Abstract
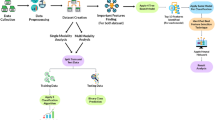
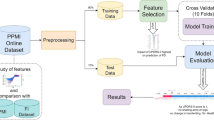
Parkinson’s disease is a neurodegenerative disorder that affects people worldwide. While the motor symptoms such as tremor, rigidity, bradykinesia and postural instability are predominant, patients experience also non-motor symptoms, such as decline of cognitive abilities, behavioural problems, sleep disturbances, and other symptoms that greatly affect their quality of life. Careful management of patient’s condition is crucial to ensure the patient’s independence and the best possible quality of life. This is achieved by personalized medication treatment based on individual patient’s symptoms and medical history. This paper explores the utility of machine learning to help development of decision models, aimed to support clinicians’ decisions regarding patients’ therapies. We propose a new multi-view methodology for determining groups of patients with similar symptoms and detecting patterns of medications changes that lead to the improvement or decline of patients’ quality of life. We identify groups of patients ordered in accordance to their quality of life assessment and find examples of therapy modifications which induce positive or negative change of patients’ symptoms. The results demonstrate that motor and autonomic symptoms are the most informative for evaluating the quality of life of Parkinson’s disease patients.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
Notes
- 1.
Data used in the preparation of this article were obtained from the Parkinsons Progression Markers Initiative (PPMI) database (www.ppmi-info.org/data). For up-to-date information on the study, visit www.ppmi-info.org. PPMI—a public-private partnership—is funded by the Michael J. Fox Foundation for Parkinson’s Research and funding partners. List of funding partners can be found at www.ppmi-info.org/fundingpartners.
References
European Parkinson’s Disease Association. http://www.epda.eu.com/. Accessed 01 July 2016
PD_manager: m-Health platform for Parkinson’s disease management. EU Framework Programme for Research and Innovation Horizon 2020, Grant number 643706, 2015–2017. http://www.parkinson-manager.eu/
SENSE-PARK. Project’s website. http://www.sense-park.eu/. Accessed 01 July 2016
Appice, A., Malerba, D.: A co-training strategy for multiple view clustering in process mining. IEEE Trans. Serv. Comput. 9(6), 832–845 (2016)
Bezdek, J.C.: Pattern Recognition with Fuzzy Objective Function Algorithms. Plenum Press, New York (1981)
Blum, A., Mitchell, T.: Combining labeled and unlabeled data with co-training. In: Proceedings of the Eleventh Annual Conference on Computational Learning Theory. COLT 1998, pp. 92–100. ACM, New York (1998)
Cai, X., Nie, F., Huang, H.: Multi-view k-means clustering on big data. In: IJCAI 2013, Proceedings of the 23rd International Joint Conference on Artificial Intelligence, Beijing, China, August 3–9, 2013, pp. 2598–2604 (2013)
Chaudhuri, K., Kakade, S.M., Livescu, K., Sridharan, K.: Multi-view clustering via canonical correlation analysis. In: Proceedings of the 26th Annual International Conference on Machine Learning, ICML 2009, pp. 129–136 (2009)
Cleuziou, G., Exbrayat, M., Martin, L., Sublemontier, J.: Cofkm: a centralized method for multiple-view clustering. In: The Ninth IEEE International Conference on Data Mining, ICDM 2009, Miami, Florida, USA, 6–9, pp. 752–757 (2009)
Dalrymple-Alford, J., MacAskill, M., Nakas, C., Livingston, L., Graham, C., Crucian, G., Melzer, T., Kirwan, J., Keenan, R., Wells, S., et al.: The MoCA: well-suited screen for cognitive impairment in Parkinson disease. Neurology 75(19), 1717–1725 (2010)
Dorsey, E., Constantinescu, R., Thompson, J., Biglan, K., Holloway, R., Kieburtz, K., Marshall, F., Ravina, B., Schifitto, G., Siderowf, A., et al.: Projected number of people with Parkinson disease in the most populous nations, 2005 through 2030. Neurology 68(5), 384–386 (2007)
N.C.C. for Chronic Conditions (UK et al. Symptomatic pharmacological therapy in Parkinsons disease) (2006)
Gatsios, D., Rigas, G., Miljkovic, D., Seljak, B.K., Bohanec, M.: m-health platform for Parkinson’s disease management. In: Proceedings of 18th International Conference on Biomedicine and Health Informatics CBHI (2016)
