Abstract
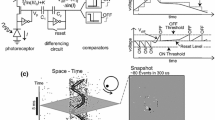
We demonstrate a spiking neural network that extracts spatial depth information from a stereoscopic visual input stream. The system makes use of a scalable neuromorphic computing platform, SpiNNaker, and neuromorphic vision sensors, so called silicon retinas, to solve the stereo matching (correspondence) problem in real-time. It dynamically fuses two retinal event streams into a depth-resolved event stream with a fixed latency of 2 ms, even at input rates as high as several 100,000 events per second. The network design is simple and portable so it can run on many types of neuromorphic computing platforms including FPGAs and dedicated silicon.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
Notes
- 1.
All code (including network and neuron parameters) and data sets necessary to reproduce the experiments are available at https://github.com/gdikov/SpikingStereoMatching.
References
Benjamin, B.V., Gao, P., McQuinn, E., Choudhary, S., Chandrasekaran, A.R., Bussat, J.M., Alvarez-Icaza, R., Arthur, J.V., Merolla, P.A., Boahen, K.: Neurogrid: a mixed-analog-digital multichip system for large-scale neural simulations. Proc. IEEE 102(5), 699–716 (2014)
Cheung, K., Schultz, S.R., Luk, W.: NeuroFlow: a general purpose spiking neural network simulation platform using customizable processors. Front. Neurosci. 9(516), 1–15 (2016)
Davies, E.: 3D vision and motion. In: Machine Vision. Signal Processing and its Applications, 3 edn., p. 443. Morgan Kaufmann, Burlington (2005)
Davison, A., Brüderle, D., Eppler, J., Kremkow, J., Muller, E., Pecevski, D., Perrinet, L., Yger, P.: PyNN: a common interface for neuronal network simulators. Front. Neuroinform. 2, 11 (2009). http://journal.frontiersin.org/article/10.3389/neuro.11.011.2008
Delbruck, T., Linares-Barranco, B., Culurciello, E., Posch, C.: Activity-driven, event-based vision sensors. In: Proceedings of 2010 IEEE International Symposium on Circuits and Systems, pp. 2426–2429, May 2010
Denk, C., Llobet-Blandino, F., Galluppi, F., Plana, L.A., Furber, S., Conradt, J.: Real-time interface board for closed-loop robotic tasks on the SpiNNaker neural computing system. In: International Conference on Artificial Neural Networks (ICANN), Sofia, Bulgaria, pp. 467–474, September 2013. http://mediatum.ub.tum.de/doc/1191903/90247.pdf
Diamond, A., Nowotny, T., Schmuker, M.: Comparing neuromorphic solutions in action: Implementing a bio-inspired solution to a benchmark classification task on three parallel-computing platforms. Front. Neurosci. 9, 491 (2016). http://journal.frontiersin.org/article/10.3389/fnins.2015.00491
Domínguez-Morales, M., Jimenez-Fernandez, A., Paz, R., López-Torres, M.R., Cerezuela-Escudero, E., Linares-Barranco, A., Jimenez-Moreno, G., Morgado, A.: An approach to distance estimation with stereo vision using address-event-representation. In: Lu, B.-L., Zhang, L., Kwok, J. (eds.) ICONIP 2011. LNCS, vol. 7062, pp. 190–198. Springer, Heidelberg (2011). doi:10.1007/978-3-642-24955-6_23
Eibensteiner, F., Kogler, J., Scharinger, J.: A high-performance hardware architecture for a frameless stereo vision algorithm implemented on a FPGA platform. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshops, pp. 623–630 (2014)
Everding, L., Walger, L., Ghaderi, V.S., Conradt, J.: A mobility device for the blind with improved vertical resolution using dynamic vision sensors. In: IEEE HealthCom 2016, Munich, Germany, September 2016
Firouzi, M., Conradt, J.: Asynchronous event-based cooperative stereo matching using neuromorphic silicon retinas. Neural Process. Lett. 43(2), 311–326 (2016)
Furber, S.B., Galluppi, F., Temple, S., Plana, L.A.: The SpiNNaker project. Proc. IEEE 102(5), 652–665 (2014)
Furber, S.B., Lester, D.R., Plana, L.A., Garside, J.D., Painkras, E., Temple, S., Brown, A.D.: Overview of the spinnaker system architecture. IEEE Trans. Comput. 62(12), 2454–2467 (2013)
Georgieva, S., Peeters, R., Kolster, H., Todd, J.T., Orban, G.A.: The processing of three-dimensional shape from disparity in the human brain. J. Neurosci. 29(3), 727–742 (2009)
Ghaderi, V.S., Mulas, M., Santos Pereira, V., Everding, L., Weikersdorfer, D., Conradt, J.: A wearable mobility device for the blind using retina-inspired dynamic vision sensors. In: 2015 37th Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society (EMBC), pp. 3371–3374, August 2015
