Abstract
Verifying that a network configuration satisfies a given boolean predicate is a fundamental problem in distributed computing. Many variations of this problem have been studied, for example, in the context of proof labeling schemes (\(\mathrm {PLS}\)), locally checkable proofs (\(\mathrm {LCP}\)), and non-deterministic local decision (\(\mathrm {NLD}\)). In all of these contexts, verification time is assumed to be constant. Korman et al. [16] presented a proof-labeling scheme for MST, with poly-logarithmic verification time, and logarithmic memory at each vertex.
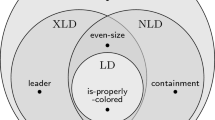
In this paper we introduce the notion of a \(t\text {-}\mathrm {PLS}\), which allows the verification procedure to run for super-constant time. Our work analyzes the tradeoffs of \(t\text {-}\mathrm {PLS}\) between time, label size, message length, and computation space. We construct a universal \(t\text {-}\mathrm {PLS}\) and prove that it uses the same amount of total communication as a known one-round universal \(\mathrm {PLS}\), and t factor smaller labels. In addition, we provide a general technique to prove lower bounds for space-time tradeoffs of \(t\text {-}\mathrm {PLS}\). We use this technique to show an optimal tradeoff for testing that a network is acyclic (cycle free). Our optimal \(t\text {-}\mathrm {PLS}\) for acyclicity uses label size and computation space \(O((\log n)/t)\). We further describe a recursive \(O(\log ^* n)\) space verifier for acyclicity which does not assume previous knowledge of the run-time t.
R. Ostrovsky—Research supported in part by NSF grant 1619348, DARPA, US-Israel BSF grant 2012366, OKAWA Foundation Research Award, IBM Faculty Research Award, Xerox Faculty Research Award, B. John Garrick Foundation Award, Teradata Research Award, and Lockheed-Martin Corporation Research Award. The views expressed are those of the authors and do not reflect position of the Department of Defense or the U.S. Government.
M. Perry—Partially supported by Apple Graduate Fellowship.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Afek, Y., Kutten, S., Yung, M.: The local detection paradigm and its application to self-stabilization. Theor. Comput. Sci. 186(1–2), 199–229 (1997)
Awerbuch, B., Ostrovsky, R.: Memory-efficient and self-stabilizing network reset (extended abstract). In: Proceedings of 13th Annual ACM Symposium on Principles of Distributed Computing, PODC 1994, pp. 254–263. ACM, New York (1994)
Awerbuch, B., Patt-Shamir, B., Varghese, G.: Self-stabilization by local checking and correction. In: 32nd Symposium on Foundations of Computer Science (FOCS), pp. 268–277. IEEE (1991)
Baruch, M., Fraigniaud, P., Patt-Shamir, B.: Randomized proof-labeling schemes. In: Proceedings of 2015 ACM Symposium on Principles of Distributed Computing, PODC, pp. 315–324 (2015)
Baruch, M., Ostrovsky, R., Rosenbaum, W.: Brief announcement: space-time tradeoffs for distributed verification. In: Proceedings of 2016 ACM Symposium on Principles of Distributed Computing, PODC 2016, pp. 357–359. ACM, New York (2016)
Baruch, M., Ostrovsky, R., Rosenbaum, W.: Space-time tradeoffs for distributed verification. CoRR, arXiv:1605.06814 (2016)
Blin, L., Fraigniaud, P., Patt-Shamir, B.: On proof-labeling schemes versus silent self-stabilizing algorithms. In: Felber, P., Garg, V. (eds.) SSS 2014. LNCS, vol. 8756, pp. 18–32. Springer, Cham (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-11764-5_2
Das Sarma, A., Holzer, S., Kor, L., Korman, A., Nanongkai, D., Pandurangan, G., Peleg, D., Wattenhofer, R.: Distributed verification and hardness of distributed approximation. SIAM J. Comput. 41(5), 1235–1265 (2012)
Feuilloley, L., Fraigniaud, P.: Survey of distributed decision. Bull. EATCS, 119 (2016)
Foerster, K.-T., Luedi, T., Seidel, J., Wattenhofer, R.: Local checkability, no strings attached. In: Proceedings of 17th International Conference on Distributed Computing and Networking, ICDCN 2016, pp. 21:1–21:10. ACM, New York (2016)
Fraigniaud, P., Korman, A., Peleg, D.: Towards a complexity theory for local distributed computing. J. ACM 60(5), 35 (2013)
Fraigniaud, P., Rajsbaum, S., Travers, C.: Locality and checkability in wait-free computing. Distrib. Comput. 26(4), 223–242 (2013)
Göös, M., Suomela, J.: Locally checkable proofs. In: 30th ACM Symposium on Principles of Distributed Computing (PODC), pp. 159–168 (2011)
Itkis, G., Levin, L.: Fast and lean self-stabilizing asynchronous protocols. In: Proceedings of 35th Annual Symposium on Foundations of Computer Science, SFCS 1994, pp. 226–239. IEEE Computer Society, Washington, DC (1994)
Korman, A., Kutten, S.: Distributed verification of minimum spanning trees. Distrib. Comput. 20, 253–266 (2007)
Korman, A., Kutten, S., Masuzawa, T.: Fast and compact self stabilizing verification, computation, and fault detection of an MST. In: 30th Annual ACM Symposium on Principles of Distributed Computing (PODC), pp. 311–320 (2011)
Korman, A., Kutten, S., Peleg, D.: Proof labeling schemes. Distrib. Comput. 22(4), 215–233 (2010)
Schmid, S., Suomela, J.: Exploiting locality in distributed SDN control. In: Proceedings of 2nd ACM SIGCOMM Workshop on Hot Topics in Software Defined Networking, HotSDN 2013, pp. 121–126. ACM, New York (2013)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2017 Springer International Publishing AG
About this paper
Cite this paper
Ostrovsky, R., Perry, M., Rosenbaum, W. (2017). Space-Time Tradeoffs for Distributed Verification. In: Das, S., Tixeuil, S. (eds) Structural Information and Communication Complexity. SIROCCO 2017. Lecture Notes in Computer Science(), vol 10641. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-72050-0_4
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-72050-0_4
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-319-72049-4
Online ISBN: 978-3-319-72050-0
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)