Abstract
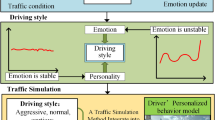
In this paper, according to the problem that existing driver model can’t reflect some situations in actual driving, a driver model which considers the factors such as driver’s emotion, personality and road condition is built, the emotion model is introduced when the driver is in the process of traffic jams, car following, overtaking, lane changing, emergency situation and so on, the influence of the emotion state, driving destination and so on to the driving decision is analyzed, in addition, the driver’s states are detected by a camera, incentive or warning strategies will be given out according to the situation. At last, a virtual vehicle simulation is experimented based on this model.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Song, H., Chen, Z.J., Kong, F.E.: Study on aiding-level judgment of pilot assistant system. J. Syst. Simul. 21(1), 208–212 (2009)
Zhang, L.: Researches on Driver Unified Decision Model for Vehicle Assistant Control [Ph. D. dissertation], Jilin University, China (2007)
Shi, W.Y., Zhao, M.H.: Application of information fuse technique in assistant-driving system. Modern Electron. Tech. 26(17), 84–87 (2003)
Wang, G., Wan, J.: Review of information perception technology for driving safety assistance system. Comput. Commun. 26(3), 50–54 (2008)
Guo, K.H., Ma, F.J., Kong, F.S.: Driver model parameter identification of the driver-vehicle-road closed-loop system. Autom. Eng. 24(1), 20–24 (2002)
Xie, L., Wang, Z., Ren, D.C., Teng, S.D.: Research of driver emotion model under simplified traffic condition. Acta Automatica Sinica 36(12), 1732–1743 (2010)
Reichardt, D.M.: Approaching driver models which integrate models of emotion and risk. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Intelligent Vehicles Symposium, Eindhoven, pp. 234–239. IEEE Press, Netherlands (2008)
Nass, C., Jonsson, I.M., Harris, H., Reaves, B., Endo, J., Brave, S.: Improving automotive safety by pairing driver emotion and car voice emotion. In: Proceedings of the CHI Extended Abstracts of Human Factors in Computing Systems, pp. 1973–1976. ACM Press, Portland, USA(2005)
Leng, H., Lin, Y., Zanzi, L.A.: An experimental study on physiological parameters toward driver emotion recognition. In: Dainoff, M.J. (ed.) EHAWC 2007. LNCS, vol. 4566, pp. 237–246. Springer, Heidelberg (2007). doi:10.1007/978-3-540-73333-1_30
Fukuda, S.: Detecting driver’s emotion: a step toward emotion-based reliability engineering. In: Pham, H. (ed.) Recent Advances in Reliability and Quality in Design, pp. 491–507. Springer, Berlin (2008)
Yu, L., He, M.: Study of driving behavior model based on agent and ambient intelligence. Technol. Dev. Enterp. 28(3), 19–21 (2009)
Leu, G., Curtis, N.J., Abbass, H.: Modeling and evolving human behaviors and emotions in road traffic networks. Procedia Soc. Behav. Sci. 54(2290), 999–1009 (2012)
Roidl, E., Siebert, F.W., Oehl, M., Höger, R.: Introducing a multivariate model for predicting driving performance: the role of driving anger and personal characteristics. J. Safety Res. 47, 47–56 (2013)
Jeon, M., Walker, B.N., Yim, J.B.: Effects of specific emotions on subjective judgment, driving performance, and perceived workload. Transp. Res. Part F: Traffic Psychol. Behav. 24, 197–209 (2014)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2017 Springer International Publishing AG
About this paper
Cite this paper
Xiao, Q., Hu, C., Ding, G. (2017). A Driver Model Based on Emotion. In: Tan, Y., Takagi, H., Shi, Y., Niu, B. (eds) Advances in Swarm Intelligence. ICSI 2017. Lecture Notes in Computer Science(), vol 10386. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-61833-3_64
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-61833-3_64
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-319-61832-6
Online ISBN: 978-3-319-61833-3
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)