Abstract
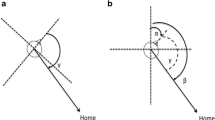
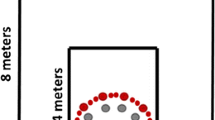
The current study investigated the ways in which environmental and idiothetic cues affect the nature of the reference frame (i.e., egocentric or allocentric) in path integration in a virtual environment. Participants navigated to multiple waypoints and then attempted to walk or point to the first waypoint. We manipulated the environmental geometry, complexity of the outbound path, availability of idiothetic cues (vestibular, proprioceptive, & efferent motor information) and initial heading in the virtual environment to examine the reference frame in path integration. Experiments 1 and 2 showed that when idiothetic cues were present, participants adopted an egocentric reference frame regardless of the environmental geometry and outbound path complexity. Experiments 3 and 4 showed that when idiothetic cues were absent, participants adopted the initial heading as the reference direction. We concluded that unlike their marked influence on reference directions in spatial memory, environmental cues had little impact on the reference frame in path integration regardless of the availability of idiothetic cues.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Etienne, A.S., Maurer, R., Boulens, V., Levy, A., Rowe, T.: Resetting the path integrator: a basic condition for route-based navigation. J. Exp. Biol. 207(9), 1491–1508 (2004)
Gallistel, C.R.: The Organization of Learning. The MIT Press, Cambridge (1990)
Wittlinger, M., Wehner, R., Wolf, H.: The ant odometer: stepping on stilts and stumps. Science 312(5782), 1965–1967 (2006)
Hafting, T., Fyhn, M., Molden, S., Moser, M.-B., Moser, E.I.: Microstructure of a spatial map in the entorhinal cortex. Nature 436(7052), 801–806 (2005)
Fyhn, M., Hafting, T., Treves, A., Moser, M.-B., Moser, E.I.: Hippocampal remapping and grid realignment in entorhinal cortex. Nature 446(7132), 190–194 (2007)
Yartsev, M.M., Witter, M.P., Ulanovsky, N.: Grid cells without theta oscillations in the entorhinal cortex of bats. Nature 479(7371), 103–107 (2011)
Killian, N.J., Jutras, M.J., Buffalo, E.A.: A map of visual space in the primate entorhinal cortex. Nature 491(7426), 761–764 (2012)
Chen, X., He, Q., Kelly, J.W., Fiete, I.R., McNamara, T.P.: Bias in human path integration is predicted by properties of grid cells. Curr. Biol. 25(13), 1771–1776 (2015)
Doeller, C.F., Barry, C., Burgess, N.: Evidence for grid cells in a human memory network. Nature 463(7281), 657–661 (2010)
Jacobs, J., et al.: Direct recordings of grid-like neuronal activity in human spatial navigation. Nat. Neurosci. 16(9), 1188–1190 (2013)
Loomis, J.M., Klatzky, R.L., Golledge, R.G., Cicinelli, J.G., Pellegrino, J.W., Fry, P.A.: Nonvisual navigation by blind and sighted: assessment of path integration ability. J. Exp. Psychol. Gen. 122(1), 73–91 (1993)
Waller, D., Hodgson, E.: Sensory contributions to spatial knowledge of real and virtual environments. In: Steinicke, F., Visell, Y., Campos, J., Lécuyer, A. (eds.) Human Walking in Virtual Environments, pp. 3–26. Springer, New York (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4419-8432-6_1
Zhao, M., Zhou, G., Mou, W., Hayward, W.G., Owen, C.B.: Spatial updating during locomotion does not eliminate viewpoint-dependent visual object processing. Vis. Cogn. 15(4), 402–419 (2007)
Fujita, N., Klatzky, R.L., Loomis, J.M., Golledge, R.G.: The encoding-error model of pathway completion without vision. Geogr. Anal. 25(4), 295–314 (1993)
Wang, R.F., Spelke, E.S.: Updating egocentric representations in human navigation. Cognition 77(3), 215–250 (2000)
Klatzky, R.L.: Allocentric and egocentric spatial representations: definitions, distinctions, and interconnections. In: Freksa, C., Habel, C., Wender, K.F. (eds.) Spatial Cognition. LNCS (LNAI), vol. 1404, pp. 1–17. Springer, Heidelberg (1998). https://doi.org/10.1007/3-540-69342-4_1
Kelly, J.W., Avraamides, M.N., Loomis, J.M.: Sensorimotor alignment effects in the learning environment and in novel environments. J. Exp. Psychol. Learn. Mem. Cogn. 33(6), 1092–1107 (2007)
