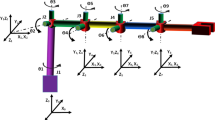
Abstract
The need for efficient automation methods has prompted the fast development in the field of Robotics. However, most robotic solutions found in industrial environments lack in both flexibility and adaptability to be applied to any generic task. A particular problem arises when robots are integrated in work cells with extra degrees of freedom, such as external axis or positioners. The specification/design of high redundancy systems, including robot selection, tool and fixture design, is a multi-variable problem with strong influence in the final performance of the work cell. This work builds on top of optimisation techniques to deal with the optimal poses reachability for high redundancy robotic systems. In this paper, it will be proposed a poses optimisation approach to be applicable within high redundancy robotic systems. The proposed methodology was validated by using real environment existent infrastructures, namely, the national CoopWeld project.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alatartsev, S., Stellmacher, S., Ortmeier, F.: Robotic task sequencing problem: a survey. J. Intell. Robot. Syst. 80(2), 279–298 (2015)
Andrisano, A.O., Leali, F., Pellicciari, M., Pini, F., Vergnano, A., Pini, F.: Integrated design of robotic workcells for high quality machining (2011)
Bennewitz, M., Burgard, W., Thrun, S.: Optimizing schedules for prioritized path planning of multi-robot systems, vol. 1, pp. 271–276 (2001)
Cheng, F.S.: Methodology for developing robotic workcell simulation models, vol. 2, pp. 1265–1271 (2000)
Chu, B., Jung, K., Chu, Y., Hong, D., Lim, M.T., Park, S., Lee, Y., Lee, S.U., Min Chul, K., Kang Ho, K.: Robotic automation system for steel beam assembly in building construction, pp. 38–43 (2009)
Deb, K.: Introduction to genetic algorithms. Sadhana - Acad. Proc. Eng. Sci. 24(4–5), 293–315 (1999)
Fathi, M., Álvarez, M., Rodríguez, V.: A new heuristic-based bi-objective simulated annealing method for U-shaped assembly line balancing. Eur. J. Ind. Eng. 10(2), 145–169 (2016)
Geller, E., Matthews, C.: Impact of robotic operative efficiency on profitability. Am. J. Obstet. Gynecol. 209(1), 20e1–20e5 (2013)
Graetz, G., Michaels, G.: Robots at Work (2015)
Gueta, L., Chiba, R., Arai, T., Ueyama, T., Ota, J.: Compact design of work cell with robot arm and positioning table under a task completion time constraint, pp. 807–813 (2009)
Hauer, S., M.V.H.C.S.K.: Design and simulation of modular robot work cells, pp. 1801–1802 (2009)
Kamezaki, M., Hashimoto, S., Iwata, H., Sugano, S.: Development of a dual robotic arm system to evaluate intelligent system for advanced construction machinery, pp. 1299–1304 (2010)
Kamoun, H., Hall, N., Sriskandarajah, C.: Scheduling in robotic cells: heuristics and cell design. Oper. Res. 47(6), 821–835 (1999)
Kirkpatrick, S., Gelatt Jr., C., Vecchi, M.: Optimization by simulated annealing. Science 220(4598), 671–680 (1983)
Mansouri, S.: A multi-objective genetic algorithm for mixed-model sequencing on JIT assembly lines. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 167(3), 696–716 (2005)
Pellegrinelli, S., Pedrocchi, N., Tosatti, L.M., Fischer, A., Tolio, T.: Multi-robot spot-welding cells for car-body assembly: design and motion planning. Robot. Comput.-Integr. Manufact. 44, 97–116 (2017)
Yang, J., Yang, J.: Intelligence optimization algorithms: a survey 3(4), 144–152 (2011)
Acknowledgments
A special word to SARKKIS robotics and INESC-TEC (in particular the ERDF – European Regional Development Fund through the Operational Programme for Competitiveness and Internationalisation - COMPETE 2020 Programme, and the FCT – Fundação para a Ciência e a Tecnologia (Portuguese Foundation for Science and Technology) within project «POCI-01-0145-FEDER-006961») for their commitment in research and development of revolutionary state-of-the-art algorithms and for their contribution regarding software tools and engineering hours availability.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2018 Springer International Publishing AG
About this paper
Cite this paper
Tavares, P., Costa, P., Veiga, G., Moreira, A.P. (2018). Poses Optimisation Methodology for High Redundancy Robotic Systems. In: Ollero, A., Sanfeliu, A., Montano, L., Lau, N., Cardeira, C. (eds) ROBOT 2017: Third Iberian Robotics Conference. ROBOT 2017. Advances in Intelligent Systems and Computing, vol 694. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-70836-2_55
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-70836-2_55
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-319-70835-5
Online ISBN: 978-3-319-70836-2
eBook Packages: EngineeringEngineering (R0)