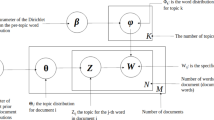
Abstract
With the explosive growth of user-generated data in social media websites such as Twitter and Weibo, a lot of research has been conducted on using user-generated data for web-based learning. Finding users’ desired data in an effective way is critical for language learners. Social media websites provide diversified data for language learners and some new words such as cyberspeak could only be learned in these online communities. In this paper, we present a system called WeiboFinder to suggest topic-based words and documents related to a target word for Chinese learners. All the words and documents are from the Chinese social media website: Weibo. Weibo is one of the largest microblog social meida websites in China which has similar functions as Twitter. The experimental results show that the proposed method is effective and better than other methods. The topics from our method are more interpretable and topic-based words are useful for Chinese learners.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Agichtein, E., Castillo, C., Donato, D., Gionis, A., Mishne, G.: Finding high-quality content in social media. In: Proceedings of the 2008 International Conference on Web Search and Data Mining, pp. 183–194. ACM (2008)
Ahmad, K., Cheng, D., Almas, Y.: Multi-lingual sentiment analysis of financial news streams. In: Proceedings of the 1st International Conference on Grid in Finance (2006)
Andrzejewski, D., Zhu, X., Craven, M.: Incorporating domain knowledge into topic modeling via dirichlet forest priors. In: Proceedings of the 26th Annual International Conference on Machine Learning, pp. 25–32. ACM (2009)
Burns, N., Bi, Y., Wang, H., Anderson, T.: Extended twofold-LDA model for two aspects in one sentence. In: Greco, S., Bouchon-Meunier, B., Coletti, G., Fedrizzi, M., Matarazzo, B., Yager, R.R. (eds.) IPMU 2012. CCIS, vol. 298, pp. 265–275. Springer, Heidelberg (2012). doi:10.1007/978-3-642-31715-6_29
Chen, Z., Mukherjee, A., Liu, B., Hsu, M., Castellanos, M., Ghosh, R.: Discovering coherent topics using general knowledge. In: Proceedings of the 22nd ACM International Conference on Information & Knowledge Management, pp. 209–218. ACM (2013)
Faizi, R., El Afia, A., Chiheb, R.: Exploring the potential benefits of using social media in education. iJEP 3(4), 50–53 (2013)
Faizi, R., El Afia, A., Chiheb, R.: Social media: an optimal virtual environment for learning foreign languages. iJET 9(5), 64–66 (2014)
Fan, R., Zhao, J., Chen, Y., Xu, K.: Anger is more influential than joy: sentiment correlation in Weibo. PLoS ONE 9(10), e110184 (2014)
Gao, Q., Abel, F., Houben, G.-J., Yu, Y.: A comparative study of users’ microblogging behavior on Sina Weibo and Twitter. In: Masthoff, J., Mobasher, B., Desmarais, M.C., Nkambou, R. (eds.) UMAP 2012. LNCS, vol. 7379, pp. 88–101. Springer, Heidelberg (2012). doi:10.1007/978-3-642-31454-4_8
Hu, M., Liu, B.: Mining opinion features in customer reviews. AAAI 4, 755–760 (2004)
Huckin, T., Coady, J.: Incidental vocabulary acquisition in a second language. Stud. Second Lang. Acquis. 21(02), 181–193 (1999)
Jo, Y., Oh, A.H.: Aspect and sentiment unification model for online review analysis. In: Proceedings of the Fourth ACM International Conference on Web Search and Data Mining, pp. 815–824. ACM (2011)
Yang, K., Cai, Y., Chen, Z., Leung, H.F., Lau, R.Y.: Exploring topic discriminating power of words in latent dirichlet allocation. In: COLING, pp. 2238–2247 (2016)
Lee, M.J., McLoughlin, C.: Teaching and learning in the web 2.0 era: empowering students through learner-generated content. Int. J. Instr. Technol. Distance Learn. 4(10), 21–34 (2007)