Goetz, C.G., Tilley, B.C., Shaftman, S.R., Stebbins, G.T., Fahn, S., Martinez-Martin, P., Poewe, W., Sampaio, C., Stern, M.B., Dodel, R., et al.: Movement disorder society-sponsored revision of the unified Parkinson’s disease rating scale (MDS-UPDRS): scale presentation and clinimetric testing results. Mov. Disord. 23(15), 2129–2170 (2008)
He, X., Kan, M.-Y., Xie, P., Chen, X.: Comment-based multi-view clustering of web 2.0 items. In: Proceedings of the 23rd International Conference on World Wide Web, pp. 771–782. ACM (2014)
Kumar, A., Daumé, H.: A co-training approach for multi-view spectral clustering. In: Proceedings of the 28th International Conference on Machine Learning, ICML, pp. 393–400 (2011)
Marek, K., Jennings, D., Lasch, S., Siderowf, A., Tanner, C., Simuni, T., Coffey, C., Kieburtz, K., Flagg, E., Chowdhury, S., et al.: The Parkinson’s progression markers initiative (PPMI). Progress Neurobiol. 95(4), 629–635 (2011)
Rousseeuw, P.J.: Silhouettes: a graphical aid to the interpretation and validation of cluster analysis. J. Comput. Appl. Math. 20, 53–65 (1987)
Samà, A., Pérez-López, C., Rodríguez-Martín, D., Moreno-Aróstegui, J.M., Rovira, J., Ahlrichs, C., Castro, R., Cevada, J., Graça, R., Guimarães, V., et al.: A double closed loop to enhance the quality of life of Parkinson’s disease patients: REMPARK system. Innov. Med. Healthcare 207, 115 (2015)
Stecher, J., Janssen, F., Fürnkranz, J.: Separating rule refinement and rule selection heuristics in inductive rule learning. In: Calders, T., Esposito, F., Hüllermeier, E., Meo, R. (eds.) ECML PKDD 2014. LNCS, vol. 8726, pp. 114–129. Springer, Heidelberg (2014). doi:10.1007/978-3-662-44845-8_8
Tzallas, A.T., Tsipouras, M.G., Rigas, G., Tsalikakis, D.G., Karvounis, E.C., Chondrogiorgi, M., Psomadellis, F., Cancela, J., Pastorino, M., Waldmeyer, M.T.A., et al.: PERFORM: a system for monitoring, assessment and management of patients with Parkinson’s disease. Sensors 14(11), 21329–21357 (2014)
Tzortzis, G., Likas, A.: Convex mixture models for multi-view clustering. In: Alippi, C., Polycarpou, M., Panayiotou, C., Ellinas, G. (eds.) ICANN 2009. LNCS, vol. 5769, pp. 205–214. Springer, Heidelberg (2009). doi:10.1007/978-3-642-04277-5_21
Valmarska, A., Lavrač, N., Fürnkranz, J., Robnik-Šikonja, M.: Refinement and selection heuristics in subgroup discovery and classification rule learning (2017). (under review)
Valmarska, A., Miljkovic, D., Lavrač, N., Robnik-Šikonja, M.: Towards multi-view approach to Parkinson’s disease quality of life data analysis. In: 5th International Workshop on New Frontiers in Mining Complex Patterns at ECML-PKDD2016 (2016)
Valmarska, A., Robnik-Šikonja, M., Lavrač, N.: Inverted heuristics in subgroup discovery. In: Proceedings of the 18th International Multiconference Information Society (2015)
Visser, M., Marinus, J., Stiggelbout, A.M., Van Hilten, J.J.: Assessment of autonomic dysfunction in Parkinson’s disease: the SCOPA-AUT. Mov. Disord. 19(11), 1306–1312 (2004)
Washburn, R.A., Smith, K.W., Jette, A.M., Janney, C.A.: The physical activity scale for the elderly (PASE): development and evaluation. J. Clin. Epidemiol. 46(2), 153–162 (1993)
Xu, C., Tao, D., Xu, C.: A survey on multi-view learning. arXiv preprint arXiv:1304.5634 (2013)
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the PD_manager project, funded within the EU Framework Programme for Research and Innovation Horizon 2020 grant 643706. We acknowledge the support of the Slovenian Research Agency and the European Commission through The Human Brain Project (HBP), grant FP7-ICT-604102.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2017 Springer International Publishing AG
About this paper
Cite this paper
Valmarska, A., Miljkovic, D., Robnik-Šikonja, M., Lavrač, N. (2017). Multi-view Approach to Parkinson’s Disease Quality of Life Data Analysis. In: Appice, A., Ceci, M., Loglisci, C., Masciari, E., Raś, Z. (eds) New Frontiers in Mining Complex Patterns. NFMCP 2016. Lecture Notes in Computer Science(), vol 10312. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-61461-8_11
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-61461-8_11
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-319-61460-1
Online ISBN: 978-3-319-61461-8
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)