Abstract
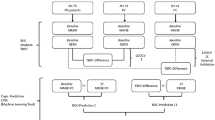
Event-related potentials (ERPs) have been shown to reflect neurodegenerative processes in Alzheimer’s disease (AD) and might qualify as non-invasive and cost-effective markers to facilitate the objectivization of AD assessment in daily clinical practice. Lately, the combination of multivariate pattern analysis (MVPA) and Gaussian process classification (GPC) has gained interest in the neuroscientific community. Here, we demonstrate how a MVPA-GPC approach can be applied to electrophysiological data. Furthermore, in order to account for the temporal information of ERPs, we develop a novel method that integrates interregional synchrony of ERP time signatures. By using real-life ERP recordings of a prospective AD cohort study (PRODEM), we empirically investigate the usefulness of the proposed framework to build neurophysiological markers for single subject classification tasks. GPC outperforms the probabilistic reference method in both tasks, with the highest AUC overall (0.802) being achieved using the new spatiotemporal method in the prediction of rapid cognitive decline.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Howe, A.S., Bani-Fatemi, A., De Luca, V.: The clinical utility of the auditory P300 latency subcomponent event-related potential in preclinical diagnosis of patients with mild cognitive impairment and Alzheimer’s disease. Brain Cogn. 86, 64–74 (2014)
Howe, A.S.: Meta-analysis of the endogenous N200 latency event-related potential subcomponent in patients with Alzheimer’s disease and mild cognitive impairment. Clin. Neurophysiol. 125, 1145–1151 (2014)
Olichney, J.M., Yang, J.C., Taylor, J., Kutas, M.: Cognitive event-related potentials: biomarkers of synaptic dysfunction across the stages of Alzheimer’s disease. J. Alzheimer’s Dis. 26(Suppl. 3), 215–228 (2011)
Challis, E., Hurley, P., Serra, L., Bozzali, M., Oliver, S., Cercignani, M.: Gaussian process classification of Alzheimer’s disease and mild cognitive impairment from resting-state fMRI. NeuroImage 112, 232–243 (2015)
Hui, J.S., Wilson, R.S., Bennett, D.A., Bienias, J.L., Gilley, D.W., Evans, D.A.: Rate of cognitive decline and mortality in Alzheimer’s disease. Neurology 61, 1356–1361 (2003)
Liu, C.C., Kanekiyo, T., Xu, H., Bu, G.: Apolipoprotein E and Alzheimer disease: risk, mechanisms and therapy. Nat. Rev. Neurol. 9, 106–118 (2013)
Rosengarten, B., Paulsen, S., Burr, O., Kaps, M.: Effect of ApoE ε4 allele on visual evoked potentials and resultant flow coupling in patients with Alzheimer. J. Geriatr. Psychiatry Neurol. 23, 165–170 (2010)
Green, J., Levey, A.I.: Event-related potential changes in groups at increased risk for Alzheimer disease. Arch. Neurol. 56, 1398–1403 (1999)
Lee, T.-W., Yu, Y.W.-Y., Hong, C.-J., Tsai, S.-J., Wu, H.-C., Chen, T.-J.: The influence of apolipoprotein E Epsilon4 polymorphism on qEEG profiles in healthy young females: a resting EEG study. Brain Topogr. 25, 431–442 (2012)
Canuet, L., Tellado, I., Couceiro, V., Fraile, C., Fernandez-Novoa, L., Ishii, R., Takeda, M., Cacabelos, R.: Resting-state network disruption and APOE genotype in Alzheimer’s disease: a lagged functional connectivity study. PLoS ONE 7, e46289 (2012)
Folstein, M.F., Folstein, S.E., McHugh, P.R.: “Mini-mental state”. A practical method for grading the cognitive state of patients for the clinician. J. Psychiatr. Res. 12, 189–198 (1975)
Carcaillon, L., Pérès, K., Péré, J.J., Helmer, C., Orgogozo, J.M., Dartigues, J.F.: Fast cognitive decline at the time of dementia diagnosis: a major prognostic factor for survival in the community. Dement. Geriatr. Cogn. Disord. 23, 439–445 (2007)
Puglielli, L., Tanzi, R.E., Kovacs, D.M.: Alzheimer’s disease: the cholesterol connection. Nat. Neurosci. 6, 345–351 (2003)
Anderer, P., Semlitsch, H.V., Saletu, B., Barbanoj, M.J.: Artifact processing in topographic mapping of electroencephalographic activity in neuropsychopharmacology. Psychiatry Res.: Neuroimaging 45, 79–93 (1992)
Delorme, A., Makeig, S.: EEGLAB: an open source toolbox for analysis of single-trial EEG dynamics including independent component analysis. J. Neurosci. Methods 134, 9–21 (2004)
Barachant, A., Congedo, M.: A Plug&Play P300 BCI Using Information Geometry. arXiv preprint arXiv:1409.0107 (2014)
Congedo, M., Barachant, A., Andreev, A.: A New Generation of Brain-Computer Interface Based on Riemannian Geometry arXiv:1310.8115 (2013)
Zeng, L.-L., Shen, H., Liu, L., Wang, L., Li, B., Fang, P., Zhou, Z., Li, Y., Hu, D.: Identifying major depression using whole-brain functional connectivity: a multivariate pattern analysis. Brain 135, 1498–1507 (2012)
Rasmussen, C.E., Williams, C.K.I.: Gaussian Processes for Machine Learning. The MIT Press, Cambridge (2006)
Adler, R.J., Taylor, J.E.: Random Fields and Geometry. Springer, New York (2007)
Rasmussen, C.E., Nickisch, H.: Gaussian processes for machine learning (GPML) toolbox. J. Mach. Learn. Res. 11, 3011–3015 (2010)
Chen, M.: Pattern Recognition and Machine Learning Toolbox. MATLAB Central File Exchange (2016)
Brodersen, K.H., Ong, C.S., Stephan, K.E., Buhmann, J.M.: The balanced accuracy and its posterior distribution. In: Proceedings of the 2010 20th International Conference on Pattern Recognition, pp. 3121–3124. IEEE Computer Society (2010)
Hanley, J.A., McNeil, B.J.: A method of comparing the areas under receiver operating characteristic curves derived from the same cases. Radiology 148, 839–843 (1983)
Stahl, D., Pickles, A., Elsabbagh, M., Johnson, M.H., The, B.T.: Novel machine learning methods for ERP analysis: a validation from research on infants at risk for autism. Dev. Neuropsychol. 37, 274–298 (2012)
Acknowledgment
The PRODEM study has been supported by the Austrian Research Promotion Agency FFG, project no. 827462, including financial contributions from Dr. Grossegger and Drbal GmbH, Vienna, Austria.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2017 Springer International Publishing AG
About this paper
Cite this paper
Fruehwirt, W. et al. (2017). Bayesian Gaussian Process Classification from Event-Related Brain Potentials in Alzheimer’s Disease. In: ten Teije, A., Popow, C., Holmes, J., Sacchi, L. (eds) Artificial Intelligence in Medicine. AIME 2017. Lecture Notes in Computer Science(), vol 10259. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-59758-4_7
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-59758-4_7
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-319-59757-7
Online ISBN: 978-3-319-59758-4
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)