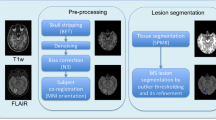
Abstract
Quantification of white matter lesion changes on brain magnetic resonance (MR) images is of major importance for the follow-up of patients with Multiple Sclerosis (MS). Many automated segmentation methods have been proposed. However, most of them focus on a single time point MR scan session and hence lack consistency when evaluating lesion changes over time. In this paper, we present MSmetrix-long, an unsupervised method that incorporates temporal consistency by jointly segmenting MS lesions of two subsequent scan sessions. The method is formulated as a Maximum A Posteriori model on the FLAIR image intensities of both time points and the difference image intensities, and optimised using an expectation maximisation algorithm. Validation is performed on two different data sets in terms of consistency and sensitivity to MS lesion changes. It is shown that MSmetrix-long outperforms MSmetrix-cross for the quantification of MS lesion evolution over time.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Blystad, I., Hakansson, I., Tisell, A., et al.: Quantitative MRI for analysis of active multiple sclerosis lesions without gadolinium-based contrast agent. Am. J. Neuroradiol. 37, 94–100 (2016)
Pham, D.: The 2015 longitudinal multiple sclerosis lesion segmentation challenge, ISBI (2015). http://iacl.ece.jhu.edu/MSChallenge
Gerig, G., Welti, D., Guttmann, C.R.G., et al.: Exploring the discriminative power of the time domain for segmentation and characterisation of active lesions in serial MR data. Med. Image Anal. 4, 31–42 (2000)
Rey, D., Subsol, G., Delingette, H., et al.: Automatic detection and segmentation of evolving processes in 3D medical images: application to multiple sclerosis. Med. Image Anal. 6, 163–179 (2002)
Sweeney, E.M., Shinohara, R.T., Shea, C.D., et al.: Automatic lesion incidence estimation and detection in multiple sclerosis using multisequence longitudinal MRI. MSmetrix Am. J. Neuroradiol. 34, 68–73 (2013)
Bernardis, E., Pohl, K.M., Davatzikos, C.: Extracting evolving pathologies via spectral clustering. In: Gee, J.C., Joshi, S., Pohl, K.M., Wells, W.M., Zöllei, L. (eds.) IPMI 2013. LNCS, vol. 7917, pp. 680–691. Springer, Heidelberg (2013). doi:10.1007/978-3-642-38868-2_57
Elliott, C., Arnold, D.L., Collins, D.L., et al.: Temporally consistent probabilistic detection of new multiple sclerosis lesions in brain MRI. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 32, 1490–1503 (2013)
Jain, S., Sima, D.M., Ribbens, A., et al.: Automatic segmentation and volumetry of multiple sclerosis brain lesions from MR images. NeuroImage Clin. 8, 367–375 (2015)
Smeets, D., Ribbens, A., Sima, D.M., et al.: Reliable measurements of brain atrophy in individual patients with multiple sclerosis. Brain Behav. 1.e00518–12.e00518 (2016). doi:10.1002/brb3.518
Lewis, E.B., Fox, N.C.: Correction of differential intensity inhomogeneity in longitudinal MR images. NeuroImage 23, 75–83 (2004)
Castleman, K.R.: Digital Image Processing, 2nd edn. Prentice Hall, New Jersey (1995)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2017 Springer International Publishing AG
About this paper
Cite this paper
Jain, S., Ribbens, A., Sima, D.M., Van Huffel, S., Maes, F., Smeets, D. (2017). Unsupervised Framework for Consistent Longitudinal MS Lesion Segmentation. In: Müller, H., et al. Medical Computer Vision and Bayesian and Graphical Models for Biomedical Imaging. BAMBI MCV 2016 2016. Lecture Notes in Computer Science(), vol 10081. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-61188-4_19
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-61188-4_19
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-319-61187-7
Online ISBN: 978-3-319-61188-4
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)