, E.M., Kurshan, R.P. (eds.) CAV 1990. LNCS, vol. 531, pp. 176–185. Springer, Heidelberg (1991). doi:10.1007/BFb0023731
Greulich, C., Edelkamp, S., Eicke, N.: Cyber-physical multiagent-simulation in production logistics. In: Müller, J.P., Ketter, W., Kaminka, G., Wagner, G., Bulling, N. (eds.) MATES 2015. LNCS (LNAI), vol. 9433, pp. 119–136. Springer, Heidelberg (2015). doi:10.1007/978-3-319-27343-3_7
Harrison, J.: Assembly-like queues. J. Appl. Probab. 10, 354–367 (1973)
Helias, A., Guerrin, F., Steyer, J.P.: Using timed automata and model-checking to simulate material flow in agricultural production systems - application to animal waste management. Comput. Electron. Agric. 63(2), 183–192 (2008)
Himoff, J., Rzevski, G., Skobelev, P.: Magenta technology multi-agent logistics i-scheduler for road transportation. In: AAMAS, pp. 1514–1521. ACM (2006)
Hoffmann, J., Kissmann, P., Torralba, Á.: “Distance”? Who cares? Tailoring merge-and-shrink heuristics to detect unsolvability. In: ECAI, pp. 441–446 (2014)
Holzmann, G.J.: The SPIN Model Checker - Primer and Reference Manual. Addison-Wesley, Boston (2004)
Hopp, W., Simon, J.: Bounds and heuristics for assembly-like queues. Queueing Syst. 4, 137–156 (1989)
Jensen, R.M., Veloso, M.M., Bowling, M.H.: OBDD-based optimistic and strong cyclic adversarial planning. In: ECP (2001)
Kautz, H., Selman, B.: Pushing the envelope: planning propositional logic, and stochastic search. In: ECAI, pp. 1194–1201 (1996)
Kupferschmid, S., Hoffmann, J., Dierks, H., Behrmann, G.: Adapting an AI planning heuristic for directed model checking. In: Valmari, A. (ed.) SPIN 2006. LNCS, vol. 3925, pp. 35–52. Springer, Heidelberg (2006). doi:10.1007/11691617_3
Lipper, E., Sengupta, E.: Assembly-like queues with finite capacity: bounds, asymptotics and approximations. Queueing Syst. 1, 67–83 (1986)
Lluch-Lafuente, A.: Symmetry reduction and heuristic search for error detection in model checking. In: MOCHART, pp. 77–86 (2003)
Manitz, M.: Queueing-model based analysis of assembly lines with finite buffers and general service times. Comput. Oper. Res. 35(8), 2520–2536 (2008)
Morales Kluge, E., Ganji, F., Scholz-Reiter, B.: Intelligent products - towards autonomous logistic processes - a work in progress paper. In: PLM, Bremen, pp. 348–357 (2010)
Nau, D., Ghallab, M., Traverso, P.: Automated Planning: Theory & Practice. Morgan Kaufmann Publishers Inc., San Francisco (2004)
Nissim, R., Brafman, R.I.: Cost-optimal planning by self-interested agents. In: AAAI (2013)
Parragh, S.N., Doerner, K.F., Hartl, R.F.: A survey on pickup and delivery problems Part II: transportation between pickup and delivery locations. J. für Betriebswirtschaft 58(2), 81–117 (2008)
Rekersbrink, H., Ludwig, B., Scholz-Reiter, B.: Entscheidungen selbststeuernder logistischer Objekte. Ind. Manag. 23(4), 25–30 (2007)
Russell, S.J., Norvig, P.: Artificial Intelligence - A Modern Approach, 3rd edn. Pearson Education, Upper Saddle River (2010)
Ruys, T.C.: Optimal scheduling using branch and bound with SPIN 4.0. In: Ball, T., Rajamani, S.K. (eds.) SPIN 2003. LNCS, vol. 2648, pp. 1–17. Springer, Heidelberg (2003). doi:10.1007/3-540-44829-2_1
Ruys, T.C., Brinksma, E.: Experience with literate programming in the modelling and validation of systems. In: Steffen, B. (ed.) TACAS 1998. LNCS, vol. 1384, pp. 393–408. Springer, Heidelberg (1998). doi:10.1007/BFb0054185
Saffidine, A.: Solving games and all that. Ph.D. thesis, University Paris-Dauphine (2014)
Valmari, A.: A stubborn attack on state explosion. In: Clarke, E.M., Kurshan, R.P. (eds.) CAV 1990. LNCS, vol. 531, pp. 156–165. Springer, Heidelberg (1991). doi:10.1007/BFb0023729
Wooldridge, M.: Reasoning About Rational Agents. The MIT Press, Cambridge (2000)
Wooldridge, M.: An Introduction to Multi-agent Systems. Wiley, Chichester (2002)
Acknowledgements
This research was partly funded by the International Graduate School for Dynamics in Logistics (IGS), University of Bremen, Germany.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2017 Springer International Publishing AG
About this paper
Cite this paper
Greulich, C., Edelkamp, S. (2017). Two Model Checking Approaches to Branch-and-Bound Optimization of a Flow Production System. In: van den Herik, J., Filipe, J. (eds) Agents and Artificial Intelligence. ICAART 2016. Lecture Notes in Computer Science(), vol 10162. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-53354-4_2
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-53354-4_2
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-319-53353-7
Online ISBN: 978-3-319-53354-4
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)