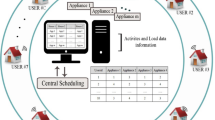
Abstract
Local energy communities are identified as a promising approach to efficiently integrate distributed generation whereas keeping costs down for prosumers. In this context, we propose a multi-agent system to collectively optimise the energy flows of a local community of prosumers. The novelty and strength of our approach resides in the use of decentralised decision making algorithms, based on the alternating direction method of multipliers, to orchestrate the demand and supply of a large number of homes. Our preliminary results show how the proposed approach can significantly increase the self-consumption level of the community while significantly reducing the energy bills of its members.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Preview
Unable to display preview. Download preview PDF.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
1. Borenstein, S., Holland, S.: On the effciency of competitive eletricity markets with time-invariant retail prices. RAND Journal of Economics 36(3), 469–493 (2005)
2. Boyd, S., Parikh, N., Chu, E., Peleato, B., Eckstein, J.: Distributed Optimization and Statistical Learning via the Alternating Direction Method of Multipliers. Foundations and Trends in Machine Learning 3(1), 1–122 (2011)
3. Cooke, D.: Empowering customer choice in electricity markets. IEA Energ Papers 2011/13, International Energy Agency (October 2011)
4. Department of Energy & Climate Change: Community energy strategy. Policy paper URN 14D/019, UK Government (January 2014)
5. Elexon: What are the profile classes?, www.elexon.co.uk/knowledgebase/profile-classes/
6. Eto, J.H., Thomas, R.J.: Computational needs for the next generation electric grid proceedings. Tech. Rep. LBNL-5105E (April 2011)
7. Faruqui, A., Sergici, S.: Household response to dynamic pricing of electricity: a survey of 15 experiments. Journal of Regulatory Economics 38(2), 193–225 (2010)
8. Kraning, M., Chu, E., Lavaei, J., Boyd, S.P.: Dynamic network energy management via proximal message passing. Foundations and Trends in Optimization 1(2), 73–126 (2014)
9. Mihaylov, M., Jurado, S., Moffaert, K.V., Avellana, N., Nowé, A.: NRG-X-Change - A Novel Mechanism for Trading of Renewable Energy in Smart Grids. In: SMART- GREENS 2014. pp. 101–106 (2014)
Acknowledgments
Authors would like to acknowledge the support of the European Union under the FP7 Grant Agreement no. 619682 (MAS2TERING project).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2018 Springer International Publishing AG
About this paper
Cite this paper
Vinyals, M., Velay, M., Sisinni, M. (2018). A multi-agent system for energy trading between prosumers. In: Omatu, S., Rodríguez, S., Villarrubia, G., Faria, P., Sitek, P., Prieto, J. (eds) Distributed Computing and Artificial Intelligence, 14th International Conference. DCAI 2017. Advances in Intelligent Systems and Computing, vol 620. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-62410-5_10
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-62410-5_10
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-319-62409-9
Online ISBN: 978-3-319-62410-5
eBook Packages: EngineeringEngineering (R0)