Abstract
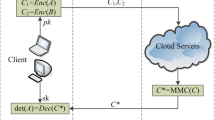
Secure inner product, namely the computation of inner product whose terms are all in encrypted form, is the central technique for various privacy-preserving applications. In this paper, we propose a generic yet efficient method to compute secure inner products of vectors (or matrices) using matrix trace properties. Indeed, our method not only applies to both LWE-based and ring-LWE-based homomorphic encryption schemes, but also is more efficient compared to previously known methods.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
Notes
- 1.
The embedding function may be a probabilistic algorithm. However, we treat it as if it was deterministic to avoid complications.
- 2.
This definition is not consistent with the normal distribution \(\mathcal {N}(0,s^2)\) whose probability density function is proportional to \(\exp (-x^2/2s^2)\). However, it is traditional among cryptographers.
- 3.
Since the scheme supports multiple homomorphic multiplications, the degree of \(c_\mathsf{mul}\) would be larger. However, in our case, we do not have to consider this.
- 4.
References
Aono, Y., Hayashi, T., Phong, L.T., Wang, L.: Efficient key-rotatable and security-updatable homomorphic encryption. In: SCC 2017, pp. 35–42. ACM (2017)
Banerjee, S., Roy, A.: Linear Algebra and Matrix Analysis for Statistics. Texts in Statistical Science, 1st edn. Chapman and Hall/CRC Press, Boca Raton (2014)
Boneh, D., Goh, E.-J., Nissim, K.: Evaluating 2-DNF formulas on ciphertexts. In: Kilian, J. (ed.) TCC 2005. LNCS, vol. 3378, pp. 325–341. Springer, Heidelberg (2005). doi:10.1007/978-3-540-30576-7_18
Brakerski, Z., Gentry, C., Halevi, S.: Packed ciphertexts in LWE-based homomorphic encryption. In: Kurosawa, K., Hanaoka, G. (eds.) PKC 2013. LNCS, vol. 7778, pp. 1–13. Springer, Heidelberg (2013). doi:10.1007/978-3-642-36362-7_1
van Dijk, M., Gentry, C., Halevi, S., Vaikuntanathan, V.: Fully homomorphic encryption over the integers. In: Gilbert, H. (ed.) EUROCRYPT 2010. LNCS, vol. 6110, pp. 24–43. Springer, Heidelberg (2010). doi:10.1007/978-3-642-13190-5_2
Ducas, L., Micciancio, D.: FHEW: bootstrapping homomorphic encryption in less than a second. In: Oswald, E., Fischlin, M. (eds.) EUROCRYPT 2015, Part I. LNCS, vol. 9056, pp. 617–640. Springer, Heidelberg (2015). doi:10.1007/978-3-662-46800-5_24
El Gamal, T.: A public key cryptosystem and a signature scheme based on discrete logarithms. In: Blakley, G.R., Chaum, D. (eds.) CRYPTO 1984. LNCS, vol. 196, pp. 10–18. Springer, Heidelberg (1985). doi:10.1007/3-540-39568-7_2
Gentry, C.: Fully homomorphic encryption using ideal lattices. In: STOC 2009, pp. 169–178. ACM (2009)
Gentry, C., Halevi, S., Vaikuntanathan, V.: A simple BGN-type cryptosystem from LWE. In: Gilbert, H. (ed.) EUROCRYPT 2010. LNCS, vol. 6110, pp. 506–522. Springer, Heidelberg (2010). doi:10.1007/978-3-642-13190-5_26
Gentry, C., Sahai, A., Waters, B.: Homomorphic encryption from learning with errors: conceptually-simpler, asymptotically-faster, attribute-based. In: Canetti, R., Garay, J.A. (eds.) CRYPTO 2013, Part I. LNCS, vol. 8042, pp. 75–92. Springer, Heidelberg (2013). doi:10.1007/978-3-642-40041-4_5
Lauter, K.E., Naehrig, M., Vaikuntanathan, V.: Can homomorphic encryption be practical? In: CCSW 2011, pp. 113–124. ACM (2011)
Lindner, R., Peikert, C.: Better key sizes (and attacks) for LWE-based encryption. In: Kiayias, A. (ed.) CT-RSA 2011. LNCS, vol. 6558, pp. 319–339. Springer, Heidelberg (2011). doi:10.1007/978-3-642-19074-2_21
Paillier, P.: Public-key cryptosystems based on composite degree residuosity classes. In: Stern, J. (ed.) EUROCRYPT 1999. LNCS, vol. 1592, pp. 223–238. Springer, Heidelberg (1999). doi:10.1007/3-540-48910-X_16
Yasuda, M., Shimoyama, T., Kogure, J., Yokoyama, K., Koshiba, T.: Practical packing method in somewhat homomorphic encryption. In: Garcia-Alfaro, J., Lioudakis, G., Cuppens-Boulahia, N., Foley, S., Fitzgerald, W.M. (eds.) DPM/SETOP 2013. LNCS, vol. 8247, pp. 34–50. Springer, Heidelberg (2014). doi:10.1007/978-3-642-54568-9_3
Yasuda, M., Shimoyama, T., Kogure, J., Yokoyama, K., Koshiba, T.: Secure pattern matching using somewhat homomorphic encryption. In: CCSW 2013, pp. 65–76. ACM (2013)
Yasuda, M., Shimoyama, T., Kogure, J., Yokoyama, K., Koshiba, T.: Secure statistical analysis using RLWE-based homomorphic encryption. In: Foo, E., Stebila, D. (eds.) ACISP 2015. LNCS, vol. 9144, pp. 471–487. Springer, Cham (2015). doi:10.1007/978-3-319-19962-7_27
Acknowlegment
This work is partially supported by JST CREST number JPMJCR168A and JSPS KAKENHI Grant Number 15K00028.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
A Formal Correctness of the Protocol in Sect. 5
A Formal Correctness of the Protocol in Sect. 5
Proof. For \(m \in \mathcal {R}=\mathbb {Z}[x]/(x^n+1)\), it is easily to check that F(m) satisfies:

Since \(x^n=-1\) and \(F^{-1}\) is inverse map, i.e., \(F^{-1}(F(m))=m\), we have results:
-
(r1)

-
(r2)

-
(r3)

Accordingly,
According to (a1)–(a4) and (r1)–(r3), the algorithms \(\mathsf{InnerP}_M\) and \(\mathsf{DecIP}_M\) over \(\mathbb {Z}_q^{n \times n}\) for the coefficient circulante matrices of elements of ring \(\mathcal {R}_q\) can be represented back to that for ring element over \(\mathcal {R}_q\) by running \(F^{-1}\). Therefore,

where \(S^*\) \(=\) \(SS^{(t)}\), \(S_M^*=F(S) F(S)^T, \tilde{S_M}=F(S)^T\in \mathbb {Z}_q^{n \times n}\), and \(\xi _M=\langle F(c_2), F(d_2) \rangle _F\) \(\in \mathbb {Z}_q\). Therefore,
The proof is completed.
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2017 Springer International Publishing AG
About this paper
Cite this paper
Wang, L., Hayashi, T., Aono, Y., Phong, L.T. (2017). A Generic yet Efficient Method for Secure Inner Product. In: Yan, Z., Molva, R., Mazurczyk, W., Kantola, R. (eds) Network and System Security. NSS 2017. Lecture Notes in Computer Science(), vol 10394. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-64701-2_16
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-64701-2_16
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-319-64700-5
Online ISBN: 978-3-319-64701-2
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)