Abstract
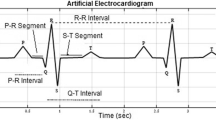
The main idea of this paper is to show that rational orthogonal function systems, called Malmquist-Takenaka (MT) systems can effectively be used for ECG heartbeat classification. The idea behind using these systems is the adaptive nature of them. Then the constructed feature vector consists of two main parts, called dynamic and morphological parameters. The latter ones contain the coefficients of the orthogonal projection with respect to the MT systems. Then Support Vector Machine algorithm was used for classifying the heartbeats into the usual 16 arrhythmia classes. The comparison test were performed on the MIT-BIH arrhythmia database. The results show that our algorithm outperforms the previous ones in many respects.
G. Bognár—Supported by the New National Excellence Program of the Ministry of Human Capacities of Hungary.
S. Fridli—This research was supported by the Hungarian Scientific Research Funds (OTKA) No. K115804.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chang, C.C., Lin, C.J.: LIBSVM: a library for support vector machines. ACM Trans. Intell. Syst. Techol. 2, 27: 1–27: 27 (2011). https://www.csie.ntu.edu.tw/~cjlin/libsvm/
de Chazal, P., O’Dwyer, M., Reilly, R.B.: Automatic classification of heartbeats using ECG morphology and heartbeat interval features. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 51(7), 1196–1206 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1109/tbme.2004.827359
Cortes, C., Vapnik, V.N.: Support-vector networks. J. Mach. Learn. 20(3), 1–25 (1995). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1022627411411
Fridli, S., Lócsi, L., Schipp, F.: Rational function systems in ECG processing. In: Moreno-Díaz, R., Pichler, F., Quesada-Arencibia, A. (eds.) EUROCAST 2011. LNCS, vol. 6927, pp. 88–95. Springer, Heidelberg (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-27549-4_12
Fridli, S., Schipp, F.: Biorthogonal systems to rational functions. Ann. Univ. Sci. Bp. Sect. Comp. 35, 95–105 (2011)
Fridli, S., Kovács, P., Lócsi, L., Schipp, F.: Rational modeling of multi-lead QRS complexes in ECG signals. Ann. Univ. Sci. Bp. Sect. Comp. 37, 145–155 (2012)
Gilián, Z., Kovács, P., Samiee, K.: Rhythm-based accuracy improvement of heart beat detection algorithms. In: Computing in Cardiology Conference, pp. 269–272 (2014)
Goldberger, A.L., et al.: PhysioBank, PhysioToolkit, and PhysioNet: components of a new research resource for complex physiologic signals. Circulation 101(23), 215–220 (2000). http://circ.ahajournals.org/cgi/content/full/101/23/e215
Heuberger, P.S.C., Van den Hof, P.M.J., Wahlberg, B. (eds.): Modelling and Identification with Rational Orthogonal Basis Functions. Springer-Verlag, London Limited, London (2005)
Jiang, X., Zhang, L.Q., Zhao, Q.B., Albayrak, S.: ECG arrhythmias recognition system based on independent component analysis feature extraction. In: Proceedings IEEE Region 10 Conference, pp. 1–4. (2006). https://doi.org/10.1109/tencon.2006.343781
Kovács, P., Lócsi, L.: RAIT: the rational approximation and interpolation toolbox for Matlab, with experiments on ECG signals. Int. J. Adv. Telecommun. Electech. Sign. Syst. 1(2–3), 67–75 (2012). https://doi.org/10.11601/ijates.v1i2-3.18
Lagerholm, M., Peterson, C., Braccini, G., Edenbrandt, L., Sornmo, L.: Clustering ECG complexes using Hermite functions and self-organizing maps. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 47(7), 838–848 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1109/10.846677
Lócsi, L.: Approximating poles of complex rational functions. Acta Univ. Sapientiae-Math. 1(2), 169–182 (2009)
Luz, E.J.S., Schwartz, W.R., Cámara-Cháveza, G., Menotti, D.: ECG-based heartbeat classification for arrhythmia detection: a survey. Comput. Methods Programs Biomed. 127, 144–164 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cmpb.2015.12.008
Moody, G.B., Mark, R.G.: The impact of the MIT-BIH arrhythmia database. IEEE Eng. Med. Biol. Mag. 20(3), 45–50 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1109/51.932724
Nelder, J.A., Mead, R.: A simplex method for function minimization. Comput. J. 7(4), 308–313 (1965). https://doi.org/10.1093/comjnl/7.4.308
Osowski, S., Hoa, L.T., Markiewic, T.: Support vector machine-based expert system for reliable heartbeat recognition. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 51(4), 582–589 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1109/TBME.2004.824138
Prasad, G.K., Sahambi, J.S.: Classification of ECG arrhythmias using multi-resolution analysis and neural networks. In: Proceeding of Conference Convergent Technology Asia-Pacific Region, pp. 227–231 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1109/TENCON.2003.1273320
Robert, K., Colleen, E.C.: Basis and Treatment of Cardiac Arrhythmias, 1st edn. Springer, New York (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/3-540-29715-4
Rodriguez, J., Goni, A., Illarramendi, A.: Real-time classification of ECGs on a PDA. IEEE Trans. Inf. Techol. Biomed. 9(1), 23–34 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1109/TITB.2004.838369
Sansone, M., Fusco, R., Pepino, A., Sansone, C.: Electrocardiogram pattern recognition and analysis based on artificial neural networks and support vector machines: a review. J. Healthc. Eng. 4(4), 465–504 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1260/2040-2295.4.4.465
Ye, C., Kumar, B.V., Coimbra, M.T.: Heartbeat classification using morphological and dynamic features of ECG signals. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 59(10), 2930–2941 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1109/TBME.2012.2213253
Zhang, D.: Wavelet approach for ECG baseline wander correction and noise reduction. In: Proceedings IEEE International Conference Engineering Medicine Biology Society, pp. 1212–1215 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1109/IEMBS.2005.1616642
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2018 Springer International Publishing AG
About this paper
Cite this paper
Bognár, G., Fridli, S. (2018). Heartbeat Classification of ECG Signals Using Rational Function Systems. In: Moreno-Díaz, R., Pichler, F., Quesada-Arencibia, A. (eds) Computer Aided Systems Theory – EUROCAST 2017. EUROCAST 2017. Lecture Notes in Computer Science(), vol 10672. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-74727-9_22
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-74727-9_22
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-319-74726-2
Online ISBN: 978-3-319-74727-9
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)