Abstract
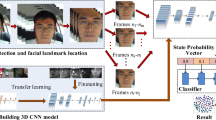
We propose a novel drowsiness detection method based on 3D-Deep Convolutional Neural Network (3D-DCNN). We design a learning architecture for the drowsiness detection, which consists of three building blocks for representation learning, scene understanding, and feature fusion. In this framework, the model generates a spatio-temporal representation from multiple consecutive frames and analyze the scene conditions which are defined as head, eye, and mouth movements. The result of analysis from the scene condition understanding model is used to auxiliary information for the drowsiness detection. Then the method subsequently generates fusion features using the spatio-temporal representation and the results of the classification of scene conditions. By using the fusion features, we show that the proposed method can boost the performance of drowsiness detection. The proposed method demonstrates with the NTHU Drowsy Driver Detection (NTHU-DDD) video dataset.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Schroeder, P., Meyers, M., Kostyniuk, L.: National survey on distracted driving attitudes and behaviors–2012. Technical report (2013)
Khushaba, R.N., Kodagoda, S., Lal, S., Dissanayake, G.: Driver drowsiness classification using fuzzy wavelet-packet-based feature-extraction algorithm. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 58, 121–131 (2011)
Patel, M., Lal, S., Kavanagh, D., Rossiter, P.: Applying neural network analysis on heart rate variability data to assess driver fatigue. Expert Syst. Appl. 38, 7235–7242 (2011)
Tran, Y., Craig, A., Wijesuriya, N., Nguyen, H.: Improving classification rates for use in fatigue countermeasure devices using brain activity. In: 2010 Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology, pp. 4460–4463. IEEE (2010)
Papadelis, C., Chen, Z., Kourtidou-Papadeli, C., Bamidis, P.D., Chouvarda, I., Bekiaris, E., Maglaveras, N.: Monitoring sleepiness with on-board electrophysiological recordings for preventing sleep-deprived traffic accidents. Clin. Neurophysiol. 118, 1906–1922 (2007)
Ersal, T., Fuller, H.J., Tsimhoni, O., Stein, J.L., Fathy, H.K.: Model-based analysis and classification of driver distraction under secondary tasks. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 11, 692–701 (2010)
Yang, J.H., Mao, Z.H., Tijerina, L., Pilutti, T., Coughlin, J.F., Feron, E.: Detection of driver fatigue caused by sleep deprivation. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cybern.-Part A: Syst. Hum. 39, 694–705 (2009)
Liu, C.C., Hosking, S.G., Lenné, M.G.: Predicting driver drowsiness using vehicle measures: recent insights and future challenges. J. Saf. Res. 40, 239–245 (2009)
Takei, Y., Furukawa, Y.: Estimate of driver’s fatigue through steering motion. In: 2005 IEEE International Conference on Systems, Man and Cybernetics, vol. 2, pp. 1765–1770. IEEE (2005)
Wakita, T., Ozawa, K., Miyajima, C., Igarashi, K., Katunobu, I., Takeda, K., Itakura, F.: Driver identification using driving behavior signals. IEICE Trans. Inf. Syst. 89, 1188–1194 (2006)
Garcia, I., Bronte, S., Bergasa, L.M., Almazán, J., Yebes, J.: Vision-based drowsiness detector for real driving conditions. In: 2012 IEEE Intelligent Vehicles Symposium (IV), pp. 618–623. IEEE (2012)
Mbouna, R.O., Kong, S.G., Chun, M.G.: Visual analysis of eye state and head pose for driver alertness monitoring. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 14, 1462–1469 (2013)
Wang, P., Shen, L.: A method of detecting driver drowsiness state based on multifeatures of face. In: 2012 5th International Congress on Image and Signal Processing (CISP), pp. 1171–1175. IEEE (2012)
Minkov, K., Zafeiriou, S., Pantic, M.: A comparison of different features for automatic eye blinking detection with an application to analysis of deceptive behavior. In: 2012 5th International Symposium on Communications Control and Signal Processing (ISCCSP), pp. 1–4. IEEE (2012)
Panning, A., Al-Hamadi, A., Michaelis, B.: A color based approach for eye blink detection in image sequences. In: 2011 IEEE International Conference on Signal and Image Processing Applications (ICSIPA), pp. 40–45. IEEE (2011)
