Abstract
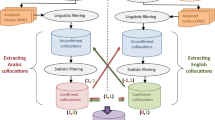
Collocation Extraction plays an important role in machine translation, information retrieval, secondary language learning, etc., and has obtained significant achievements in other languages, e.g. English and Chinese. There are some studies for Arabic collocation extraction using POS annotation to extract Arabic collocation. We used a hybrid method that included POS patterns and syntactic dependency relations as linguistics information and statistical methods for extracting the collocation from Arabic corpus. The experiment results showed that using this hybrid method for extracting Arabic words can guarantee a higher precision rate, which heightens even more after dependency relations are added as linguistic rules for filtering, having achieved 85.11%. This method also achieved a higher precision rate rather than only resorting to syntactic dependency analysis as a collocation extraction method.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
Notes
- 1.
It is worth mentioning that the present study is focused on word pairs, i.e. only lexical collocations containing two words are included. Situations in which the two words are separated are taken into account, but not situations with multiple words.
- 2.
One Arabic word could have more than one from in corpus because Arabic morphology is rich, so
 has 55 different variants.
has 55 different variants. - 3.
Bigrams sorted by their dependency score (ds), which actually is the Point Mutual Information Score.
References
Attia, M.A.: Accommodating multiword expressions in an arabic LFG grammar. In: Salakoski, T., Ginter, F., Pyysalo, S., Pahikkala, T. (eds.) FinTAL 2006. LNCS, vol. 4139, pp. 87–98. Springer, Heidelberg (2006). doi:10.1007/11816508_11
Benson, M.: Collocations and general-purpose dictionaries. Int. J. Lexicogr. 3(1), 23–34 (1990)
Benson, M.: The Structure of the Collocational Dictionary. Int. J. Lexicography, 2(1) (1989)
Bounhas, I., Slimani, Y.: A hybrid approach for Arabic multi-word term extraction. In: International Conference on Natural Language Processing and Knowledge Engineering 2009, NLP-KE, vol. 30, pp. 1–8. IEEE (2009)
Church, K.W., Hanks, P., Hindle, D.: Using Statistics in Lexical Analysis. Lexical Acquisition (1991)
Choueka, Y., Klein, T., Neuwitz, E.: Automation Retrieval of Frequent Idiomatic and Collocational Expressions in a Large Corpus. J. Literary Linguist. Comput. 4 (1983)
Frantzi, K., Sophia, A., Hideki, M.: Automatic recognition of multi-word terms: the C-value/NC-value method. Int. J. Digital Libraries 3, 115–130 (2000)
Halliday, M.A.K.: Lexical relations. System and Function in Language. Oxford University Press, Oxford (1976)
Pecina, P.: An extensive empirical study of collocation extraction methods. ACL 2005, Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics, pp. 13–18, University of Michigan, USA (2005)
Saif, A.M., Aziz, M.J.A.: An automatic collocation extraction from Arabic corpus. J. Comput. Sci. 7(1), 6 (2011)
Sinclair, J.: Corpus, Concordance, Collocation. Oxford University Press, Oxford (1991)
Smadja, F.: Retrieving collocations from text: extract. Comput. Linguist. 19(19), 143–177 (1993)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2017 Springer International Publishing AG
About this paper
Cite this paper
Akef, A.M., Wang, Y., Yang, E. (2017). Arabic Collocation Extraction Based on Hybrid Methods. In: Sun, M., Wang, X., Chang, B., Xiong, D. (eds) Chinese Computational Linguistics and Natural Language Processing Based on Naturally Annotated Big Data. NLP-NABD CCL 2017 2017. Lecture Notes in Computer Science(), vol 10565. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-69005-6_1
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-69005-6_1
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-319-69004-9
Online ISBN: 978-3-319-69005-6
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)




 has 55 different variants.
has 55 different variants.