Grossberg, S., Howe, P.D.: A laminar cortical model of stereopsis and three-dimensional surface perception. Vis. Res. 43(7), 801–829 (2003)
Hartley, R., Zisserman, A.: Multiple View Geometry in Computer Vision. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge (2003)
Jany, R., Richter, C., Woltmann, C., Pfanzelt, G., Förg, B., Rommel, M., Reindl, T., Waizmann, U., Weis, J., Mundy, J.A., et al.: Monolithically integrated circuits from functional oxides. Adv. Mater. Interfaces 1(1) (2014)
Kogler, J., Humenberger, M., Sulzbachner, C.: Event-based stereo matching approaches for frameless address event stereo data. In: Bebis, G., et al. (eds.) ISVC 2011. LNCS, vol. 6938, pp. 674–685. Springer, Heidelberg (2011). doi:10.1007/978-3-642-24028-7_62
Layher, G., Brosch, T., Neumann, H.: Real-time biologically inspired action recognition from key poses using a neuromorphic architecture. Front. Neurorobot. 11 (2017). http://journal.frontiersin.org/article/10.3389/fnbot.2017.00013/full
Li, C., Brandli, C., Berner, R., Liu, H., Yang, M., Liu, S.C., Delbruck, T.: Design of an RGBW color VGA rolling and global shutter dynamic and active-pixel vision sensor. In: 2015 IEEE International Symposium on Circuits and Systems (ISCAS), pp. 718–721. IEEE (2015)
Lichtsteiner, P., Posch, C., Delbruck, T.: A \(128 \, \times \, 128\) \(120 \, \text{ db } \; 15 \, {\upmu }\)s latency asynchronous temporal contrast vision sensor. IEEE J. Solid State Circ. 43(2), 566–576 (2008)
Liu, Q., Pineda-Garca, G., Stromatias, E., Serrano-Gotarredona, T., Furber, S.B.: Benchmarking spike-based visual recognition: a dataset and evaluation. Front. Neurosci. 10, 496 (2016). http://journal.frontiersin.org/article/10.3389/fnins.2016.00496
Lorenz, M., Rao, M.S.R., Venkatesan, T., Fortunato, E., Barquinha, P., Branquinho, R., Salgueiro, D., Martins, R., Carlos, E., Liu, A., Shan, F.K., Grundmann, M., Boschker, H., Mukherjee, J., Priyadarshini, M., DasGupta, N., Rogers, D.J., Teherani, F.H., Sandana, E.V., Bove, P., Rietwyk, K., Zaban, A., Veziridis, A., Weidenkaff, A., Muralidhar, M., Murakami, M., Abel, S., Fompeyrine, J., Zuniga-Perez, J., Ramesh, R., Spaldin, N.A., Ostanin, S., Borisov, V., Mertig, I., Lazenka, V., Srinivasan, G., Prellier, W., Uchida, M., Kawasaki, M., Pentcheva, R., Gegenwart, P., Granozio, F.M., Fontcuberta, J., Pryds, N.: The 2016 oxide electronic materials and oxide interfaces roadmap. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 49(43), 433001 (2016). http://stacks.iop.org/0022-3727/49/i=43/a=433001
Mahowald, M.A., Delbrück, T.: Cooperative Stereo Matching Using Static and Dynamic Image Features, pp. 213–238. Springer, Boston (1989). doi:10.1007/978-1-4613-1639-8_9
Marr, D., Poggio, T.: Cooperative computation of stereo disparity. Science 194(4262), 283–287 (1976)
Merolla, P.A., Arthur, J.V., Alvarez-Icaza, R., Cassidy, A.S., Sawada, J., Akopyan, F., Jackson, B.L., Imam, N., Guo, C., Nakamura, Y., et al.: A million spiking-neuron integrated circuit with a scalable communication network and interface. Science 345(6197), 668–673 (2014)
Müller, G.R., Conradt, J.: A miniature low-power sensor system for real time 2D visual tracking of led markers. In: 2011 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Biomimetics (ROBIO), pp. 2429–2434, December 2011
Ohzawa, I., DeAngelis, G.C., Freeman, R.D., et al.: Stereoscopic depth discrimination in the visual cortex: neurons ideally suited as disparity detectors. Science 249(4972), 1037–1041 (1990)
Piatkowska, E., Belbachir, A.N., Gelautz, M.: Cooperative and asynchronous stereo vision for dynamic vision sensors. Meas. Sci. Technol. 25(5), 1–8 (2014)
Posch, C., Matolin, D., Wohlgenannt, R.: A QVGA \(143\,\text{ dB }\) dynamic range frame-free PWM image sensor with lossless pixel-level video compression and time-domain CDS. IEEE J. Solid State Circ. 46(1), 259–275 (2011)
Qiao, N., Mostafa, H., Corradi, F., Osswald, M., Stefanini, F., Sumislawska, D., Indiveri, G.: A reconfigurable on-line learning spiking neuromorphic processor comprising 256 neurons and 128k synapses. Front. Neurosci. 9 (2015). http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4413675/
Rast, A.D., et al.: Transport-independent protocols for universal AER communications. In: Arik, S., Huang, T., Lai, W.K., Liu, Q. (eds.) ICONIP 2015. LNCS, vol. 9492, pp. 675–684. Springer, Cham (2015). doi:10.1007/978-3-319-26561-2_79
