Abstract
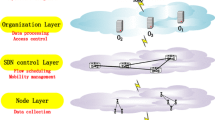
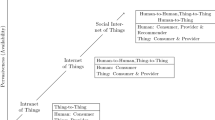
Current large-scale Internet-of-Things systems and architectures incorporate many components, such as devices or services, geographic and conceptually very sparse. Thus, for final applications, it is very complicated to deeply know, manage or control the underlying components, which, at the end, generate and process the data they employ. Therefore, new tools to avoid or remove malicious components based only on the available information at high level are required. In this paper we describe a statistical framework for knowledge discovery in order to estimate the uncertainty level associated with the received data by a certain application. Moreover, these results are used as input in a reputation model focused on locating the malicious components. Finally, an experimental validation is provided in order to evaluate the performance of the proposed solution.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Sarkar, A.N.: Significance of smart cities in 21st century: an international business perspective. FOCUS: J. Int. Bus. 2(2), 53–82 (2016). doi:10.17492/focus.v2i2.8623
Hong, K., Lillethun, D., Ramachandran, U.: Mobile fog: a programming model for large-scale applications on the internet of things. In: Proceedings of the Second ACM SIGCOMM Workshop on Mobile Cloud Computing, pp. 15–20. ACM (2013)
Lee, H., Jo, S.K., Lee, N., Lee, H.W.: A method for co-existing heterogeneous IoT environments based on compressive sensing. In: 18th International Conference on Advanced Communication Technology (ICACT), pp. 206–209. IEEE (2016)
Robles, T., Alcarria, R., Martın, D., Navarro, M.: An IoT based reference architecture for smart water management processes. J. Wirel. Mob. Netw. Ubiquit. Comput. Dependable Appl. 6(1), 4–23 (2015)
Bordel, B., Alcarria, R., Martín, D., Robles, T.: Self-configuration in humanized cyber-physical systems. J. Ambient Intell. Human. Comput. 1–12 (2016). doi:10.1007/s12652-016-0410-3
Stankovic, J.: A research directions for the internet of things. IEEE Internet Things J. 1(1), 3–9 (2014)
Cardenas, A.A., Amin, S., Sastry, S.: Secure control: towards survivable cyber-physical systems. In: System (2008)
Zhu, Q., Başar, T.: Robust and resilient control design for cyber-physical systems with an application to power systems. In: 2011 50th IEEE Conference on Decision and Control and European Control Conference, pp. 4066–4071. IEEE (2011)
Zhang, M., Selic, B., Ali, S., Yue, T., Okariz, O., Norgren, R.: Understanding uncertainty in cyber-physical systems: a conceptual model. In: Wąsowski, A., Lönn, H. (eds.) ECMFA 2016. LNCS, vol. 9764, pp. 247–264. Springer, Cham (2016). doi:10.1007/978-3-319-42061-5_16
Aggarwal, C.C., Ashish, N., Sheth, A.: The internet of things: a survey from the data-centric perspective. In: Aggarwal, C.C. (ed.) Managing and Mining Sensor Data, pp. 383–428. Springer, New York (2013)
Hasan, S., Curry, E.: Approximate semantic matching of events for the internet of things. ACM Trans. Internet Technol. (TOIT) 14(1), 2 (2014)
Chen, D., Chang, G., Sun, D.: TRM-IoT: a trust management model based on fuzzy reputation for internet of things. Comput. Sci. Inf. Syst. 8(4), 1207–1228 (2011)
Boukercha, A., Xua, L., EL-Khatibb, K.: Trust-based security for wireless ad hoc and sensor networks. Comput. Commun. 30(11–12), 2413–2427 (2007)
Bao, F., Chen, R.: Trust management for the internet of things and its application to service composition. In: World of Wireless, Mobile and Multimedia Networks (WoWMoM), pp. 1–6. IEEE (2012)
Chen, L., Yan, Z., Zhang, W.: TruSMS: A trustworthy SMS spam control system based on trust management. Future Gener. Comput. Syst. 49, 77–93 (2015)
Liu, Y., Chen, Z., Xia, F., Lv, X., Bu, F.: A trust model based on service classification in mobile services. In: Green Computing and Communications (GreenCom), pp. 572–577. IEEE (2010)
Liu, Y., Wang, K.: Trust control in heterogeneous networks for internet of things. In: International Conference on Computer Application and System Modeling (2010)
Scholz, F.W.: Maximum likelihood estimation. In: Encyclopedia of Statistical Sciences (1985)
Acknowledgments
Borja Bordel has received funding from the Ministry of Education through the FPU program (grant number FPU15/03977). Additionally, the research leading to these results has received funding from the Ministry of Economy and Competitiveness through SEMOLA project (TEC2015-68284-R) and from the Autonomous Region of Madrid through MOSI-AGIL-CM project (grant P2013/ICE-3019, co-funded by EU Structural Funds FSE and FEDER).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2017 Springer International Publishing AG
About this paper
Cite this paper
Bordel, B., Alcarria, R., Sánchez-de-Rivera, D. (2017). Detecting Malicious Components in Large-Scale Internet-of-Things Systems and Architectures. In: Rocha, Á., Correia, A., Adeli, H., Reis, L., Costanzo, S. (eds) Recent Advances in Information Systems and Technologies. WorldCIST 2017. Advances in Intelligent Systems and Computing, vol 569. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-56535-4_16
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-56535-4_16
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-319-56534-7
Online ISBN: 978-3-319-56535-4
eBook Packages: EngineeringEngineering (R0)