Abstract
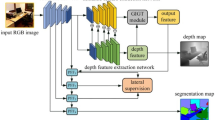
Depth cue is crucial for perception of spatial layout and understanding the cluttered indoor scenes. However, there is little study of leveraging depth information within the image scene classification systems, mainly because the lack of depth labeling in existing monocular image datasets. In this paper, we introduce a framework to overcome this limitation by incorporating the predicted depth descriptor of the monocular images for indoor scene classification. The depth prediction model is firstly learned from existing RGB-D dataset using the multiscale convolutional network. Given a monocular RGB image, a representation encoding the predicted depth cue is generated. This predicted depth descriptors can be further fused with features from color channels. Experiments are performed on two indoor scene classification benchmarks and the quantitative comparisons demonstrate the effectiveness of proposed scheme.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
Notes
References
Lazebnik, S., Schmid, C., Ponce, J.: Beyond bags of features: spatial pyramid matching for recognizing natural scene categories. In: CVPR, pp. 2169–2178 (2006)
Quattoni, A., Torralba, A.: Recognizing indoor scenes. In: CVPR (2009)
Xiao, J., Hays, J., Ehinger, K.A., Oliva, A., Torralba, A.: Sun database: large-scale scene recognition from abbey to zoo. In: CVPR, pp. 3485–3492 (2010)
Shotton, J., Sharp, T., Kipman, A., Fitzgibbon, A., Finocchio, M., Blake, A., Cook, M., Moore, R.: Real-time human pose recognition in parts from single depth images. Commun. ACM 56(1), 116–124 (2013)
Silberman, N., Hoiem, D., Kohli, P., Fergus, R.: Indoor segmentation and support inference from RGBD images. In: Fitzgibbon, A., Lazebnik, S., Perona, P., Sato, Y., Schmid, C. (eds.) ECCV 2012, Part V. LNCS, vol. 7576, pp. 746–760. Springer, Heidelberg (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-33715-4_54
Ren, X., Bo, L., Fox, D.: RGB-(D) scene labeling: features and algorithms. In: CVPR, pp. 2759–2766 (2012)
Gupta, S., Girshick, R., Arbeláez, P., Malik, J.: Learning rich features from RGB-D images for object detection and segmentation. In: Fleet, D., Pajdla, T., Schiele, B., Tuytelaars, T. (eds.) ECCV 2014, Part VII. LNCS, vol. 8695, pp. 345–360. Springer, Cham (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-10584-0_23
Gupta, S., Arbelaez, P., Malik, J.: Perceptual organization and recognition of indoor scenes from RGB-D images. In: CVPR, pp. 564–571 (2013)
Song, S., Lichtenberg, S.P., Xiao, J.: Sun RGB-D: a RGB-D scene understanding benchmark suite. In: CVPR (2015)
Liao, Y., Kodagoda, S., Wang, Y., Shi, L., Liu, Y.: Understand scene categories by objects: a semantic regularized scene classifier using convolutional neural networks. In: ICRA (2016)
Zhu, H., Weibel, J.B., Lu, S.: Discriminative multi-modal feature fusion for RGBD indoor scene recognition. In: CVPR (2016)
Wang, A., Cai, J., Lu, J., Cham, T.J.: Modality and component aware feature fusion for RGB-D scene classification. In: CVPR (2016)
Song, X., Herranz, L., Jiang, S.: Depth CNNs for RGB-D scene recognition: learning from scratch better than transferring from RGB-CNNs. In: AAAI (2017)
Oliva, A., Torralba, A.: Modeling the shape of the scene: a holistic representation of the spatial envelope. IJCV 42(3), 145–175 (2001)
Li, L.J., Su, H., Xing, E.P., Fei-Fei, L.: Object bank: a high-level image representation for scene classification semantic feature sparsification. In: NIPS (2010)
Juneja, M., Vedaldi, A., Jawahar, C.V., Zisserman, A.: Blocks that shout: distinctive parts for scene classification. In: CVPR, pp. 923–930 (2013)
