Abstract
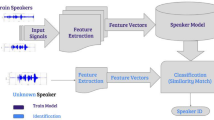
In order to improve speaker verification accuracy in the complex environment, a two-layer Gaussian mixture model-universal background model (GMM-UBM) model based on speaker verification method is proposed. For different layer, a GMM-UBM model was trained by different combination of speech features. The voice data of 3 days (36 h) were recorded from the complex environment, and the collected data was manually segmented into four classes: quiet, noise, target speaker and other speaker. Not only the segment data can be used to train GMM-UBM model, but also it can provide a criterion to assess the effectiveness of the model. The results show that the highest recall for the second and third day were 0.75 and 0.74 respectively, and the corresponding specificity were 0.29 and 0.19, which indicates the proposed GMM-UBM model is viable to verify the target speaker in the complex environment.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chen, J., Zhong, N.: Data-brain modeling for systematic brain informatics. In: Brain Informatics, International Conference, BI, Beijing, China, October 22–24 (2009)
Zhong, N., Motomura, S.: Agent-enriched data mining: a case study in brain informatics. IEEE Intell. Syst. 24, 38–45 (2009)
Li, N., Mak, M.W.: SNR-invariant PLDA modeling in nonparametric subspace for robust speaker verification. IEEE/ACM Trans. Audio Speech/Language Process. 23, 1648–1659 (2015)
Ding, I.J., Yen, C.T., Ou, D.C.: A method to integrate GMM, SVM and DTW for speaker recognition. Int. J. Eng. Technol. Innov. 4, 38–47 (2014)
Wu, H., Wang, Y., Huang, J.: Blind detection of electronic disguised voice. In: IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing, pp. 3013–3017 (2013)
Wang, X., Yang, T., Yu, Y., Zhang, R., Guo, F.: Footstep-identification system based on walking interval. Intell. Syst. IEEE 30, 46–52 (2015)
Turner, C., Joseph, A.: A wavelet packet and mel-frequency cepstral coefficients-based feature extraction method for speaker identification. Procedia Comput. Sci. 61, 416–421 (2015)
Haris, B.C., Sinha, R.: Low-Complexity Speaker Verification with Decimated Supervector Representations. Elsevier Science Publishers B. V., Amsterdam (2015)
Wang, Y., Wu, H., Huang, J.: Verification of Hidden Speaker Behind Transformation Disguised Voices. Academic Press, Inc, Orlando (2015)
Kanagasundaram, A., Dean, D., Sridharan, S.: Improving PLDA speaker verification with limited development data. In: IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing, pp. 1665–1669 (2014)
Rajan, P., Afanasyev, A., Hautamki, V., Kinnunen, T.: From single to multiple enrollment i-vectors: practical PLDA scoring variants for speaker verification. Digit. Signal Proc. 31, 93–101 (2014)
Xu, L., Yang, Z.: Speaker identification based on state space model. Int. J. Speech Technol. 19, 1–8 (2016)
Rakhmanenko, I., Meshcheryakov, R.: Speech Features Evaluation for Small Set Automatic Speaker Verification Using GMM-UBM System (2016)
Sarkar, A.K., Tan, Z.H.: Text Dependent Speaker Verification Using un-supervised HMM-UBM and Temporal GMM-UBM. In: Interspeech (2016)
Dehak, N., Kenny, P.J., Dehak, R., Dumouchel, P., Ouellet, P.: Front-end factor analysis for speaker verification. IEEE Trans. Audio Speech Language Process. 19, 788–798 (2011)
Jagtap, S.S., Bhalke, D.G.: Speaker verification using Gaussian mixture model. In: International Conference on Pervasive Computing, pp. 1–5 (2015)
Acknowledgments
This work is partially supported by the National Basic Research Program of China (No. 2014CB744600), National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 61420106005), Beijing Natural Science Foundation (No. 4164080), and Beijing Outstanding Talent Training Foundation (No. 2014000020124G039).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2017 Springer International Publishing AG
About this paper
Cite this paper
He, Q., Wan, Z., Zhou, H., Yang, J., Zhong, N. (2017). Speaker Verification Method Based on Two-Layer GMM-UBM Model in the Complex Environment. In: Zeng, Y., et al. Brain Informatics. BI 2017. Lecture Notes in Computer Science(), vol 10654. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-70772-3_14
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-70772-3_14
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-319-70771-6
Online ISBN: 978-3-319-70772-3
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)