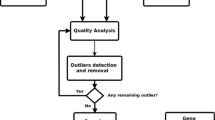
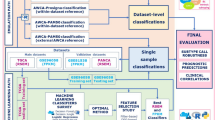
Abstract
Although Next-Generation Sequencing (NGS) has more impact nowadays than microarray sequencing, there is a huge volume of microarray data that has not still been processed. The last represents the most important source of biological information nowadays due largely to its use over many years, and a very important potential source of genetic knowledge deserving appropriate analysis. Thanks to the two techniques, there is now a huge amount of data that allows us to obtain robust results from its integration. This paper deals with the integration of RNASeq data with microarrays data in order to find breast cancer biomarkers as expressed genes. These integrated data has been used to create a classifier for an early diagnosis of breast cancer.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anders, S., Pyl, P.T., Huber, W.: HTSeq-a python framework to work with high-throughput sequencing data. Bioinformatics 31(2), 166–169 (2014). btu638
Barrett, T., Troup, D.B., Wilhite, S.E., Ledoux, P., Rudnev, D., Evangelista, C., Kim, I.F., Soboleva, A., Tomashevsky, M., Edgar, R.: NCBI GEO: mining tens of millions of expression profiles—database and tools update. Nucleic Acids Res. 35(suppl 1), D760–D765 (2007)
Ding, C., Peng, H.: Minimum redundancy feature selection from microarray gene expression data. In: Computer System Bioinformatics, CSB 2003, Proceedings of 2003 IEEE Bioinformatics (2003)
Gohlmann, H., Talloen, W.: Gene Expression Studies Using Affymetrix Microarrays. CRC Press, Boca Raton (2009)
Heider, A., Alt, R.: virtualArray: a R/bioconductor package to merge raw data from different microarray platforms. BMC Bioinform. 14(1), 75 (2013)
Illumina: Illumina genes expression arrays (2009). http://www.illumina.com/techniques/microarrays/gene-expression-arrays.html
Kim, D., Pertea, G., Trapnell, C., Pimentel, H., Kelley, R., Salzberg, S.L.: TopHat2: accurate alignment of transcriptomes in the presence of insertions, deletions and gene fusions. Genome Biol. 14(4), R36 (2013)
Langmead, B., Salzberg, S.L.: Fast gapped-read alignment with Bowtie 2. Nat. Methods 9(4), 357–359 (2012)
Li, H., Handsaker, B., Wysoker, A., Fennell, T., Ruan, J., Homer, N., Marth, G., Abecasis, G., Durbin, R., et al.: The sequence alignment/map format and samtools. Bioinformatics 25(16), 2078–2079 (2009)
Noble, W.S.: What is a support vector machine? Nat. Biotechnol. 24, 1565–1567 (2006)
Nookaew, I., Papini, M., Pornputtpong, N., Scalcinati, G., Fagerberg, L., Uhlén, M., Nielsen, J.: A comprehensive comparison of RNA-seq-based transcriptome analysis from reads to differential gene expression and cross-comparison with microarrays: a case study in saccharomyces cerevisiae. Nucleic Acids Res. 40(20), 10084–10097 (2012). gks804
OMS: Women’s Health (2013). http://www.who.int/mediacentre/factsheets/fs334/en/
Peirson, S.N., Butler, J.N.: Quantitative polymerase chain reaction. In: Rosato, E. (ed.) Circadian Rhythms: Methods and Protocols, pp. 349–362. Springer, Heidelberg (2007)
Ritchie, M.E., Phipson, B., Wu, D., Hu, Y., Law, C.W., Shi, W., Smyth, G.K.: limma powers differential expression analyses for RNA-sequencing and microarray studies. Nucleic Acids Res. 43(7), e47 (2015). gkv007
Shao, J.: Linear model selection by cross-validation. J. Am. Stat. Assoc. 88(422), 486–494 (1993)
Tarazona, S., García, F., Ferrer, A., Dopazo, J., Conesa, A.: NOIseq: a RNA-seq differential expression method robust for sequencing depth biases. EMBnet. J. 17(B), 18 (2012)
Wang, Z., Gerstein, M., Snyder, M.: RNA-seq: a revolutionary tool for transcriptomics. Nat. Rev. Genet. 10(1), 57–63 (2009)
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by Project TIN2015-71873-R (Spanish Ministry of Economy and Competitiveness -MINECO- and the European Regional Development Fund -ERDF).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2017 Springer International Publishing AG
About this paper
Cite this paper
Castillo, D., Galvez, J.M., Herrera, L.J., Rojas, I. (2017). Breast Cancer Microarray and RNASeq Data Integration Applied to Classification. In: Rojas, I., Joya, G., Catala, A. (eds) Advances in Computational Intelligence. IWANN 2017. Lecture Notes in Computer Science(), vol 10305. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-59153-7_11
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-59153-7_11
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-319-59152-0
Online ISBN: 978-3-319-59153-7
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)