Abstract
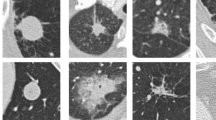
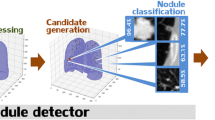
Computed tomography (CT) is the preferred method for non-invasive lung cancer screening. Early detection of potentially malignant lung nodules will greatly improve patient outcome, where an effective computer-aided diagnosis (CAD) system may play an important role. Two-dimensional convolutional neural network (CNN) based CAD methods have been proposed and well-studied to extract hierarchical and discriminative features for classifying lung nodules. It is often questioned if the transition to 3D will be a key to major step forward in performance. In this paper, we propose a novel 3D CNN on the 1018-patient Lung Image Database Consortium collection (LIDC-IDRI). To the best of our knowledge, this is the first time to directly compare three different strategies: slice-level 2D CNN, nodule-level 2D CNN and nodule-level 3D CNN. Using comparable network architectures, we achieved nodule malignancy risk classification accuracies of \(86.7\%\), \(87.3\%\) and \(87.4\%\) against the personal opinion of four radiologists, respectively. In the experiments, our results and analyses demonstrates that the nodule-level 2D CNN can better capture the z-direction features of lung nodule than a slice-level 2D approach, whereas nodule-level 3D CNN can further integrate nodule-level features as well as context features from all three directions in a 3D patch in a limited extent, resulting in a slightly better performance than the other two strategies.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Siegel, R.L., Miller, K.D., Jemal, A.: Cancer statistics, 2016. CA Cancer J. Clin. 66, 7–30 (2016)
Stewart, B., Wild, C.P., et al.: World cancer report 2014. World (2015)
Team, N., et al.: Reduced lung-cancer mortality with low-dose computed tomographic screening. N. Engl. J. Med. 365, 395 (2011)
Erasmus, J.J., Gladish, G.W., Broemeling, L., Sabloff, B.S., Truong, M.T., Herbst, R.S., Munden, R.F.: Interobserver and intraobserver variability in measurement of non-small-cell carcinoma lung lesions: implications for assessment of tumor response. J. Clin. Oncol. 21, 2574–2582 (2003)
Swensen, S.J., Jett, J.R., Hartman, T.E., Midthun, D.E., Mandrekar, S.J., Hillman, S.L., Sykes, A.M., Aughenbaugh, G.L., Bungum, A.O., Allen, K.L.: CT screening for lung cancer: five-year prospective experience 1. Radiology 235, 259–265 (2005)
Armato, S.G., McLennan, G., Bidaut, L., McNitt-Gray, M.F., Meyer, C.R., Reeves, A.P., Zhao, B., Aberle, D.R., Henschke, C.I., Hoffman, E.A., et al.: The lung image database consortium (LIDC) and image database resource initiative (IDRI): a completed reference database of lung nodules on ct scans. Med. Phys. 38, 915–931 (2011)
Rubin, G.D., Lyo, J.K., Paik, D.S., Sherbondy, A.J., Chow, L.C., Leung, A.N., Mindelzun, R., Schraedley-Desmond, P.K., Zinck, S.E., Naidich, D.P., et al.: Pulmonary nodules on multi-detector row CT scans: performance comparison of radiologists and computer-aided detection 1. Radiology 234, 274–283 (2005)
Furuya, K., Murayama, S., Soeda, H., Murakami, J., Ichinose, Y., Yauuchi, H., Katsuda, Y., Koga, M., Masuda, K.: New classification of small pulmonary nodules by margin characteristics on highresolution CT. Acta Radiol. 40, 496–504 (1999)
Gurney, J.W., Swensen, S.J.: Solitary pulmonary nodules: determining the likelihood of malignancy with neural network analysis. Radiology 196, 823–829 (1995)
Kawata, Y., Niki, N., Ohmatsu, H., Kusumoto, M., Kakinuma, R., Mori, K., Nishiyama, H., Eguchi, K., Kaneko, M., Moriyama, N.: Computerized analysis of 3-d pulmonary nodule images in surrounding and internal structure feature spaces. In: Proceedings of 2001 International Conference on Image Processing, vol. 2, pp. 889–892. IEEE (2001)
