Abstract
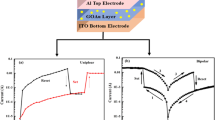
Resistive random access memory ReRAM has attracted great attention due to its potential for flash memory replacement in next generation nonvolatile memory applications. Among the main characteristics of this type of memory, we have: low energy consumption, high-speed switching, durability, scalability and friendly manufacturing process. This device is based on resistive switching phenomenon for operation, which is reversible and can be played back repeatedly. In this work, eight different devices are developed and fabrication is made as follows: thin films are obtained by dip coating technique. The dip coating apparatus basically consists of a clamp which holds the substrate is dipped in a GO solution (graphene oxide) which containing dopant (cupper, iron or silver) or CuO (copper oxide). ITO (indium tin oxide) and aluminum contacts were evaporated. The devices were developed with purpose: intention is record and read information dynamically with appropriate algorithm. There is even the possibility of storing images. With these functions, it would be promising to enter the neuromorphic computing area that is one of the resistive memory applications. ReRAM technology advent represents a paradigm shift for artificial neural networks, being the best candidate for emulation of synaptic plasticity and learning mode.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Lanza, M.: A review on resistive switching in high-k dielectrics: a nanoscale point of view using conductive atomic force microscope. Materials 7, 2155–2182 (2014)
Marinella, M.J.: Emerging resistive switching memory technologies: overview and current status. IEEE (2014)
Akinaga, H., Shima, H.: ReRAM technology; challenges and prospects. IEIEC Electr. Express 9, 795–807 (2012)
Gale, E.M.: TiO2-based Memristors and ReRAM: materials, mechanisms and models (a review). Semicond. Sci. Technol. 29, 104004 (2014)
Choi, H.: Main degradation mechanism in AsTeGeSiN threshold switching devices. Microelectr. Reliabil. 56, 61–65 (2016)
Katsukis, G., Romero-Nieto, C., Malig, J., Ehli, C., Guldi, D.M.: Interfacing nanocarbons with organic and inorganic semiconductors: from nanocrystals/quantum dots to extended tetrathiafulvalenes. Langmuir 28, 11662–11675 (2012)
Kaminska, I., Barras, A., Coffinier, Y., Lisowski, W., et al.: Preparation of a responsive carbohydrate-coated biointerface based on graphene/azido-terminated tetrathiafulvalene nanohybrid material. Appl. Mater. Interfaces 4, 5386–5393 (2012)
Kaminska, I., Das, M.R., Coffinier, Y., Niedziolka-Jonsson, J., et al.: Preparation of graphene/tetrathiafulvalene nanocomposite switchable surfaces. Chem. Commun. 48, 1221–1223 (2012)
Denis, P.A.: Chemical reactivity of electron-doped and hole-doped graphene. J. Phys. Chem. C 117, 3895–3902 (2013)
Lu, W., Soukiassian, P., Boeckl, J.: Graphene: fundamentals and functionalities. MRS Bull. 37, 1119–1124 (2012)
Siemon, A., Menzel, S., Waser, R., Linn, E.: A complementary resistive switch-based crossbar array adder. IEEE J. Emerg. Sel. Top. Circuits Syst. 5(1), 64–74 (2015)
Lee, J.S., Lee, S., Noh, T.W.: Resistive switching phenomena: a review of statistical physics approaches. Appl. Phys. Rev. 2, 031303 (2015)
Yoo, D., Cuong, T.V., Hahn, S.H.: Effect of copper oxide on the resistive switching responses of graphene oxide film. Curr. Appl. Phys 14, 1301–1303 (2014)
Xu, J., Xie, D., Feng, T., et al.: Scaling-down characteristics of nanoscale diamond-like carbon based resistive switching memories. Carbon 75, 255–261 (2014)
Tanaka, H., Kinoshita, K., Yoshihara, M., Kishida, S.: Correlation between filament distribution and resistive switching properties in resistive random access memory consisting of binary transition-metal oxides. AIP Adv. 2, 022141 (2012)
Zhang, R., et al.: Transparent amorphous memory cell: a bipolar resistive switching in ZnO/Pr(0.7)Ca(0.3)MnO(3)/ITO for invisible electronics application. J. Non-Cryst. Solids 406, 102–106 (2014)
Indiveri, G., Linn, E., Ambrogio, S.: ReRAM-based neuromorphic computing. In: Ielmini, D., Waser, R. (eds.) Resistive Switching: From Fundamentals of Nanoionic Redox Processes to Memristive Device Applications. Wiley-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA (2016)
DeSalvo, B., Vianello, E., Garbin, D., Bichler, O., Perniola, L.: From memory in our brain to emerging resistive memories in neuromorphic systems. IEEE (2015)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2017 Springer International Publishing AG
About this paper
Cite this paper
Sparvoli, M., Silva, M.F.P., Gazziro, M. (2017). Development of Doped Graphene Oxide Resistive Memories for Applications Based on Neuromorphic Computing. In: Rojas, I., Joya, G., Catala, A. (eds) Advances in Computational Intelligence. IWANN 2017. Lecture Notes in Computer Science(), vol 10305. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-59153-7_50
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-59153-7_50
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-319-59152-0
Online ISBN: 978-3-319-59153-7
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)