Abstract
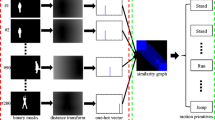
The segmentation of motion capture data is to separate the different types of human motion data contains long movement sequence into motion clips with independent semantics in order to facilitate the storage in the database as well as medical analysis. This paper proposed a method for human motion capture data segmentation based on Laplacian Eigenmaps (LE) algorithm. Firstly, the LE algorithm is used to reduce the dimension of original data by realizing the mapping from the high dimensional data to the low dimensional space. And then a specified window was drawn in the low dimensional space which was used to calculate the space distance from frames in the specified window to each frame in the former fragment. Finally we detected the similarity to get the final segmentation points, thus obtained motion clips with independent semantics. The validity of the segmentation method is verified by experiment.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Barbic, J., Safonova, A., Pan, J.Y., et al.: Segmenting motion capture data into distinct behaviors. In: Proceedings of Graphics Interface, pp. 185–194. Canadian Human-Computer Communications Society, Canada (2004)
Wold, S., Esbensen, K., Geladi, P.: Principal component analysis. Chemom. Intell. Laboatory Syst. 2(1), 37–52 (1987)
Liu, X.P., Lu, J.T., Xia, X.Y.: Motion captured data segmentation based on PCA and mahalanobis distance. J. Hefei Univ. Technol. (Natural Science) 37(5), 563–566 (2014)
Xiao, J., Zhuang, Y.T., Wu, F.: Getting distinct movements from motion capture data. In: 19th Proceeding of the International Conference on Computer Animation and Social Agents, pp. 33–42 (2006)
Tenenbaum, J.B., De, S.V., Langford, J.C.: A global geometric framework for nonlinear dimensionality reduction. J. Sci. 290(5500), 2319 (2000)
Peng, S.J.: Motion segmentation using central distance features and low-pass filter. In: International Conference on Computational Intelligence and Security, pp. 223–226 (2010)
Baum, L.E., Petrie, T.: Statistical inference for probabilistic functions of finite state Markov chains. Annal. Math. Stat. 37(6), 1554–1563 (2012)
Reynolds, D.A., Rose, R.C.: Robust text-independent speaker identification using Gaussian mixture speaker models. IEEE Trans. Speech Audio Process. 3(1), 72–83 (1995)
Lin, F.S., Kulić, D.: Online segmentation of human motion for automated rehabilitation exercise analysis. IEEE Trans. Neural Syst. Rehabil. Eng. 22(1), 168 (2014). A Publication of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine & Biology Society
Lu, C.M., Ferrier, N.J.: Repetitive motion analysis: segmentation and event classification. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 26(2), 258–263 (2004)
Wang, M.J., Wang, W., Li, Y., et al.: Motion capture data segmentation using kernel dynamic texture. In: International Conference on Audio Language and Image Processing, pp. 592–596. IEEE (2010)
Doretto, G., Chiuso, A., Wu, Y.N., et al.: Dynamic textures. Int. J. Comput. Vis. 51(2), 91–109 (2003)
Yang, Y., Chen, J.F., Liu, Z.Z., et al.: Low level segmentation of motion capture data based on hierarchical clustering with cosine distance. Int. J. Database Theory Appl. 8(4), 231–240 (2015)
Arikan, O., Forsyth, D.A., O’Brien, J.F.: Motion synthesis from annotations. In: ACM Siggeraph, pp. 402–408 (2003)
Cortes, C., Vapnik, V.: Support-vector networks. J. Mach. Learn. 20(3), 273–297 (1995)
Zhou, F., Torre, F., Hodgins, J.K.: Aligned cluster analysis for temporal segmentation of human motion. In: 8th IEEE International Conference: Automatic Face and Gesture Recognition, pp. 1–7. IEEE (2008)
Mavroeidis, D., Marchiori, E.: Feature selection for k-means clustering stability: theoretical analysis and an algorithm. J. Data Mining Knowl. Discov. 28(4), 918–960 (2014)
Zhou, F., De, l.T.F., Hodgins, J.K.: Hierarchical aligned cluster analysis for temporal clustering of human motion. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 35(3), 582–596 (2013)
Yang, Y.D., Wang, L.L., Hao, A.M.: Motion String: a motion capture data representation for behavior segmentation. J. Comput. Res. Dev. 45(3), 527–534 (2008)
Xiao, J.: Feature visualization and interactive segmentation of 3D human motion. J. Softw. 19(8), 1995–2003 (2008)
Hu, X.Y., Sun, B., Zhu, X.M., et al.: Motion capture data segmentation based on spectral clustering. J. Comput.-Aided Des. Comput. Graph. 28(08), 1306–1315 (2016)
Jin, C.B., Cui, R.Y., Jin, X.F.: Improvement of Laplacian eigenmaps for human action recognition. J. Appl. Res. Comput. 31(12), 3613–3616 (2014)
Liu, H.H., Zhou, C.H.: Semi-supervised Laplacian Eigenmap. J. Comput. Eng. Design. 33(2), 601–605 (2012)
Zhou, M., Liu, B.H.: Classifier design based on Laplacian Eigenmap. J. Comput. Eng. 35(16), 178–180 (2009)
Peng, S.J.: Double-feature combination based approach to motion capture data behavior segmentation. J. Comput. Sci. 40(8), 303–308 (2013)
Acknowledgement
This work is supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 61370141, 61300015), the Program for Dalian High-level Talent’s Innovation (2015R088).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2017 Springer International Publishing AG
About this paper
Cite this paper
Xie, X., Liu, R., Zhou, D., Wei, X., Zhang, Q. (2017). Segmentation of Human Motion Capture Data Based on Laplasse Eigenmaps. In: Chen, H., Zeng, D., Karahanna, E., Bardhan, I. (eds) Smart Health. ICSH 2017. Lecture Notes in Computer Science(), vol 10347. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-67964-8_13
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-67964-8_13
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-319-67963-1
Online ISBN: 978-3-319-67964-8
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)