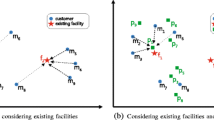
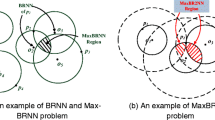
Abstract
Consider a two dimensional Euclidean space, let F be a set of points representing facilities and U be a set of points representing users. Spatial influence of a facility is the number of users who have this facility as one of their k nearest facilities. This is because that users normally prefer to go to their nearby facilities and are naturally influenced the most by their nearest facilities. Given a facility bundle of size t, spatial influence of the bundle is the number of distinct users influenced by any one of them. Existing works on facility selection problem find out top-t facilities with the highest spatial influence. However, the literature lacks study on this problem when the t facilities have the highest spatial influence as a bundle. We are the first to study the problem of Maximizing Bundled Reverse k Nearest Neighbors (MB-RkNN), where the spatial influence of a facility bundle of size t is maximized. We prove its NP-hardness, and propose a branch-and-bound best first search algorithm that greedily select the currently best facility until we get t facilities. We introduce the concept of kNN region such that a group of users have their kNN facilities all belong to the same kNN region. This sharing property of kNN region allows us to avoid redundant calculation with dynamic programming technique. We conduct experiments on real data sets and show that our algorithm is orders of magnitudes better than our baseline algorithm both in terms of CPU time and IO cost.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
Notes
- 1.
- 2.
\(yelp\_academic\_dataset\_business.json\).
- 3.
\(yelp\_academic\_dataset\_tip.json\).
References
Cheema, M.A., Lin, X., Zhang, W., Zhang, Y.: Influence zone: efficiently processing reverse k nearest neighbors queries. In: Proceedings of the 27th International Conference on Data Engineering, ICDE 2011, Hannover, Germany, 11–16 April 2011, pp. 577–588 (2011)
Chen, F., Lin, H., Qi, J., Li, P., Gao, Y.: Collective-k optimal location selection. In: Gertz, M., Renz, M., Zhou, X., Hoel, E., Ku, W.-S., Voisard, A., Zhang, C., Chen, H., Tang, L., Huang, Y., Lu, C.-T., Ravada, S. (eds.) SSTD 2017. LNCS, vol. 10411, pp. 339–356. Springer, Cham (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-64367-0_18
Gkorgkas, O., Vlachou, A., Doulkeridis, C., Nørvåg, K.: Finding the most diverse products using preference queries. In: Proceedings of the 18th International Conference on Extending Database Technology, EDBT 2015, Brussels, Belgium, 23–27 March 2015, pp. 205–216 (2015)
Huang, J., Wen, Z., Qi, J., Zhang, R., Chen, J., He, Z.: Top-k most influential locations selection. In: Proceedings of the 20th ACM Conference on Information and Knowledge Management, CIKM 2011, Glasgow, United Kingdom, 24–28 October 2011, pp. 2377–2380 (2011)
Koh, J., Lin, C., Chen, A.L.P.: Finding k most favorite products based on reverse top-t queries. VLDB J. 23(4), 541–564 (2014)
Korn, F., Muthukrishnan, S.: Influence sets based on reverse nearest neighbor queries. In: Proceedings of the 2000 ACM SIGMOD International Conference on Management of Data, Dallas, Texas, USA, 16–18 May 2000, pp. 201–212 (2000)
Li, C., Wang, E.T., Huang, G., Chen, A.L.P.: Top-n query processing in spatial databases considering bi-chromatic reverse k-nearest neighbors. Inf. Syst. 42, 123–138 (2014)
Stanoi, I., Agrawal, D., El Abbadi, A.: Reverse nearest neighbor queries for dynamic databases. In: 2000 ACM SIGMOD Workshop on Research Issues in Data Mining and Knowledge Discovery, Dallas, Texas, USA, 14 May 2000, pp. 44–53 (2000)
Sun, Y., Zhang, R., Xue, A.Y., Qi, J., Du, X.: Reverse nearest neighbor heat maps: a tool for influence exploration. In: 32nd IEEE International Conference on Data Engineering, ICDE 2016, Helsinki, Finland, 16–20 May 2016, pp. 966–977 (2016)
Tao, Y., Papadias, D., Lian, X.: Reverse kNN search in arbitrary dimensionality. In: Proceedings of the Thirtieth International Conference on Very Large Data Bases, Toronto, Canada, 31 August - 3 September 2004, pp. 744–755 (2004)
Vlachou, A., Doulkeridis, C., Nørvåg, K., Kotidis, Y.: Identifying the most influential data objects with reverse top-k queries. PVLDB 3(1), 364–372 (2010)
Wang, S., Cheema, M.A., Zhang, Y., Lin, X.: Selecting representative objects considering coverage and diversity. In: Second International ACM Workshop on Managing and Mining Enriched Geo-Spatial Data, GeoRich@SIGMOD 2015, Melbourne, VIC, Australia, 31 May 2015, pp. 31–38 (2015)
Wong, R.C., Özsu, M.T., Fu, A.W., Yu, P.S., Liu, L., Liu, Y.: Maximizing bichromatic reverse nearest neighbor for lp-norm in two- and three-dimensional spaces. VLDB J. 20(6), 893–919 (2011)
Wong, R.C., Özsu, M.T., Yu, P.S., Fu, A.W., Liu, L.: Efficient method for maximizing bichromatic reverse nearest neighbor. PVLDB 2(1), 1126–1137 (2009)
Xia, T., Zhang, D., Kanoulas, E., Du, Y.: On computing top-t most influential spatial sites. In: Proceedings of the 31st International Conference on Very Large Data Bases, Trondheim, Norway, 30 August - 2 September 2005, pp. 946–957 (2005)
Yang, S., Cheema, M.A., Lin, X., Zhang, Y.: SLICE: reviving regions-based pruning for reverse k nearest neighbors queries. In: IEEE 30th International Conference on Data Engineering, Chicago, ICDE 2014, IL, USA, 31 March - 4 April 2014, pp. 760–771 (2014)
Zhan, L., Zhang, Y., Zhang, W., Lin, X.: Finding top k most influential spatial facilities over uncertain objects. In: 21st ACM International Conference on Information and Knowledge Management, CIKM 2012, Maui, HI, USA, 29 October - 02 November 2012, pp. 922–931 (2012)
Zhan, L., Zhang, Y., Zhang, W., Lin, X.: Finding top k most influential spatial facilities over uncertain objects. IEEE Trans. Knowl. Data Eng. 27(12), 3289–3303 (2015)
Zhou, Z., Wu, W., Li, X., Lee, M., Hsu, W.: MaxFirst for MaxBRkNN. In: Proceedings of the 27th International Conference on Data Engineering, ICDE 2011, Hannover, Germany, 11–16 April 2011, pp. 828–839 (2011)
Acknowledgment
Ying Zhang is supported by ARC FT170100128 and DP180103096.Xuemin Lin is supported by NSFC61672235, DP170101628 and DP180103096. Muhammad Aamir Cheema is supported by ARC DP180103411.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2018 Springer International Publishing AG, part of Springer Nature
About this paper
Cite this paper
Wang, S., Zhang, Y., Lin, X., Cheema, M.A. (2018). Maximize Spatial Influence of Facility Bundle Considering Reverse k Nearest Neighbors. In: Pei, J., Manolopoulos, Y., Sadiq, S., Li, J. (eds) Database Systems for Advanced Applications. DASFAA 2018. Lecture Notes in Computer Science(), vol 10827. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-91452-7_44
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-91452-7_44
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-319-91451-0
Online ISBN: 978-3-319-91452-7
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)