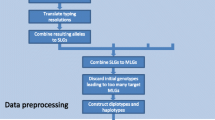
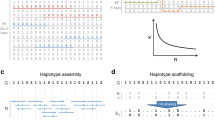
Abstract
An important problem in Bioinformatics is Haplotype Inference (HI), that consists of computationally inferring haplotype sequences from genotype data. Haplotype data is highly informative for illness propensity detection, but it is much costly and time consuming to acquire; that gives the HI Problem an overwhelming relevance. In this paper, we formally demonstrate that specific genomic data features can be very strong indicators of error propensity in each one of four well-known HI methods studied. We apply Statistical analyses to explore the relevance of biologically meaningful properties extracted from the genotype sequences, and develop models to predict the accuracy expected in the haplotype inference results, for different methods and error metrics. The quality and the stability of our models are demonstrated by statistical evidence. One of our estimated models presents nearly perfect accuracy for all four methods studied. Our results provide useful insights to help develop more effective HI methods.
R.S. Rosa—This work was developed with financial support from Brazilian sponsoring agency CAPES, which the authors gratefully acknowledge.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Lin, D., Wang, L., Li, Y.: Haplotype-based statistical inference for population-based case-control and cross-sectional studies with complex sample designs. J. Surv. Stat. Methodol 4(2), 188–214 (2016)
Laehnemann, D., Borkhardt, A., McHardy, A.C.: Denoising dna deep sequencing data-high-throughput sequencing errors and their correction. Brief. Bioinf. 17(1), 154–179 (2016)
O’Connell, J., et al.: A general approach for haplotype phasing across the full spectrum of relatedness. PLoS Genetics 10(4), e1004234 (2014)
Howie, B.N., Donnelly, P., Marchini, J.: A flexible and accurate genotype imputation method for the next generation of genome-wide association studies. PLoS Genet. 5(6), e1000529 (2009)
Browning, B.L., Browning, S.R.: A fast, powerful method for detecting identity by descent. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 88(2), 173–182 (2011)
Eronen, L., Geerts, F., Toivonen, H.: Haplorec: efficient and accurate large-scale reconstruction of haplotypes. BMC Bioinf. 7, 542 (2006)
Scheet, P., Stephens, M.: A fast and flexible statistical model for large-scale population genotype data: applications to inferring missing genotypes and haplotypic phase. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 78(4), 629–644 (2006)
Li, Z., Zhou, W., Zhang, X.S., Chen, L.: A parsimonious tree-grow method for haplotype inference. Bioinformatics 21, 3475–3481 (2005)
Rosa, R.S., Guimarães, K.S.: Insights on haplotype inference on large genotype datasets. In: Ferreira, C.E., Miyano, S., Stadler, P.F. (eds.) BSB 2010. LNCS, vol. 6268, pp. 47–58. Springer, Heidelberg (2010). doi:10.1007/978-3-642-15060-9_5
Stephens, J.C., et al.: Haplotype variation and linkage disequilibrium in 313 human genes. Science 293(5529), 489–493 (2001)
The International HapMap Consortium: The international hapmap consortium. Nature 426, 789–796 (2003)
Niu, T., Qin, Z.S., Xu, X., Liu, J.S.: Bayesian haplotype inference for multiple linked single-nucleotide polymorphisms. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 70, 157–169 (2002)
Lin, S., Cutler, D.J., Zwick, M.E., Chakravarti, A.: Haplotype inference in random population samples. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 71(5), 1129–1137 (2002)
Montgomery, D., Runger, G.: Applied statistics and probability for engineers, 4th edn. LTC, São Paulo (2003)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2017 Springer International Publishing AG
About this paper
Cite this paper
Rosa, R.S., Guimarães, K.S. (2017). Accurate Prediction of Haplotype Inference Errors by Feature Extraction. In: Cai, Z., Daescu, O., Li, M. (eds) Bioinformatics Research and Applications. ISBRA 2017. Lecture Notes in Computer Science(), vol 10330. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-59575-7_27
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-59575-7_27
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-319-59574-0
Online ISBN: 978-3-319-59575-7
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)