Liang, H., Tsai, F.S., Kwee, A.T.: Detecting novel business blogs. In: Proceedings of the 7th International Conference on Information (2009)
Liu, X., Ye, S., Li, X., Luo, Y., Rao, Y.: ZhihuRank: a topic-sensitive expert finding algorithm in community question answering websites. In: Li, F.W.B., Klamma, R., Laanpere, M., Zhang, J., Manjón, B.F., Lau, R.W.H. (eds.) ICWL 2015. LNCS, vol. 9412, pp. 165–173. Springer, Cham (2015). doi:10.1007/978-3-319-25515-6_15
Mimno, D., Wallach, H.M., Talley, E., Leenders, M., McCallum, A.: Optimizing semantic coherence in topic models. In: Proceedings of the Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing, pp. 262–272. Association for Computational Linguistics (2011)
Mukherjee, A., Liu, B.: Aspect extraction through semi-supervised modeling. In: Proceedings of the 50th Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics: Long Papers, vol. 1, pp. 339–348. Association for Computational Linguistics (2012)
Peng, F., Feng, F., McCallum, A.: Chinese segmentation and new word detection using conditional random fields. In: Proceedings of the 20th International Conference on Computational Linguistics, p. 562. Association for Computational Linguistics (2004)
Wang, T., Cai, Y., Leung, H.f., Cai, Z., Min, H.: Entropy-based term weighting schemes for text categorization in VSM. In: 2015 IEEE 27th International Conference on Tools with Artificial Intelligence (ICTAI), pp. 325–332. IEEE (2015)
Wilson, A.T., Chew, P.A.: Term weighting schemes for latent dirichlet allocation. In: Human Language Technologies: The 2010 Annual Conference of the North American Chapter of the Association for Computational Linguistics, pp. 465–473. Association for Computational Linguistics (2010)
Xie, H., Zou, D., Lau, R.Y., Wang, F.L., Wong, T.L.: Generating incidental word-learning tasks via topic-based and load-based profiles. IEEE Multimed. 23(1), 60–70 (2016)
Yang, F., Liu, Y., Yu, X., Yang, M.: Automatic detection of rumor on Sina Weibo. In: Proceedings of the ACM SIGKDD Workshop on Mining Data Semantics, p. 13. ACM (2012)
Zou, D., Xie, H., Wong, T.-L., Rao, Y., Wang, F.L., Wu, Q.: Predicting pre-knowledge on vocabulary from e-Learning assignments for language learners. In: Gong, Z., Chiu, D.K.W., Zou, D. (eds.) ICWL 2015. LNCS, vol. 9584, pp. 111–117. Springer, Cham (2016). doi:10.1007/978-3-319-32865-2_12
Zourou, K.: On the attractiveness of social media for language learning: a look at the state of the art. Alsic. Apprentissage des Langues et Systèmes d’Information et de Communication 15(1) (2012)
Acknowledgments
This work is supported by the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities, SCUT (NO. 2017ZD0482015ZM136), Tiptop Scientific and Technical Innovative Youth Talents of Guangdong special support program (No. 2015TQ01X633), Science and Technology Planning Project of Guangdong Province, China (No. 2016A030310423), Science and Technology Program of Guangzhou (International Science & Technology Cooperation Program No. 201704030076) and Science and Technology Planning Major Project of Guangdong Province (No. 2015A070711001).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2017 Springer International Publishing AG
About this paper
Cite this paper
Chen, W. et al. (2017). WeiboFinder: A Topic-Based Chinese Word Finding and Learning System. In: Xie, H., Popescu, E., Hancke, G., Fernández Manjón, B. (eds) Advances in Web-Based Learning – ICWL 2017. ICWL 2017. Lecture Notes in Computer Science(), vol 10473. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-66733-1_4
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-66733-1_4
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-319-66732-4
Online ISBN: 978-3-319-66733-1
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)