Abstract
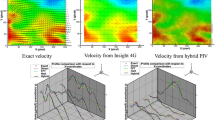
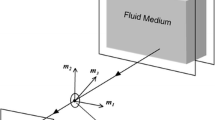
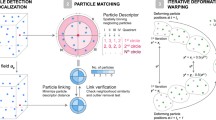
The Particle-Image Velocimetry (PIV) is a standard optical contactless measurement technique to determine the velocity field of a fluid flow for example around an obstacle such as an airplane wing. Tiny density neutral and light-reflecting particles are added to the otherwise invisible fluid flow. Then two consecutive images (A and B) of a thin laser illuminated light sheet are taken by a CCD camera with a time-lag of a few milliseconds. From these two images one tries to estimate the local shift of the particles, for which it is common to use a cross-correlation function. Based on the displacement of the tracers and the time-lag, the local velocities can be determined. This method requires a high level of experience by its user, fine tuning of several parameters, and multiple pre- and post-processing steps of the data in order to obtain meaningful results. We present a new approach that is based on the matching problem in bipartite graphs. Ideally, each particle in image A is assigned to exactly one particle in image B, and in an optimal assignment, the sum of shift distances of all particles in A to particles in B is minimal. However, the real-world situation is far from being ideal, because of inhomogeneous particle sizes and shapes, inadequate illumination of the images, or particle losses due to a divergence out of the two-dimensional light sheet area into the surrounding three-dimensional space, to name just a few sources of imperfection. Our new method is implemented in MATLAB with a graphical user interface. We evaluate and compare it with the cross-correlation method using real measured data. We demonstrate that our new method requires less interaction with the user, no further post-processing steps, and produces less erroneous results. This article is based on the master thesis [5], written by the first coauthor, and supervised by all other coauthors.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
Notes
- 1.
This statement was formalized and rigorously proven by Fabian Gnegel at Helmut-Schmidt-University Hamburg.
References
Adrian, R.J.: Particle-imaging techniques for experimental fluid mechanics. Annu. Rev. Fluid Mech. 23(1), 261–304 (1991)
Barbe, D.F.: Imaging devices using the charge-coupled concept. Proc. IEEE 63(1), 38–67 (1975)
Burkard, R., Dell’Amico, M., Martello, S.: Society for industrial and applied mathematics. In: Assignment Problems. Philadelphia (2012)
Butz, F.-F.: Entwicklung und Implementierung eines Algorithmus zur Detektion von Streuteilchen in PIV-Aufnahmen. Angewandte Mathematik und Optimierung, Schriftenreihe AMOS#40. Helmut-Schmidt-University, Hamburg (2016)
Butz, F.-F.: Entwicklung und Implementierung von Analysemethoden zum Erfassen von Geschwindigkeitsfeldern mit dem PIV-Verfahren. Angewandte Mathematik und Optimierung, Schriftenreihe AMOS#45. Helmut-Schmidt-University, Hamburg (2016)
Raffel, M., Willert, C.E., Kompenhans, J.: Particle Image Velocimetry: A Practical Guide. Engineering online library. Springer, Berlin (1998)
Westerweel, J.: Fundamentals of digital particle image velocimetry. Meas. Sci. Tech. 8(12), 1379–1392 (1997)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2018 Springer International Publishing AG
About this paper
Cite this paper
Butz, FF., Fügenschuh, A., Wood, J.N., Breuer, M. (2018). Particle-Image Velocimetry and the Assignment Problem. In: Fink, A., Fügenschuh, A., Geiger, M. (eds) Operations Research Proceedings 2016. Operations Research Proceedings. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-55702-1_33
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-55702-1_33
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-319-55701-4
Online ISBN: 978-3-319-55702-1
eBook Packages: Business and ManagementBusiness and Management (R0)