Abstract
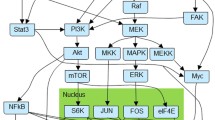
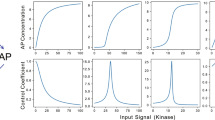
PI3K/AKT signaling pathway plays a crucial role in the control of functions related to cancer biology, including cellular proliferation, survival, migration, angiogenesis and apoptosis; what makes this signaling pathway one of the main processes involved in cancer development. The analysis and prediction of the anticancer targets acting over the PI3K/AKT signaling pathway requires of a deep understanding of its signaling elements, the complex interactions that take place between them, as well as the global behaviors that arise as a result, that is, a systems biology approach. Following this methodology, in this work, we propose an in silico modeling and simulation approach of the PI3K class I and III signaling pathways, for exploring its effect over AKT and SGK proteins, its relationship with the deregulated growth control in cancer, its role in metastasis, as well as for identifying possible control points. The in silico approach provides symbolic abstractions and accurate algorithms that allow dealing with crucial aspects of the cellular signal transduction such as compartmentalization, topology and timing. Our results show that the activation or inhibition of target signaling elements in the overall signaling pathway can change the outcome of the cell, turning it into apoptosis or proliferation.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Lien, E.C., Dibble, C.C., Toker, A.: PI3K signaling in cancer: beyond AKT. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 45, 62–71 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceb.2017.02.007
Alves, R., Antunes, F., Salvador, A.: Tools for kinetic modeling of biochemical networks. Nat. Biotechnol. 24(6), 667–672 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1038/nbt0606-667
Ciocchetta, F., Duguid, A., Guerriero, M.L.: A compartmental model of the cAMP/PKA/MAPK pathway in bio-PEPA. In: Third Workshop on Membrane Computing and Biologically Inspired Process Calculi (MeCBIC) (2009). http://dx.doi.org/10.4204/EPTCS.11.5
Kerr, R.A., Bartol, T.M., Kaminsky, B., Dittrich, M., Chang, J.C., Baden, S.B., Sejnowski, T.J., Stiles, J.R.: Fast Monte Carlo simulation methods for biological reaction-diffusion systems in solution and on surfaces. SIAM J. Sci. Comput. 30(36), 3126–3149 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1137/070692017
Hoops, S., Sahle, S., Gauges, R., Lee, C., Pahle, J., Simus, N., Singhal, M., Xu, L., Mendes, P., Kummer, U.: COPASI: a complex pathway simulator. Bioinformatics 22(24), 3067–3074 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/btl485
Cowan, A.E., Moraru, I.I., Schaff, J.C., Slepchenko, B.M., Loew, L.M.: Spatial modeling of cell signaling networks. Methods Cell Biol. 110, 195–221 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-12-388403-9.00008-4
Swat, M., Thomas, G.L., Belmonte, J.M., Shirinifard, A., Hmeljak, D., Glazier, J.A.: Multi-scale modeling of tissues using CompuCell 3D. Methods Cell Biol. 110, 325–366 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-12-388403-9.00013-8
González-Pérez, P.P., Omicini, A., Sbaraglia, M.: A biochemically inspired coordination-based model for simulating intracellular signalling pathway. J. Simul. 27(3), 216–226 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1057/jos.2012.28
Cárdenas-García, M., González-Pérez, P.P., Montagna, S., Cortés Sánchez, O., Caballero, E.H.: Modeling intercellular communication as a survival strategy of cancer cells: an in silico approach on a flexible bioinformatics framework. Bioinform. Biol. Insights 10, 5–18 (2016). https://doi.org/10.4137/BBI.S38075
Gelernter, D.: Generative communication in Linda. ACM Trans. Program. Lang. Syst. 7(1), 80–112 (1985). https://doi.org/10.1145/2363.2433
Gillespie, D.T.: Exact stochastic simulation of coupled chemical reactions. J. Phys. Chem. 81(25), 2340–2361 (1977). https://doi.org/10.1021/j100540a008
Downward, J.: Targeting RAS signalling pathways in cancer therapy. Nat. Rev. Cancer 3(1), 11–22 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1038/nrc969
Goodsell, D.S.: The molecular perspective: the ras oncogene. Oncologist 4(3), 263–264 (1999)
Neves, S.R., Ram, P.T., Iyengar, R.: G protein pathways. Science 296(5573), 1636–1639 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1071550
González-Pérez, P.P., Cárdenas, M., Camacho, D., Franyuti, A., Rosas, O., Lagúnez-Otero, J.: Cellulat: an agent-based intracellular signalling model. Biosystems 68(2–3), 171–185 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1016/S0303-2647(02)00094-1
Reyton-González, M.L., Cornell-Kennon, S., Schaefer, E., Kuzmic, P.: An algebraic model to determine substrate kinetic parameters by global nonlinear fit of progress curves. Anal. Biochem. 1(518), 16–24 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ab.2016.11.001
Azevedo-Silva, J., Queirós, O., Ribeiro, A., Baltazar, F., Young, K.H., Pedersen, P.L., Preto, A., Casal, M.: The cytotoxicity of 3-bromopyruvate in breast cáncer cells depends on extracelular pH. Biochem. J. 467(2), 247–258 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1042/BJ20140921
Blokh, D., Stambler, I., Afrimzon, E., Shafran, Y., Korech, E., Sandbank, J., Orda, R., Zurgil, N., Deutsch, M.: The information-theory analysis of Michaelis-menten constants for detection of breast cáncer. Cancer Detec. Prev. 31(6), 489–498 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cdp.2007.10.010
Paradiso, A., Cardone, R.A., Bellizzi, A., Bagorda, A., Guerro, L., Tommasino, M., Casavola, V., Reshkin, S.J.: The Na+-H+ exchanger-1 induces cytoskeletal changes involving reciprocal RhoA and Rac1 signaling, resulting in motility and invasión in MDA-MB-435 cells. Breast Cancer Res. 6(6), R616–R628 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1186/bcr922
Fritz, J., Dwyer-Nield, L., Malkinson, A.M.: Stimulation of neoplastic mouse lung cell proliferation by alveolar macrophage-derived, insulin-like growth factor-1 can be blocked by inhibiting MEK and PI3K activation. Mol. Cancer 10, 76–96 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1186/1476-4598-10-76
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2018 Springer International Publishing AG, part of Springer Nature
About this paper
Cite this paper
González-Pérez, P.P., Cárdenas-García, M. (2018). Inspecting the Role of PI3K/AKT Signaling Pathway in Cancer Development Using an In Silico Modeling and Simulation Approach. In: Rojas, I., Ortuño, F. (eds) Bioinformatics and Biomedical Engineering. IWBBIO 2018. Lecture Notes in Computer Science(), vol 10813. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-78723-7_7
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-78723-7_7
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-319-78722-0
Online ISBN: 978-3-319-78723-7
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)