Abstract
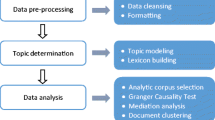
In recent years, the growing prevalence of social networks makes it possible to utilize human users as sensors to inspect city environment and human activities. Consequently, valuable insights can be gained by applying data mining techniques to the data generated through social networks. In this work, a practical approach to combine data mining techniques with statistical analysis is proposed to implement crowd sensing in a smart city. A case study to analyze the relationship between weather conditions and traffic congestion in Beijing based on tweets posted on Sina Weibo platform is presented to demonstrate the proposed approach. Following the steps of raw dataset pre-processing, target dataset processing and statistical data analysis, analytic corpus containing tweets related to different weather conditions, traffic congestion and human outdoor activity is selected to test causal relationships by Granger Causality Test. The mediation analysis is also implemented to verify human outdoor activity as a mediator variable significantly carrying the influence of good weather to traffic congestion. The result demonstrates that outdoor activity serves as a mediator transmitting the effect of good weather on traffic congestion.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Derek, D., Karl, S., Swapna, S.G., Aldo, D.: Social media enabled human sensing for smart cities. AI Commun. 29(1), 57–75 (2015)
Anjaria, M., Guddeti, R.M.R.: Influence factor based opinion mining of Twitter data using supervised learning. In: COMSNETS, January 2014, pp. 1–8 (2014)
Wu, X., Xie, F., Wu, G., Ding, W.: Personalized news filtering and summarization on the web. In: Proceedings of the 2011 IEEE 23rd International Conference on Tools with Artificial Intelligence, Washington, DC, USA, pp. 414–421 (2011)
Nathan, K.C., Amanda, L.G.: Health behavior interventions in the age of Facebook. Am. J. Prev. Med. 43(5), 571–572 (2012)
Fisher, J., Clayton, M.: Who gives a Tweet: assessing patients’ interest in the use of social media for health care. Worldviews Evid Based Nurs. 9(2), 100–108 (2012)
Wang, S.L., Paul, M.J., Dredze, M.: Social media as a sensor of air quality and public response in China. J. Med. Internet Res. 17(3) (2015)
Pan, B., Zheng, Y., Wilkie, D., Shahabi, C.: Crowd sensing of traffic anomalies based on human mobility and social media. In: ACM SIGSPATIAL GIS pp. 344–353 (2013)
Cools, M., Moons, E., Wets, G.: Assessing the impact of weather on traffic intensity. Weather Clim. Soc. 2, 60–68 (2010)
Zeng, K., Liu, W.L., Wang, X., Chen, S.H.: Traffic congestion and social media in China. Intell. Syst. 28(1), 72–77 (2013)
Chifor, B.C., Bica, I., Patriciu, V.V.: Sensing service architecture for smart cities using social network platforms. Soft Comput. 21, 1–10 (2016)
Granger, C.W.J.: Investigating causal relations by econometric models and cross-spectral methods. Econometrica 37(3), 424–438 (1969)
Dickey, D.A., Fuller, W.A.: Distribution of the estimators for autoregressive time series with a unit root. J. Am. Stat. Assoc. 14(366), 427–431 (1979)
Box, G.E.P., Jenkins, G.M., Reinsel, G.C.: Time Series Analysis: Forecasting and Control, 3rd edn. Prentice Hall, Englewood Cliffs (1994)
Anderson, O.: Time Series Analysis and Forecasting: The Box-Jenkins Approach. Butterworths, London (1976)
MacKinnon, D.P.: Introduction to Statistical Mediation Analysis. Erlbaum, New York (2008)
MacKinnon, D.P., Fairchild, A.J., Fritz, M.S.: Mediation analysis. Annu. Rev. Psychol. 58, 593–614 (2007)
Sobel, M.E.: Asymptotic confidence intervals for indirect effects in structural equation models. Sociol. Methodol. 13, 290–312 (1982)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2017 ICST Institute for Computer Sciences, Social Informatics and Telecommunications Engineering
About this paper
Cite this paper
Tse, R., Zhang, L.F., Lei, P., Pau, G. (2017). Crowd Sensing of Weather Conditions and Traffic Congestion Based on Data Mining in Social Networks. In: Gaggi, O., Manzoni, P., Palazzi, C., Bujari, A., Marquez-Barja, J. (eds) Smart Objects and Technologies for Social Good. GOODTECHS 2016. Lecture Notes of the Institute for Computer Sciences, Social Informatics and Telecommunications Engineering, vol 195. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-61949-1_37
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-61949-1_37
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-319-61948-4
Online ISBN: 978-3-319-61949-1
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)