Abstract
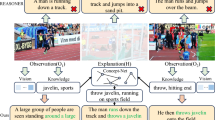
Most agents obtain knowledges from natural scenes through some single preestablished rules. In practice, those single rules can’t achieve the aim to freely awareness the natural scenes, such as the visual scenes. Inspired by biological visual cortex (V1) and higher brain areas perceiving visual features, in this paper we propose an improved visual awareness module, called as visual scenes mining module, for the agent ABGP-CNN in order to directly mine the visual scenes information. Then ABGP-CNN with the visual scenes mining module is deployed on a toy car. The visual information mining from the nature scenes is served as the knowledges of the agent ABGP-CNN to drive the toy car. The toy car deployed the agent ABGP-CNN can easily understand the special natural visual scenes, and has the ability to plan its behaviors according to the visual information mining from the nature scenes. The application of the agent ABGP-CNN with visual scenes mining module enhances the capability of communication between the toy car and the natural visual scenes.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Preview
Unable to display preview. Download preview PDF.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bratman, M.E.: Intention, Plans, and Practical Reason. Cambridge University Press (1987)
Ciresan, D.C., Meier, U., Masci, J., Maria Gambardella, L., Schmidhuber, J.: Flexible, high performance convolutional neural networks for image classification. In: Proceedings of the 21th International Joint Conference on Artificial Intelligence, Vol. 22, pp. 1237–1242 (2011)
Ciresan, D., Meier, U., Schmidhuber, J.: Multi-column deep neural networks for image classification. In: Proceedings of the 25th Conference on Computer Vision an Pattern Recognition, pp. 3642–3649. IEEE (2012)
Department of Applied Mathematics in Tongji University: Advanced Mathematics. Higher Education Press, Beijing (2014)
Duan, X.: Improvement of Matching Algorithm Based on Gray Image. Master’s thesis, Central South University (2012)
Hindriks, K.V., de Boer, F.S., van der Hoek, W., Meyer, J.J.C.: Agent programming in 3apl. Journal of Autonomous Agents and Multi-Agent Systems 2(4), 357–401 (1999)
Jarrett, K., Kavukcuoglu, K., Lecun, Y.: What is the best multi-stage architecture for object recognition?. In: IEEE 12th International Conference on Computer Vision, pp. 2146–2153 (2009)
Johnson, J.L., Padgett, M.L.: Pcnn models and applications. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks 10(3), 480–498 (1999)
Korekado, K., Morie, T., Nomura, O., Ando, H., Nakano, T., Matsugu, M., Iwata, A.: A convolutional neural network VLSI for image recognition using merged/mixed analog-digital architecture. In: Palade, V., Howlett, R.J., Jain, L. (eds.) KES 2003. LNCS, vol. 2774, pp. 169–176. Springer, Heidelberg (2003). doi:10.1007/978-3-540-45226-3_24
Lehman, J.F., Laird, J., Rosenbloom, P.: A gentle introduction to soar, an architecture for human cognition. Invitation to Cognitive Science 4, 212–249 (1996)
Lindblad, T., Kinser, J.: Image Processing Using Pulse-Coupled Neural Networks. Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg (2005)
Lyu, S., Simoncelli, E.P., Hughes, H.: Nonlinear image representation using divisive normalization. In: Proceedings of the 21th Conference on Computer Vision an Pattern Recognition, pp. 23–28 (2008)
Ma, G., Yang, X., Lu, C., Zhang, B., Shi, Z.: A visual awareness pathway in cognitive model abgp. High Technology Letters 22(41), 395–403 (2016)
Kephart, J.O., Walsh, W.E.: An artificial intelligence perspective on autonomic computing policies. In: Proceedings of the Fifth IEEE International Workshop on Policies for Distributed Systems and Networks, pp. 3–12 (2004)
Pokahr, A., Braubach, L.: The active components approach for distributed systems development. International Journal of Parallel, Emergent and Distributed Systems 28(4), 321–369 (2013)
Rao, A.S., Georgeff, M.P.: Bdi agents: from theory to practice. In: Proceedings of the First International Conference on Multi-Agent Systems, pp. 312–319 (1995)
Shi, Z., Wang, X., Yue, J.: Cognitive cycle in mind model cam. International Journal of Intelligence Science 1(2), 25–34 (2011)
Shi, Z., Zhang, J., Yue, J., Yang, X.: A cognitive model for multi-agent collaboration. International Journal of Intelligence Science 4(1), 1–6 (2013)
Shoham, Y.: Agent-oriented programming. Artificial Intelligence 60(1), 51–92 (1993)
Simard, P.Y., Steinkraus, D., Platt, J.C.: Best practices for convolutional neural networks applied to visual document analysis. In: The 12th International Conference on Document Analysis and Recognition, pp. 958–963 (2003)
Wang, Z., Ma, Y., Gu, J.: Multi-focus image fusion using pcnn. Pattern Recognition 43(6), 2003–2016 (2010)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2017 Springer International Publishing AG
About this paper
Cite this paper
Ma, G., Tang, Z., Yang, X., Shi, Z., Yang, K. (2017). Visual Scenes Mining for Agent Awareness Module. In: Perner, P. (eds) Advances in Data Mining. Applications and Theoretical Aspects. ICDM 2017. Lecture Notes in Computer Science(), vol 10357. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-62701-4_13
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-62701-4_13
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-319-62700-7
Online ISBN: 978-3-319-62701-4
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)