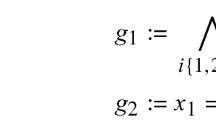Abstract
Multi-agent systems consist of agents and their environment. the agents in a multi-agent system could equally well be robots, humans or human teams. And may contain combined human-agent.
Multi-agent systems can be used to solve problems that are difficult or impossible for an individual agent or a monolithic system to solve. Intelligence may include some methodic, functional, procedural approach, algorithmic search or reinforcement learning.
In a system with agents that have their own objectives and schedules, when tasks are dependent on one another or when resources are to be shared, it can be important to add the function of coordination to the system, otherwise there is a risk of redundancy or even of a “locked” situation occurring.
With the modeling in Event-B we are now ready to make precise what we mean by a “faultless” system, which represents our ultimate goal as the title of this prologue indicates.
In this paper and with the abstract machine, we are going to present a formal approach to develop the addressing and the relation between Multi-Agents and its convenient scope achieving the allocated missions.
On the refinement machine the technique of adding auxiliary resources is considered during the mission life-cycle.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Brahnam, S., Jain, L.C.: Dhuʻl-H. 17, 1435 AH – Computers, 291 p. Springer, Heidelberg
Cellular Automata and Agent - based Models - A Theoritical Framework. http://wgbis.ces.iisc.ernet.in/energy/paper/TR100/tr100_cel.htm
Kaminka, G.A.: Robots are Agents, Too! AgentLink News, pp. 16–17, December 2004
Kubera, Y., Mathieu, P., Picault, S.: Everything can be Agent! (PDF). In: Proceedings of the Ninth International Joint Conference on Autonomous Agents and Multi-Agent Systems (AAMAS 2010), Toronto, Canada, pp. 1547–1548 (2010)
Ferber, J.: Multi-Agent System: An Introduction to Distributed Artificial Intelligence. Addison Wesley Longman, Harlow (1999). Paper: ISBN 0-201-36048-9
Abrial, J-R.: The B book: Assigning Programs to Meanings. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge (1996)
Abrial, J-R.: Extending B without changing it (for developing distributed systems). In: First B Conference Putting Into Practice Methods and Tools for Information System Design, Nantes, pp. 169–190 (1996)
Metayer, C., Abrial, J., Voisin, L.: Event-B Language. Technical report D7, z RODIN Project Deliverable (2005)
Butler, M.: Mastering System Analysis and Design through Abstraction and Refinement. Deploy (2012)
Butler, M.: Reasoned Modelling with Event-B, 30 January 2017
Abrial, J.-R.: Modeling in Event-B: System and Software Engineering. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge (2010)
Acknowledgement
This work was supported by the Ministry of Education, Youth and Sports of the Czech Republic within the National Sustainability Programme project No. LO1303 (MSMT-7778/2014) and by the European Regional Development Fund under the project CEBIA-Tech No. CZ.1.05/2.1.00/03.0089. Also supported by grant No. IGA/CebiaTech/2017/007 from IGA (Internal Grant Agency) of Tomas Bata University in Zlin.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2019 Springer International Publishing AG, part of Springer Nature
About this paper
Cite this paper
Kadi, M., Krayem, S., Jasek, R., Zacek, P., Chramcov, B. (2019). Multi-agent Systems Interacting (Addressing Scopes, Control Resources). In: Silhavy, R. (eds) Cybernetics and Algorithms in Intelligent Systems . CSOC2018 2018. Advances in Intelligent Systems and Computing, vol 765. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-91192-2_24
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-91192-2_24
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-319-91191-5
Online ISBN: 978-3-319-91192-2
eBook Packages: Intelligent Technologies and RoboticsIntelligent Technologies and Robotics (R0)