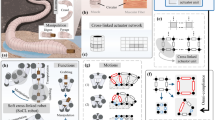
Abstract
In this paper, we introduce a design principle to develop novel soft modular robots based on tensegrity structures and inspired by the cytoskeleton of living cells. We describe a novel strategy to realize tensegrity structures using planar manufacturing techniques, such as 3D printing. We use this strategy to develop icosahedron tensegrity structures with programmable variable stiffness that can deform in a three-dimensional space. We also describe a tendon-driven contraction mechanism to actively control the deformation of the tensegrity modules. Finally, we validate the approach in a modular locomotory worm as a proof of concept.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Burks, A.: Essays on Cellular Automata. University of Illinois Press, Urbana (1970)
Fukuda, T., Nakagawa, S., Kawauchi, Y., Buss M.: Self organizing robots based on cell structures – CEBOT. In: IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation, pp. 145–150, 31 October–2 November 1989
Moubarak, P., Ben-Tzvi, P.: Modular and reconfigurable mobile robotics. Robot. Auton. Syst. 60(12), 1648–1663 (2012)
Yim, B.M., Shen, W.-M., Salemi, B., Rus, D., Moll, M., Lipson, H., Klavins, E., Chirikjian, G.S.: Modular self-reconfigurable robot systems: challenges and opportunities for the future. IEEE Robot. Autom. Mag. 14(1), 43–52 (2007)
Morin, S.A., et al.: Elastomeric tiles for the fabrication of inflatable structures. Adv. Funct. Mater. 24(35), 5541–5549 (2014)
Vergara, A., Lau, Y., Mendoza-Garcia, R.-F., Zagal, J.C.: Soft modular robotic cubes: toward replicating morphogenetic movements of the embryo. PLoS ONE 12(1), e0169179 (2017)
Onal, C.D., Rus, D.: A modular approach to soft robotics. In: 4th IEEE RAS/EMBS International Conference on Biomedical Robotics and Biomechatronics (BioRob), Rome, Italy, pp. 1038–1045, 24–27 June 2012
Lee, J.Y., Kim, W.B., Choi, W.Y., Cho, K.J.: Soft robotic blocks: introducing SoBL, a fast-build modularized design block. IEEE Robot. Autom. Mag. 23(3), 30–41 (2016)
Yim, S., Sitti, M.: SoftCubes: toward a soft modular matter. In: IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), Karlsruhe, Germany, pp. 530–536, 6–10 May 2013
Wang, W., Rodrigue, H., Ahn, S.-H.: Deployable soft composite structures. Sci. Rep. 6 (2016)
Jenett, B., et al.: Digital morphing wing: active wing shaping concept using composite lattice-based cellular structures. Soft Robot. 4, 33–48 (2016)
Germann, J., Maesani, A., Pericet, Camara R., Floreano, D.: Soft cell for programmable self-assembly of robotic modules. Soft Robot. 1(4), 239–245 (2014)
Germann, J.: Soft cells for modular robots. Ph.D. dissertation, nr. 6217, EPFL, CH (2014)
Alberts, B., Bray, D., Lewis, J., Raff, M., Roberts, K., Watson, J.D.: Molecular Biology of the Cell. Garland Publishing, New York (1983)
Ingber, D.E., Wang, N., Stamenovic, D.: Tensegrity, cellular biophysics, and the mechanics of living systems. Rep. Prog. Phys. (2014)
Ingber, D.E.: The architecture of life. Sci. Am. 278(1), 48–57 (1998)
Krause, F., Wilke, J., Vogt, L., Banzer, W.: Intermuscular force transmission along myofascial chains: a systematic review. J. Anat. 77(12) (2006)
Yu, C., Haller, K., Ingber, D., Nagpal, R.: Morpho: a Self-deformable modular robot inspired by cellular structure. In: IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robot and Systems, Nice, France, 22–26 September 2008
Rieffel, J., Trimmer, B., Lipson, H.: Mechanism as mind - what tensegrities and caterpillars can teach us about soft robotics. In: Artificial Life: Proceedings of the Eleventh International Conference on the Simulation and Synthesis of Living Systems, Cambridge, MA, pp. 506–512, 5–8 August 2008
Bruce, J., Caluwaerts, K., Iscen, A., Sabelhaus, A.P., SunSpiral, V.: Design and evolution of a modular tensegrity platform. In: IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation, (ICRA), Hong Kong, China, 31 May– 7 June 2014
de Oliveira, M.C., Skelton, R.E.: Tensegrity Systems, Chap. 1. Springer, New York (2009). doi:10.1007/978-0-387-74242-7
Agogino, A., SunSpiral V., Atkinson, D.: SuperBall bot – structure for planetary landing and exploration. Final Report for the NASA Innovative Advanced Concepts, NASA Ames Reasearch Center, Intelligent Systems Division, July 2013
Umedachi, T., Vikas, V., Trimmer, B.A., et al.: Softworms: the design and control of non-pneumatic, 3D-printed, deformable robots. Bionspir. Biomim. 11(2) (2016)
Kanu, E.N., Daltorio, K.A., Quinn, R.D., Chiel, H.J.: Correlating kinetics and kinematics of earthworm peristaltic locomotion. In: 4th International Conference of Living Machines, Barcelona, Spain, pp. 92–96, 28–31 July 2015
Mirletz, B.T., Park, I., Quinn, R.D., Sunspiral, V.: Towards bridging the reality gap between tensegrity simulation and robotic hardware. In: IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Systems (IROS), Hamburg, Germany, 28 September–2 October 2015
Singh, M., Haverinen, H.M., Dhagat, P., Jabbour, G.E.: Inkjet printing-process and its applications. Adv. Mater. 22(6), 673–685 (2010)
Gad-el-Hak, M.: The MEMS Handbook. CRC Press, Boca Raton (2010)
Whitney, J.P., Sreetharan, P.S., Ma, K.Y., Wood, R.J.: Pop-up book MEMS. J. Micromech. Microeng. 21(11) (2011)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2017 Springer International Publishing AG
About this paper
Cite this paper
Zappetti, D., Mintchev, S., Shintake, J., Floreano, D. (2017). Bio-inspired Tensegrity Soft Modular Robots. In: Mangan, M., Cutkosky, M., Mura, A., Verschure, P., Prescott, T., Lepora, N. (eds) Biomimetic and Biohybrid Systems. Living Machines 2017. Lecture Notes in Computer Science(), vol 10384. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-63537-8_42
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-63537-8_42
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-319-63536-1
Online ISBN: 978-3-319-63537-8
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)