Abstract
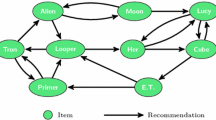
The success of Google’s PageRank algorithm popularized graphs as a tool to model the web’s navigability. At that time, the web topology was resulting from human edition of hyper-links. Nowadays, that topology is mostly resulting from algorithms. In this paper, we propose to study the topology realized by a class of such algorithms: recommenders. By modeling the output of recommenders as graphs, we show that a vast array of topological observations become easily accessible, using a simple web-crawler. We give models and illustrations for those graph representations. We then propose a graph-based methodology for addressing an algorithmic transparency problem: recommendation bias detection. We illustrate this approach on YouTube crawls, targeting the prediction of “Recommended for you” links.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
Notes
- 1.
We note that these graph structures and their dynamics relate them to time-varying networks and time-varying graphs [3].
- 2.
“Lady Gaga’s FULL Pepsi Zero Sugar Super Bowl LI Halftime Show | NFL”, https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=txXwg712zw4.
References
Bashir, M.A., Arshad, S., Wilson, C.: “Recommended for you”: A first look at content recommendation networks. In: IMC (2016)
Blum, A., Chan, T.H.H., Rwebangira, M.R.: A random-surfer web-graph model. In: ANALCO (2006)
Casteigts, A., Flocchini, P., Quattrociocchi, W., Santoro, N.: Time-varying graphs and dynamic networks. In: Frey, H., Li, X., Ruehrup, S. (eds.) ADHOC-NOW (2011)
Covington, P., Adams, J., Sargin, E.: Deep neural networks for youtube recommendations. In: RecSys (2016)
Davidson, J., Liebald, B., Liu, J., Nandy, P., Van Vleet, T., Gargi, U., Gupta, S., He, Y., Lambert, M., Livingston, B., Sampath, D.: The youtube video recommendation system. In: RecSys (2010)
Girvan, M., Newman, M.E.J.: Community structure in social and biological networks. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 99(12), 7821–7826 (2002)
Lamprecht, D., Strohmaier, M., Helic, D.: A method for evaluating the navigability of recommendation algorithms. In: International Workshop on Complex Networks and their Applications (2016)
Le Merrer, E., Trédan, G.: Uncovering influence cookbooks : Reverse engineering the topological impact in peer ranking services. In: CSCW (2017)
Lécuyer, M., Ducoffe, G., Lan, F., Papancea, A., Petsios, T., Spahn, R., Chaintreau, A., Geambasu, R.: Xray: Enhancing the web’s transparency with differential correlation. In: USENIX Security Symposium (2014)
Mirza, B.J., Keller, B.J., Ramakrishnan, N.: Studying recommendation algorithms by graph analysis. J. Intell. Inf. Syst. 20(2), 131–160 (2003)
Ricci, F., Rokach, L., Shapira, B., Kantor, P.B.: Recommender Systems Handbook, 1st edn. (2010)
Seyerlehner, K., Knees, P., Schnitzer, D., Widmer, G.: Browsing music recommendation networks. In: ISMIR (2009)
Sinha, S., Rashmi, K.S., Sinha, R.: Beyond algorithms: An HCI perspective on recommender systems (2001)
Tramèr, F., Zhang, F., Juels, A., Reiter, M.K., Ristenpart, T.: Stealing machine learning models via prediction apis. In: USENIX Security Symposium (2016)
Watts, D.J., Strogatz, S.H.: Collective dynamics of’small-world’networks. Nature 393(6684), 409–10 (1998)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2018 Springer International Publishing AG
About this paper
Cite this paper
Le Merrer, E., Trédan, G. (2018). The Topological Face of Recommendation. In: Cherifi, C., Cherifi, H., Karsai, M., Musolesi, M. (eds) Complex Networks & Their Applications VI. COMPLEX NETWORKS 2017. Studies in Computational Intelligence, vol 689. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-72150-7_72
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-72150-7_72
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-319-72149-1
Online ISBN: 978-3-319-72150-7
eBook Packages: EngineeringEngineering (R0)