Abstract
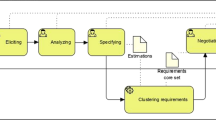
The main objective of the paper is to present the suitability and effects of several different clustering methods for improving accuracy of software size estimation. For software size estimation was used the Algorithmic Optimisation Method (AOM), which is based Use Case Points (UCP) method. The comparison of K-means, Hierarchical and Density-based clustering is provided. Gap, Silhouette and Calinski-Harabasz criterion were selected as an evaluation criterion for clustering quality. Estimation ability of clustered model is compared on Sum of squared error (SSE). Results shows that clustering improves an estimation ability.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Jorgensen, M., Shepperd, M.: Systematic review of software development cost estimation studies. IEEE Trans. Softw. Eng. 33(1), 33–53 (2007)
Karner, G.: Metrics for objectory’. Diploma, University of Linkoping, Sweden, No. LiTH-IDA-Ex-9344 21 (1993)
Braz, M.R., Vergilio, S.R.: Software effort estimation based on use cases. In: 30th Annual International Computer Software and Applications Conference, COMPSAC 2006 (2006)
Diev, S.: Use cases modeling and software estimation. ACM SIGSOFT Softw. Eng. Not. 31(6), 1–4 (2006). doi:10.1145/1218776.1218780
Mohagheghi, P., Anda, B., Conradi, R.: Effort estimation of use cases for incremental large-scale software development (2005). doi:10.1109/icse.2005.1553573
Wang, F., Yang, X., Zhu, X., Chen, L.: Extended use case points method for software cost estimation (2009). doi:10.1109/cise.2009.5364706
Ochodek, M., Nawrocki, J., Kwarciak, K.: Simplifying effort estimation based on use case points. Inf. Softw. Technol. 53, 200–213 (2011). doi:10.1016/j.infsof.2010.10.005
Silhavy, R., Silhavy, P., Prokopova, Z.: Algorithmic optimisation method for improving use case points estimation. PLoS ONE 10, e0141887 (2015)
Jain, A.K., Dubes, R.C.: Algorithms for Clustering Data. Prentice Hall, Englewood Cliffs (1988). Book available online at http://www.cse.msu.edu/~jain/Clustering_Jain_Dubes.pdf
Kaufman, L., Rousseeuw, P.J.: Finding Groups in Data: An Introduction to Cluster Analysis. Wiley, New York (1990)
Tan, P. N., Steinbach, M., Kumar, V.: Cluster analysis: Basic Concepts and Algorithms. Introduction to Data Mining (2006). Book available online at http://www-users.cs.umn.edu/~kumar/dmbook/index.php
Milligan, G.W.: Clustering validation: results and implications for applied analyses. In: Clustering and Classification, pp. 345–375. World Scientific, Singapore (1996)
Montgomery, D.C., Peck, E.A., Vining, G.G.: Introduction to Linear Regression Analysis, 5th edn. Wiley, Hoboken (2012)
Jorgensen, M.: Regression models of software development effort estimation accuracy and bias. Empir. Softw. Eng. 9, 297–314 (2004)
Mathworks: Cluster Analysis (2016). https://www.mathworks.com/help/stats/hierarchical-clustering.html
Tibshirani, R., Walther, G., Hastie, T.: Estimating the number of clusters in a data set via the gap statistic. J. Roy. Stat. Soc. Ser. B 63(Pt. 2), 411–423 (2001)
Rousseeuw, P.J.: Silhouettes: a graphical aid to the interpretation and validation of cluster analysis. Comput. Appl. Math. 20, 53–65 (1987). doi:10.1016/0377-0427(87)90125-7
Calinski, T., Harabasz, J.: A dendrite method for cluster analysis. Commun. Stat. 3(1), 1–27 (1974)
Silhavy, R., Silhavy, P., Prokopova, Z.: Analysis and selection of a regression model for the Use Case Points method using a stepwise approach. J. Syst. Softw. 125, 1–14 (2017)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2017 Springer International Publishing AG
About this paper
Cite this paper
Prokopova, Z., Silhavy, R., Silhavy, P. (2017). The Effects of Clustering to Software Size Estimation for the Use Case Points Methods. In: Silhavy, R., Silhavy, P., Prokopova, Z., Senkerik, R., Kominkova Oplatkova, Z. (eds) Software Engineering Trends and Techniques in Intelligent Systems. CSOC 2017. Advances in Intelligent Systems and Computing, vol 575. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-57141-6_51
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-57141-6_51
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-319-57140-9
Online ISBN: 978-3-319-57141-6
eBook Packages: EngineeringEngineering (R0)