Abstract
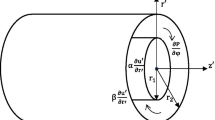
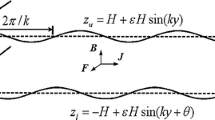
This paper presents the effect of a wall deformation on the boundaries conditions of a shear flow of the viscous fluid over a deformable wall which has a periodic deformation and small amplitude. The Reynolds number for the flow over a wall is low and the creeping flow equations apply. The no-slip boundary condition on the deformable wall applies. By using an asymptotic expansion, the analytic expression is obtained for the slip length.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Batchelor, G.K.: An Introduction to Fluid Dynamics. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge (2000)
Beebe, D.J., Mensing, G.A., Walker, G.M.: Physics and applications of microfluidics in biology. Ann. Rev. Biomed. Eng. 4(1), 261–286 (2002)
Hocking, L.: A moving fluid interface on a rough surface. J. Fluid Mech. 76(4), 801–817 (1976)
Jansons, K.M.: Determination of the macroscopic (partial) slip boundary condition for a viscous flow over a randomly rough surface with a perfect slip microscopic boundary condition. Phys. Fluids 31(1), 15–17 (1988)
Lamb, H.: Hydro Dynamics. 6th ed. 738. Dover, New York (1932)
Priezjev, N.V.: Effect of surface roughness on rate-dependent slip in simple fluids. J. Chem. Phys. 127(14), 144708 (2007)
Priezjev, N.V., Darhuber, A.A., Troian, S.M.: Slip behavior in liquid films on surfaces of patterned wettability: comparison between continuum and molecular dynamics simulations. Phys. Rev. E 71(4), 041608 (2005)
Squires, T.M., Quake, S.R.: Microfluidics: fluid physics at the nanoliter scale. Rev. Mod. Phys. 77(3), 977 (2005)
Tuck, E., Kouzoubov, A.: A laminar roughness boundary condition. J. Fluid Mech. 300, 59–70 (1995)
Vinogradova, O.I., Yakubov, G.E.: Surface roughness and hydrodynamic boundary conditions. Phys. Rev. E 73(4), 045302 (2006)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2018 Springer International Publishing AG
About this paper
Cite this paper
Assoudi, R., Lamzoud, K., Chaoui, M. (2018). Influence of Wall Deformation on a Slip Length. In: Ben Ahmed, M., Boudhir, A. (eds) Innovations in Smart Cities and Applications. SCAMS 2017. Lecture Notes in Networks and Systems, vol 37. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-74500-8_83
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-74500-8_83
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-319-74499-5
Online ISBN: 978-3-319-74500-8
eBook Packages: EngineeringEngineering (R0)