Mou, W., McNamara, T.P., Valiquette, C.M., Rump, B.: Allocentric and egocentric updating of spatial memories. J. Exp. Psychol. Learn. Mem. Cogn. 30(1), 142–157 (2004)
Mou, W., Zhang, H., McNamara, T.P.: Novel-view scene recognition relies on identifying spatial reference directions. Cognition 111(2), 175–186 (2009)
Klatzky, R.L., Loomis, J.M., Beall, A.C., Chance, S.S., Golledge, R.G.: Spatial updating of self-position and orientation during real, imagined, and virtual locomotion. Psychol. Sci. 9(4), 293–298 (1998)
Kelly, J.W., McNamara, T.P.: Spatial memories of virtual environments: how egocentric experience, intrinsic structure, and extrinsic structure interact. Psychon. Bull. Rev. 15(2), 322–327 (2008)
Wiener, J.M., Berthoz, A., Wolbers, T.: Dissociable cognitive mechanisms underlying human path integration. Exp. Brain Res. 208(1), 61–71 (2011)
Etienne, A.S., Jeffery, K.J.: Path integration in mammals. Hippocampus 14(2), 180–192 (2004)
Wiener, J.M., Mallot, H.A.: Path complexity does not impair visual path integration. Spat. Cogn. Comput. 6(4), 333–346 (2006)
Rump, B., McNamara, T.P.: Representations of interobject spatial relations in long-term memory. Mem. Cogn. 41(2), 201–213 (2013)
Rouder, J.N., Speckman, P.L., Sun, D., Morey, R.D., Iverson, G.: Bayesian \(t\) tests for accepting and rejecting the null hypothesis. Psychon. Bull. Rev. 16(2), 225–237 (2009)
Richard, L., Waller, D.: Toward a definition of intrinsic axes: the effect of orthogonality and symmetry on the preferred direction of spatial memory. J. Exp. Psychol. Learn. Mem. Cogn. 39(6), 1914–1929 (2013)
Kelly, J.W., McNamara, T.P., Bodenheimer, B., Carr, T.H., Rieser, J.J.: The shape of human navigation: how environmental geometry is used in maintenance of spatial orientation. Cognition 109(2), 281–286 (2008)
Kelly, J.W., McNamara, T.P., Bodenheimer, B., Carr, T.H., Rieser, J.J.: Individual differences in using geometric and featural cues to maintain spatial orientation: cue quantity and cue ambiguity are more important than cue type. Psychon. Bull. Rev. 16(1), 176–181 (2009)
Shelton, A.L., McNamara, T.P.: Multiple views of spatial memory. Psychon. Bull. Rev. 4(1), 102–106 (1997)
Shelton, A.L., McNamara, T.P.: Systems of spatial reference in human memory. Cogn. Psychol. 43(4), 274–310 (2001)
Manning, J.R., Lew, T.F., Li, N., Sekuler, R., Kahana, M.J.: MAGELLAN: a cognitive map-based model of human wayfinding. J. Exp. Psychol. Gen. 143(3), 1314–1330 (2014)
Meilinger, T., Riecke, B.E., Bülthoff, H.H.: Local and global reference frames for environmental spaces. Q. J. Exp. Psychol. 67(3), 542–569 (2014)
Meilinger, T.: The network of reference frames theory: a synthesis of graphs and cognitive maps. In: Freksa, C., Newcombe, N.S., Gärdenfors, P., Wölfl, S. (eds.) Spatial Cognition 2008. LNCS (LNAI), vol. 5248, pp. 344–360. Springer, Heidelberg (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-540-87601-4_25
Mou, W., McNamara, T.P., Zhang, L.: Global frames of reference organize configural knowledge of paths. Cognition 129(1), 180–193 (2013)
Acknowledgments
We are grateful to two anonymous reviewers for their helpful comments on the previous version of this article. This research was supported in part by National Science Foundation Grant 1526448.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2017 Springer International Publishing AG
About this paper
Cite this paper
He, Q., McNamara, T.P., Kelly, J.W. (2017). Environmental and Idiothetic Cues to Reference Frame Selection in Path Integration. In: Barkowsky, T., Burte, H., Hölscher, C., Schultheis, H. (eds) Spatial Cognition X. Spatial Cognition KogWis 2016 2016. Lecture Notes in Computer Science(), vol 10523. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-68189-4_9
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-68189-4_9
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-319-68188-7
Online ISBN: 978-3-319-68189-4
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)