Abstract
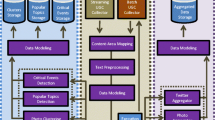
Every day, vast amounts of social networking data is being produced and consumed at a constantly increasing rate. A user’s digital footprint coming from social networks or mobile devices, such as comments, check-ins and GPS traces contains valuable information about her behavior under normal as well as emergency conditions. The collection and analysis of mobile and social networking data before, during and after a disaster opens new perspectives in areas such as real-time event detection, crisis management and personalization and provides valuable insights about the extent of the disaster, its impact on the affected population and the rate of disaster recovery. Traditional storage and processing systems are unable to cope with the size of the collected data and the complexity of the applied analysis, thus distributed approaches are usually employed. In this work, we propose an open-source distributed platform that can serve as a backend for applications and services related to crisis detection and management by combining spatio-textual user generated data. The system focuses on scalability and relies on a combination of state-of-the art Big Data frameworks. It currently supports the most popular social networks, being easily extensible to any social platform. The experimental evaluation of our prototype attests its performance and scalability even under heavy load, using different query types over various cluster sizes.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
Notes
- 1.
The vast majority of the users has performed between 140 and 200 visits in different POIs.
References
Apache HBase. http://hbase.apache.org
Apache Mahout. https://mahout.apache.org/
Digital in 2017: Global Overview. https://wearesocial.com/special-reports/digital-in-2017-global-overview
Facebook Safety Check. https://www.facebook.com/about/safetycheck/
Facebook Stats. https://newsroom.fb.com/company-info/
Postgresql. http://www.postgresql.org/
Twitter Usage Statistics. http://www.internetlivestats.com/twitter-statistics/
He, Y., Tan, H., Luo, W., Mao, H., Ma, D., Feng, S., Fan, J.: MR-DBSCAN: an efficient parallel density-based clustering algorithm using mapreduce. In: ICPADS (2011)
Imran, M., Castillo, C., Lucas, J., Meier, P., Vieweg, S.: AIDR: artificial intelligence for disaster response. In: Proceedings of the 23rd International Conference on World Wide Web, pp. 159–162. ACM (2014)
Lazreg, M.B., Goodwin, M., Granmo, O.-C.: Deep learning for social media analysis in crises situations. In The 29th Annual Workshop of the Swedish Artificial Intelligence Society (SAIS) 2–3 June 2016, Malmö, Sweden, p. 31 (2016)
Mytilinis, I., Giannakopoulos, I., Konstantinou, I., Doka, K., Koziris, N.: MoDisSENSE: a distributed platform for social networking services over mobile devices. In: 2014 IEEE International Conference on Big Data (Big Data), pp. 49–51. IEEE (2014)
Mytilinis, I., Giannakopoulos, I., Konstantinou, I., Doka, K., Tsitsigkos, D., Terrovitis, M., Giampouras, L., Koziris, N.: MoDisSENSE: a distributed spatio-temporal and textual processing platform for social networking services. In: Proceedings of the 2015 ACM SIGMOD International Conference on Management of Data, pp. 895–900. ACM (2015)
Pastor-Escuredo, D., Morales-Guzmán, A., Torres-Fernández, Y., Bauer, J.-M., Wadhwa, A., Castro-Correa, C., Romanoff, L., Lee, J.G., Rutherford, A., Frias-Martinez, V., et al.: Flooding through the lens of mobile phone activity. In: 2014 IEEE Global Humanitarian Technology Conference (GHTC), pp. 279–286. IEEE (2014)
Purohit, H., Sheth, A.P.: Twitris v3: from citizen sensing to analysis, coordination and action. In: ICWSM (2013)
Ranganath, S., Wang, S., Hu, X., Tang, J., Liu, H.: Facilitating time critical information seeking in social media. IEEE Trans. Knowl. Data Eng. PP(99), 1–14 (2017)
Zielinski, A., Middleton, S.E., Tokarchuk, L.N., Wang, X.: Social media text mining and network analysis for decision support in natural crisis management, pp. 840–845. Proc. ISCRAM. Baden-Baden, Germany (2013)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2017 Springer International Publishing AG
About this paper
Cite this paper
Doka, K. et al. (2017). Exploiting Social Networking and Mobile Data for Crisis Detection and Management. In: Dokas, I., Bellamine-Ben Saoud, N., Dugdale, J., Díaz, P. (eds) Information Systems for Crisis Response and Management in Mediterranean Countries. ISCRAM-med 2017. Lecture Notes in Business Information Processing, vol 301. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-67633-3_3
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-67633-3_3
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-319-67632-6
Online ISBN: 978-3-319-67633-3
eBook Packages: Business and ManagementBusiness and Management (R0)