Kurylyak, Y., Lamonaca, F., Mirabelli, G.: Detection of the eye blinks for human’s fatigue monitoring. In: 2012 IEEE International Symposium on Medical Measurements and Applications Proceedings (MeMeA), pp. 1–4. IEEE (2012)
Suzuki, M., Yamamoto, N., Yamamoto, O., Nakano, T., Yamamoto, S.: Measurement of driver’s consciousness by image processing-a method for presuming driver’s drowsiness by eye-blinks coping with individual differences. In: 2006 IEEE International Conference on Systems, Man and Cybernetics, vol. 4, pp. 2891–2896. IEEE (2006)
Dwivedi, K., Biswaranjan, K., Sethi, A.: Drowsy driver detection using representation learning. In: 2014 IEEE International Advance Computing Conference (IACC), pp. 995–999. IEEE (2014)
Ren, S., He, K., Girshick, R., Sun, J.: Faster R-CNN: towards real-time object detection with region proposal networks. In: Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, pp. 91–99 (2015)
Girshick, R., Donahue, J., Darrell, T., Malik, J.: Region-based convolutional networks for accurate object detection and segmentation. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 38, 142–158 (2016)
Du, Y., Wang, W., Wang, L.: Hierarchical recurrent neural network for skeleton based action recognition. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 1110–1118 (2015)
Qi, X., Li, C.G., Zhao, G., Hong, X., Pietikainen, M.: Dynamic texture and scene classification by transferring deep image features. Neurocomputing 171, 1230–1241 (2016)
Xu, D., Ricci, E., Yan, Y., Song, J., Sebe, N.: Learning deep representations of appearance and motion for anomalous event detection. arXiv preprint arXiv:1510.01553 (2015)
Tran, D., Bourdev, L., Fergus, R., Torresani, L., Paluri, M.: Learning spatiotemporal features with 3D convolutional networks. In: 2015 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), pp. 4489–4497. IEEE (2015)
Krizhevsky, A., Sutskever, I., Hinton, G.E.: Imagenet classification with deep convolutional neural networks. In: Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, pp. 1097–1105 (2012)
Le Cun, B.B., Denker, J.S., Henderson, D., Howard, R.E., Hubbard, W., Jackel, L.D.: Handwritten digit recognition with a back-propagation network. In: Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems. Citeseer (1990)
Xu, K., Ba, J., Kiros, R., Cho, K., Courville, A., Salakhutdinov, R., Zemel, R.S., Bengio, Y.: Show, attend and tell: neural image caption generation with visual attention. arXiv preprint arXiv:1502.03044, 2, 5 (2015)
Memisevic, R.: Learning to relate images. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 35, 1829–1846 (2013)
Hong, S., Oh, J., Han, B., Lee, H.: Learning transferrable knowledge for semantic segmentation with deep convolutional neural network. arXiv preprint arXiv:1512.07928 (2015)
Farfade, S.S., Saberian, M.J., Li, L.J.: Multi-view face detection using deep convolutional neural networks. In: Proceedings of the 5th ACM on International Conference on Multimedia Retrieval, pp. 643–650. ACM (2015)
Acknowledgment
This work was supported by Institute for Information & communications Technology Promotion (IITP) grant funded by the Korea government (MSIP) (No. B0101-15-0525, Development of global multi-target tracking and event prediction techniques based on real-time large-scale video analysis) and Center for Integrated Smart Sensors as Global Frontier (CISS-2013M3A6A6073718).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2017 Springer International Publishing AG
About this paper
Cite this paper
Yu, J., Park, S., Lee, S., Jeon, M. (2017). Representation Learning, Scene Understanding, and Feature Fusion for Drowsiness Detection. In: Chen, CS., Lu, J., Ma, KK. (eds) Computer Vision – ACCV 2016 Workshops. ACCV 2016. Lecture Notes in Computer Science(), vol 10118. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-54526-4_13
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-54526-4_13
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-319-54525-7
Online ISBN: 978-3-319-54526-4
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)