Abstract
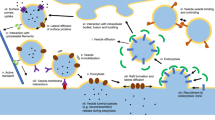
This study is a “morphosis” of the presented modified stochastic synaptic model (MSSM) with major validations using evidences from a number of clinical as well computational studies addressing the general question of copying the dynamics of synaptic transmission. The MSSM represents a, relatively, complex model-compilation of the synaptic connecting process with a focus on copying the relevant biophysical details in order to capture to the computational capacity of biological neural circuitry. The use of MSSM in large scale simulations has been mainly challenged due to the heavy mathematical functional execution, and more importantly due its sensitivity to high (>60 Hz) input firing rates. The presented analysis addresses both aspects with slightly new implementation of the model. It shows that the new understanding about vesicles dynamics helps the MSSM to present a richer repertoire of dynamics and meets the required functional synaptic heterogeneity.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alabi, A.A., Tsien, R.W.: Synaptic vesicle pools and dynamics. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 4(8), a013680 (2012)
Branco, T., Staras, K.: The probability of neurotransmitter release: variability and feedback control at single synapses. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 10, 373–383 (2009)
Chamberland, S., Tóth, K.: Functionally heterogeneous synaptic vesicle pools support diverse synaptic signalling. J. Physiol. 594(4), 825–835 (2016)
El-Laithy, K., Bogdan, M.: Synchrony state generation in artificial neural networks with stochastic synapses. In: Alippi, C., Polycarpou, M., Panayiotou, C., Ellinas, G. (eds.) ICANN 2009. LNCS, vol. 5768, pp. 181–190. Springer, Heidelberg (2009). doi:10.1007/978-3-642-04274-4_19
El-Laithy, K., Bogdan, M.: Predicting spike-timing of a thalamic neuron using a stochastic synaptic model. In: ESANN Proceedings, pp. 357–362 (2010)
El-laithy, K., Bogdan, M.: Synchrony state generation: an approach using stochastic synapses. J. Artif. Intell. Soft Comput. Res. 1, 17–26 (2011)
El-Laithy, K., Bogdan, M.: Temporal finite-state machines: a novel framework for the general class of dynamic networks. In: Huang, T., Zeng, Z., Li, C., Leung, C.S. (eds.) ICONIP 2012. LNCS, vol. 7664, pp. 425–434. Springer, Heidelberg (2012). doi:10.1007/978-3-642-34481-7_52
El-Laithy, K., Bogdan, M.: Synaptic energy drives the information processing mechanisms in spiking neural networks. Math. Biosci. Eng. 11(2), 233–256 (2014)
Hoffmann, J., El-Laithy, K., Güttler, F., Bogdan, M.: Simulating biological-inspired spiking neural networks with OpenCL. In: Diamantaras, K., Duch, W., Iliadis, L.S. (eds.) ICANN 2010. LNCS, vol. 6352, pp. 184–187. Springer, Heidelberg (2010). doi:10.1007/978-3-642-15819-3_23
Maass, W., Zador, A.M.: Dynamic stochastic synapses as computational units. Neural Comput. 11, 903–917 (1999)
Stimberg, M., Goodman, D., Benichoux, V., Brette, R.: Equation-oriented specification of neural models for simulations. Front. Neuroinf. 8, 6 (2014)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2017 Springer International Publishing AG
About this paper
Cite this paper
Ellatihy, K., Bogdan, M. (2017). Enhancements on the Modified Stochastic Synaptic Model: The Functional Heterogeneity. In: Lintas, A., Rovetta, S., Verschure, P., Villa, A. (eds) Artificial Neural Networks and Machine Learning – ICANN 2017. ICANN 2017. Lecture Notes in Computer Science(), vol 10613. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-68600-4_45
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-68600-4_45
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-319-68599-1
Online ISBN: 978-3-319-68600-4
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)