Abstract
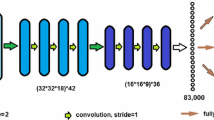
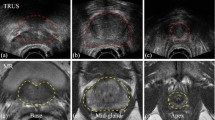
Prostate size inference from abdominal ultrasound images is crucial for many medical applications but it remains a challenging task due to very weak prostate borders and high image noise. This paper presents a novel method that enforces image patch prior information on multi-task deep learning followed by a global prostate shape estimation. The patch prior information is learned by multi-task Deep Convolutional Neural Networks (DCNNs) trained on multi-scale image patches to capture both local and global image information. We produce tens of thousands of image patches for the DCNN training that needs a large amount of training data which usually is not available for medical images. The three learned tasks for the DCNN are the distance between the patch center and the nearest contour point, the angle of the line segment between the patch center and the prostate center, and the contour curvature value for the patch center. During the prostate shape inference time, the labels returned from the multi-task DCNN are used in a global shape fitting process to obtain the final prostate contours which are then used for size inference. We performed experiments on transverse abdominal ultrasound images which are very challenging for automatic analysis.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Astudillo, R.F., Amir, S., Ling, W., Silva, M., Trancoso, I.: Learning word representations from scarce and noisy data with embedding subspaces. In: ACL, vol. 1, pp. 1074–1084 (2015)
Betrouni, N., Vermandel, M., Pasquier, D., Maouche, S., Rousseau, J.: Segmentation of abdominal ultrasound images of the prostate using a priori information and an adapted noise filter. Comput. Med. Imaging Graph. 29(1), 43–51 (2005)
Carneiro, G., Nascimento, J.C., Freitas, A.: The segmentation of the left ventricle of the heart from ultrasound data using deep learning architectures and derivative-based search methods. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 21(3), 968–982 (2012)
Choi, Y.J., Kim, J.K., Kim, H.J., Cho, K.S.: Interobserver variability of transrectal ultrasound for prostate volume measurement according to volume and observer experience. Am. J. Roentgenol. 192(2), 444–449 (2009)
De Sio, M., Darmiento, M., Di Lorenzo, G., Damiano, R., Perdonà, S., De Placido, S., Autorino, R.: The need to reduce patient discomfort during transrectal ultrasonography-guided prostate biopsy: what do we know? BJU Int. 96(7), 977–983 (2005)
Deng, J., Dong, W., Socher, R., Li, L.J., Li, K., Fei-Fei, L.: ImageNet: a large-scale hierarchical image database. In: IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition 2009, CVPR 2009, pp. 248–255. IEEE (2009)
Ghanei, A., Soltanian-Zadeh, H., Ratkewicz, A., Yin, F.F.: A three-dimensional deformable model for segmentation of human prostate from ultrasound images. Med. Phys. 28(10), 2147–2153 (2001)
Ghose, S., Oliver, A., Martí, R., Lladó, X., Vilanova, J.C., Freixenet, J., Mitra, J., Sidibé, D., Meriaudeau, F.: A survey of prostate segmentation methodologies in ultrasound, magnetic resonance and computed tomography images. Comput. Methods Programs Biomed. 108(1), 262–287 (2012)
Jia, Y., Shelhamer, E., Donahue, J., Karayev, S., Long, J., Girshick, R., Guadarrama, S., Darrell, T.: Caffe: convolutional architecture for fast feature embedding. In: Proceedings of the 22nd ACM International Conference on Multimedia, pp. 675–678. ACM (2014)
Krizhevsky, A., Sutskever, I., Hinton, G.E.: ImageNet classification with deep convolutional neural networks. In: Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, pp. 1097–1105 (2012)
Lee, H., Grosse, R., Ranganath, R., Ng, A.Y.: Convolutional deep belief networks for scalable unsupervised learning of hierarchical representations. In: Proceedings of the 26th Annual International Conference on Machine Learning, pp. 609–616. ACM (2009)
Liao, S., Gao, Y., Oto, A., Shen, D.: Representation learning: a unified deep learning framework for automatic prostate MR segmentation. In: Mori, K., Sakuma, I., Sato, Y., Barillot, C., Navab, N. (eds.) MICCAI 2013. LNCS, vol. 8150, pp. 254–261. Springer, Heidelberg (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-40763-5_32
Xu, Y., Mo, T., Feng, Q., Zhong, P., Lai, M., Eric, I., Chang, C.: Deep learning of feature representation with multiple instance learning for medical image analysis. In: 2014 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP), pp. 1626–1630. IEEE (2014)
Yuan, J., Qiu, W., Ukwatta, E., Rajchl, M., Tai, X.C., Fenster, A.: Efficient 3D endfiring trus prostate segmentation with globally optimized rotational symmetry. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 2211–2218 (2013)
Zhang, Y., Matuszewski, B.J., Histace, A., Precioso, F., Kilgallon, J., Moore, C.: Boundary delineation in prostate imaging using active contour segmentation method with interactively defined object regions. In: Madabhushi, A., Dowling, J., Yan, P., Fenster, A., Abolmaesumi, P., Hata, N. (eds.) Prostate Cancer Imaging 2010. LNCS, vol. 6367, pp. 131–142. Springer, Heidelberg (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-15989-3_15
Acknowledgements
This study is supported by TUBITAK project 114E536.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2017 Springer International Publishing AG
About this paper
Cite this paper
Albayrak, N.B., Yildirim, E., Akgul, Y.S. (2017). Prostate Size Inference from Abdominal Ultrasound Images with Patch Based Prior Information. In: Blanc-Talon, J., Penne, R., Philips, W., Popescu, D., Scheunders, P. (eds) Advanced Concepts for Intelligent Vision Systems. ACIVS 2017. Lecture Notes in Computer Science(), vol 10617. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-70353-4_22
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-70353-4_22
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-319-70352-7
Online ISBN: 978-3-319-70353-4
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)