Abstract
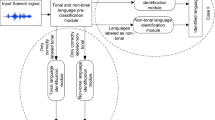
In this article we make use of the characteristics of tonal languages and machine learning methodologies to understand the patterns in them. Instead of analyzing the absolute pitch or frequency, we analyze how one tone transitions to another in speech. Features (namely, zero crossing count, short time energy, minimum formant frequency, maximum formant frequency) are extracted using the tonal transitions over segments of audio signals. We have developed a multi-classifier system using four classifiers, namely maximum likelihood estimate (MLE), minimum distance classifier (MDC), k-nearest neighbor (kNN) classifier and fuzzy k-NN classifier to automatically identify tonal languages from audio signals. Initially, each individual classifier is trained with existing known data represented by the extracted features. The trained classifier is then used for language identification. Results obtained from these classifiers are combined to generate the final output. Experiments are conducted using three different tonal languages, namely, Chinese, Thai and Vietnamese. The output reveals that the developed multi-classifier model is able to produce promising results. The extracted features produced better results in comparison to usually used frequency value (as a feature). Ensemble of classifiers is a better tool than using individual classifiers.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Jurafsky, D., Martin, J.H.: Speech and Language Processing, 2nd edn. Pearson, New Delhi (2014)
Muthusamy, Y.K., Barnard, E., Cole, R.A.: Reviewing automatic language identification. IEEE Sign. Process. Mag. 11, 33–41 (1994)
Zissman, M.A.: Automatic language identification of telephone speech. Lincoln Laboratory Manual, MIT, USA, vol. 8, no. 2, pp. 115–144 (1995)
Ambikairajah, E., Li, H., Wang, L., Yin, B., Sethu, V.: Language identification: a tutorial. IEEE Circ. Syst. Mag. 11(2), 82–108 (2011)
Ng, R.W.M., Lee, T., Leung, C., Ma, B., Li, H.: Spoken language recognition with prosodic features. IEEE Trans. Audio Speech Lang. Process. 21(9), 1841–1852 (2013)
Itahashi, S., Zhou, J.X., Tanaka, K.: Spoken language discrimination using speech fundamental frequency. In: Proceedings of Third International Conference on Spoken Language Processing, Japan, vol. 4, pp. 1899–1902 (1994)
Tong, R., Ma, B., Zhu, D., Li, H., Chng, E.S.: Integrating acoustic, prosodic and phonotactic features for spoken language identification. In: Proceedings of IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP), pp. I 205–I 208 (2006)
Rao, K.S., Yegnanarayana, B.: Intonation modeling for Indian languages. J. Comput. Speech Lang. 23, 240–256 (2009)
Newman, J.L., Cox, S.J.: Language identification using visual features. IEEE Trans. Audio Speech Lang. Process. 20(7), 1936–1947 (2012)
Segbroeck, M., Travadi, R., Narayanan, S.S.: Rapid language identification. IEEE Trans. Audio Speech Lang. Process. 23(7), 1118–1129 (2015)
Yencken, L.: The great language game (2013). www.greatlanguagegame.com
Duda, R.O., Hart, P.E., Stork, D.G.: Pattern Classification, 2nd edn. Wiley, New York (2001)
Theodoridis, S., Koutroumbas, K.: Pattern Recognition, 4th edn. Elsevier, New York (2008)
Gonzalez, R.C., Woods, R.E.: Digital Image Processing, 3rd edn. Pearson Education, New Delhi (2009)
Cannam, C., Landone, C., Sandler, M.: Sonic visualiser: an open source application for viewing, analysing, and annotating music audio files. In: Proceedings of the 18th ACM International Conference on Multimedia, pp. 1467–1468 (2010)
Acknowledgment
An earlier version of this work has been presented at the Intel International Science and Engineering Fair (Intel ISEF), held at Los Angeles, USA in May 2017 and won a Grand Award. The author would like to acknowledge her School teacher, Dr. Partha Pratim Roy, for advising her throughout the course of this work. Thanks are due to the Intel Initiative for Research and Innovation in Science (IRIS) Scientific Review Committee and her mentors, for their valuable comments. The author also acknowledges Rahul Roy and Ajoy Mondal, her parents’ students, for helping her in conducting the experiments.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2017 Springer International Publishing AG
About this paper
Cite this paper
Ghosh, S. (2017). Language Identification Based on the Variations in Intonation Using Multi-classifier Systems. In: Ghosh, A., Pal, R., Prasath, R. (eds) Mining Intelligence and Knowledge Exploration. MIKE 2017. Lecture Notes in Computer Science(), vol 10682. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-71928-3_8
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-71928-3_8
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-319-71927-6
Online ISBN: 978-3-319-71928-3
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)