Read, J.: Early computational processing in binocular vision and depth perception. Prog. Biophys. Mol. Biol. 87(1), 77–108 (2005)
Richter, C., Jentzsch, S., Hostettler, R., Garrido, J.A., Ros, E., Knoll, A.C., Röhrbein, F., van der Smagt, P., Conradt, J.: Musculoskeletal robots: scalability in neural control. IEEE Robot. Autom. Mag. 23(4), 128–137 (2016). doi:10.1109/MRA.2016.2535081
Rogister, P., Benosman, R., Ieng, S.H., Lichtsteiner, P., Delbruck, T.: Asynchronous event-based binocular stereo matching. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst. 23(2), 347–353 (2012)
Rowley, A.G.D., Stokes, A.B., Knight, J., Lester, D.R., Hopkins, M., Davies, S., Rast, A., Bogdan, P., Davidson, S.: PyNN on SpiNNaker software 2015.004, July 2015. http://dx.doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.19230
Schemmel, J., Brüderle, D., Grübl, A., Hock, M., Meier, K., Millner, S.: A wafer-scale neuromorphic hardware system for large-scale neural modeling. In: Proceedings of 2010 IEEE International Symposium on Circuits and systems (ISCAS), pp. 1947–1950. IEEE (2010)
Schraml, S., Schön, P., Milosevic, N.: Smartcam for real-time stereo vision-address-event based embedded system. In: VISApp (2), pp. 466–471 (2007)
Serrano-Gotarredona, T., Linares-Barranco, B., Galluppi, F., Plana, L., Furber, S.: ConvNets experiments on SpiNNaker. In: 2015 IEEE International Symposium on Circuits and Systems (ISCAS), pp. 2405–2408, May 2015
Shi, B.E., Tsang, E.K.: A neuromorphic multi-chip model of a disparity selective complex cell. In: Thrun, S., Saul, L.K., Schölkopf, P.B. (eds.) Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, vol. 16, pp. 1051–1058. MIT Press, Cambridge (2004)
Shimonomura, K., Kushima, T., Yagi, T.: Binocular robot vision emulating disparity computation in the primary visual cortex. Neural Netw. 21(23), 331–340 (2008). Advances in Neural Networks Research: International Joint Conference on Neural Networks, IJCNN 2007, July 2007. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S089360800700247X
Stewart, T.C., Kleinhans, A., Mundy, A., Conradt, J.: Serendipitous offline learning in a neuromorphic robot. Front. Neurorobot. 10, 1–11 (2016)
Sugiarto, I., Liu, G., Davidson, S., Plana, L.A., Furber, S.B.: High performance computing on SpiNNaker neuromorphic platform: a case study for energy efficient image processing. In: 2016 IEEE 35th International Performance Computing and Communications Conference (IPCCC), pp. 1–8, December 2016
Walter, F., Röhrbein, F., Knoll, A.: Neuromorphic implementations of neurobiological learning algorithms for spiking neural networks. Neural Netw. 72(C), 152–167 (2015)
Yang, M., Liu, S.C., Delbruck, T.: A dynamic vision sensor with 1% temporal contrast sensitivity and in-pixel asynchronous delta modulator for event encoding. IEEE J. Solid State Circ. 50(9), 2149–2160 (2015)
Zitnick, C.L., Kanade, T.: A cooperative algorithm for stereo matching and occlusion detection. IEEE Trans. Pattern Analy. Mach. Intell. 22(7), 675–684 (2000)
Acknowledgements
We thank S. Temple and the SpiNNaker Manchester team for their invaluable hardware, software and support. We also acknowledge I. Krawczuk and L. Everding for fruitful discussions, technical assistance with benchmarks and power measurements as well as for help in obtaining good stereo-DVS datasets. The research leading to these results has received funding from the European Union Seventh Framework Programme (FP7/2007–2013) under grant agreement no. 720270 (Human Brain Project) and the Bundesministerium für Bildung und Forschung via grant no. 01GQ0440 (Bernstein Center for Computational Neuroscience Munich).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2017 Springer International Publishing AG
About this paper
Cite this paper
Dikov, G., Firouzi, M., Röhrbein, F., Conradt, J., Richter, C. (2017). Spiking Cooperative Stereo-Matching at 2 ms Latency with Neuromorphic Hardware. In: Mangan, M., Cutkosky, M., Mura, A., Verschure, P., Prescott, T., Lepora, N. (eds) Biomimetic and Biohybrid Systems. Living Machines 2017. Lecture Notes in Computer Science(), vol 10384. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-63537-8_11
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-63537-8_11
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-319-63536-1
Online ISBN: 978-3-319-63537-8
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)