Doersch, C., Gupta, A., Efros, A.A.: Mid-level visual element discovery as discriminative mode seeking. In: NIPS, pp. 494–502 (2013)
Razavian, A., Azizpour, H., Sullivan, J., Carlsson, S.: CNN features off-the-shelf: an astounding baseline for recognition. In: CVPR Workshops, pp. 806–813 (2014)
Zhou, B., Lapedriza, A., Xiao, J., Torralba, A., Oliva, A.: Learning deep features for scene recognition using places database. In: NIPS, pp. 487–495 (2014)
Gong, Y., Wang, L., Guo, R., Lazebnik, S.: Multi-scale orderless pooling of deep convolutional activation features. In: Fleet, D., Pajdla, T., Schiele, B., Tuytelaars, T. (eds.) ECCV 2014, Part VII. LNCS, vol. 8695, pp. 392–407. Springer, Cham (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-10584-0_26
Deng, J., Dong, W., Socher, R., Li, L., Li, K., Fei-Fei, L.: ImageNet: a large-scale hierarchical image database. In: CVPR (2009)
Saxena, A., Sun, M., Ng, A.Y.: Make3d: learning 3d scene structure from a single still image. IEEE Trans. PAMI 31(5), 824–840 (2009)
Liu, B., Gould, S., Koller, D.: Single image depth estimation from predicted semantic labels. In: CVPR (2010)
Eigen, D., Fergus, R.: Predicting depth, surface normals and semantic labels with a common multi-scale convolutional architecture. In: ICCV, pp. 2650–2658 (2015)
Liu, F., Shen, C., Lin, G.: Deep convolutional neural fields for depth estimation from a single image. In: CVPR (2015)
Zoran, D., Isola, P., Krishnan, D., Freeman, W.T.: Learning ordinal relationships for mid-level vision. In: ICCV (2015)
Wang, P., Shen, X., Lin, Z., Cohen, S., Price, B., Yuille, A.: Towards unified depth and semantic prediction from a single image. In: CVPR, pp. 2800–2809 (2015)
Chen, W., Fu, Z., Yang, D., Deng, J.: Single-image depth perception in the wild. In: NIPS (2016)
Krizhevsky, A., Sutskever, I., Hinton, G.E.: ImageNet classification with deep convolutional neural networks. In: NIPS (2012)
Simonyan, K., Zisserman, A.: Very deep convolutional networks for large-scale image recognition. In: ICLR (2015)
Pandey, M., Lazebnik, S.: Scene recognition and weakly supervised object localization with deformable part-based models. In: ICCV (2011)
Zheng, Y., Jiang, Y.-G., Xue, X.: Learning hybrid part filters for scene recognition. In: Fitzgibbon, A., Lazebnik, S., Perona, P., Sato, Y., Schmid, C. (eds.) ECCV 2012, Part V. LNCS, vol. 7576, pp. 172–185. Springer, Heidelberg (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-33715-4_13
Janoch, A., Karayev, S., Jia, Y., Barron, J.T., Fritz, M., Saenko, K., Darrell, T.: A category-level 3d object dataset: putting the kinect to work. In: Consumer Depth Cameras for Computer Vision, pp. 141–165 (2013)
Xiao, J., Owens, A., Torralba, A.: Sun3d: a database of big spaces reconstructed using SFM and object labels. In: ICCV, pp. 1625–1632 (2013)
Acknowledgments
This work was supported in part by grants from NSFC (No. 61602459) and STCSM’s program (No. 17511101902 and No. 17YF1427100).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2018 Springer International Publishing AG, part of Springer Nature
About this paper
Cite this paper
Zheng, Y., Pu, J., Wang, H., Ye, H. (2018). Indoor Scene Classification by Incorporating Predicted Depth Descriptor. In: Zeng, B., Huang, Q., El Saddik, A., Li, H., Jiang, S., Fan, X. (eds) Advances in Multimedia Information Processing – PCM 2017. PCM 2017. Lecture Notes in Computer Science(), vol 10736. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-77383-4_2
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-77383-4_2
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-319-77382-7
Online ISBN: 978-3-319-77383-4
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)