Kido, S., Kuriyama, K., Higashiyama, M., Kasugai, T., Kuroda, C.: Fractal analysis of internal and peripheral textures of small peripheral bronchogenic carcinomas in thin-section computed tomography: comparison of bronchioloalveolar cell carcinomas with nonbronchioloalveolar cell carcinomas. J. Comput. Assist. Tomogr. 27, 56–61 (2003)
Shiraishi, J., Abe, H., Engelmann, R., Aoyama, M., MacMahon, H., Doi, K.: Computer-aided diagnosis to distinguish benign from malignant solitary pulmonary nodules on radiographs: ROC analysis of radiologists’ performance - initial experience 1. Radiology 227, 469–474 (2003)
Armato, S.G., Altman, M.B., Wilkie, J., Sone, S., Li, F., Doi, K., Roy, A.S.: Automated lung nodule classification following automated nodule detection on CT: a serial approach. Med. Phys. 30, 1188–1197 (2003)
Mori, K., Niki, N., Kondo, T., Kamiyama, Y., Kodama, T., Kawada, Y., Moriyama, N.: Development of a novel computer-aided diagnosis system for automatic discrimination of malignant from benign solitary pulmonary nodules on thin-section dynamic computed tomography. J. Comput. Assist. Tomogr. 29, 215–222 (2005)
Yang, J., Yu, K., Gong, Y., Huang, T.: Linear spatial pyramid matching using sparse coding for image classification. In: IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition 2009, CVPR 2009, pp. 1794–1801. IEEE (2009)
Krizhevsky, A., Sutskever, I., Hinton, G.E.: Imagenet classification with deep convolutional neural networks. In: Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, pp. 1097–1105 (2012)
Shen, W., Zhou, M., Yang, F., Yang, C., Tian, J.: Multi-scale convolutional neural networks for lung nodule classification. In: Ourselin, S., Alexander, D.C., Westin, C.-F., Cardoso, M.J. (eds.) IPMI 2015. LNCS, vol. 9123, pp. 588–599. Springer, Heidelberg (2015). doi:10.1007/978-3-319-19992-4_46
Kumar, D., Wong, A., Clausi, D.A.: Lung nodule classification using deep features in CT images. In: 2015 12th Conference on Computer and Robot Vision (CRV), pp. 133–138. IEEE (2015)
Hua, K.L., Hsu, C.H., Hidayati, S.C., Cheng, W.H., Chen, Y.J.: Computer-aided classification of lung nodules on computed tomography images via deep learning technique. Onco Target Ther. 8, 2015–2022 (2015)
Nair, V., Hinton, G.E.: Rectified linear units improve restricted Boltzmann machines. In: Proceedings of the 27th International Conference on Machine Learning (ICML 2010), pp. 807–814 (2010)
Srivastava, N., Hinton, G., Krizhevsky, A., Sutskever, I., Salakhutdinov, R.: Dropout: a simple way to prevent neural networks from overfitting. J. Mach. Learn. Res. 15, 1929–1958 (2014)
Tran, D., Bourdev, L.D., Fergus, R., Torresani, L., Paluri, M.: C3D: generic features for video analysis. CoRR, abs/1412.0767 2 7 (2014)
Ji, S., Xu, W., Yang, M., Yu, K.: 3D convolutional neural networks for human action recognition. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 35, 221–231 (2013)
Collobert, R., Kavukcuoglu, K., Farabet, C.: Torch7: a matlab-like environment for machine learning (2011)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2017 Springer International Publishing AG
About this paper
Cite this paper
Yan, X. et al. (2017). Classification of Lung Nodule Malignancy Risk on Computed Tomography Images Using Convolutional Neural Network: A Comparison Between 2D and 3D Strategies. In: Chen, CS., Lu, J., Ma, KK. (eds) Computer Vision – ACCV 2016 Workshops. ACCV 2016. Lecture Notes in Computer Science(), vol 10118. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-54526-4_7
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-54526-4_7
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-319-54525-7
Online ISBN: 978-3-319-54526-4
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)