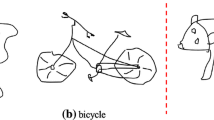
Abstract
In this paper, we employ aspects of machine learning, computer vision, and qualitative representations to build a classifier of plain sketches. The paper proposes a hybrid technique for accurately recognizing hand-drawn sketches, by relying on a set of qualitative relations between the strokes that compose such sketches, and by taking advantage of two major perspectives for processing images. Our implementation shows promising results for recognizing sketches that have been hand-drawn by human participants.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
Notes
- 1.
Think of the 9 relations filling a \(3\times 3\) tic-tac-toe-like board:
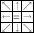
.
- 2.
Note that the labeling of the strokes is intended to reflect the successiveness of the strokes; e.g., \(s_{4}\) is sketched after \(s_{3}\). This is vital, especially because the presented positional relations are not commutative (except \(\equiv \), of course).
- 3.
This is one of the predefined functions within the Matlab computer vision toolbox.
References
Abdel-Fattah, A.M.H., Zakaria, W., Abdelghaffar, N., Abdelmoneim, N., Elsaadany, N., Schwering, A., Kühnberger, K.U.: Towards the modeling of sketch-based understanding: can computers interpret what non-artists draw? In: SHAPES 3.0 - The shape of Things, Larnaca, Cyprus, 2–6 November 2015 (2015)
Abdel-Fattah, A.M.H., Zakaria, W., Abdelghaffar, N., Abdelmoneim, N., Schneider, S., Kühnberger, K.U.: A preliminary assessment of conceptual salience for automatic sketching. In: The 4th International Workshop on Artificial Intelligence and Cognition. CEUR-WS (2016)
Dalal, N., Triggs, B., Schmid, C.: Human detection using oriented histograms of flow and appearance. In: Leonardis, A., Bischof, H., Pinz, A. (eds.) ECCV 2006. LNCS, vol. 3952, pp. 428–441. Springer, Heidelberg (2006). doi:10.1007/11744047_33
Eitz, M., Hays, J., Alexa, M.: How do humans sketch objects? ACM Trans. Graph. 31(4), 1–10 (2012)
Lovett, A., Dehghani, M., Forbus, K.D.: Efficient learning of qualitative descriptions for sketch recognition. In: Proceedings of the 20th International Workshop on Qualitative Reasoning (2006)
McLure, M.D., Friedman, S.E., Lovett, A., Forbus, K.D.: Edge-cycles: a qualitative sketch representation to support recognition. In: Proceedings of the 25th International Workshop on Qualitative Reasoning (2011)
Paulson, B., Hammond, T.: Paleosketch: accurate primitive sketch recognition and beautification. In: Proceedings of the 13th International Conference on Intelligent User Interfaces, IUI 2008, pp. 1–10. ACM, New York (2008). http://doi.acm.org/10.1145/1378773.1378775
Wang, S., Wang, G., Gao, M., Yu, S.: Using fuzzy hybrid features to classify strokes in interactive sketches. Adv. Mech. Eng. 5 (2013). doi:10.1155/2013/259152
Acknowledgements
The authors acknowledge the role of the Artificial Intelligence and Cognitive Science Lab that has recently been established at the Faculty of Science, Ain Shams University, Cairo, Egypt, supported by the Institute of Cognitive Science at the University of Osnabrück in Germany. The work in this paper is part of the activities of the JESICS project, which has been funded by the German Academic Exchange Service (DAAD) within the framework of the German-Arab Research partnerships Programme Line 4 under grant agreement 57247603.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2017 Springer International Publishing AG
About this paper
Cite this paper
Abdelfattah, A.M.H., Zakaria, W. (2017). Employing a Restricted Set of Qualitative Relations in Recognizing Plain Sketches. In: Kern-Isberner, G., Fürnkranz, J., Thimm, M. (eds) KI 2017: Advances in Artificial Intelligence. KI 2017. Lecture Notes in Computer Science(), vol 10505. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-67190-1_1
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-67190-1_1
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-319-67189-5
Online ISBN: 978-3-319-67190-1
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)