Abstract
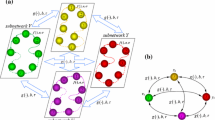
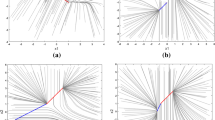
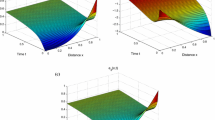
A continuous attractor of a recurrent neural network is a set of connected stable equilibrium points. The continuous attractors of neural networks with symmetric connection weights have been studied widely. However, most of the matrixes are asymmetric. In this paper, the continuous attractors of 3-D discrete-time ring networks with circulant weight matrix are studied. The circulant matrix is asymmetric. The eigenvalues of asymmetric matrix may be complex. Based on the complex eigenvalues, the conditions that guarantee the networks with circulant weight matrix to have continuous attractors are obtained.
J. Yu—This work is supported by National Natural Science Foundation of China under Grant 61572112, 61103041, 61432012, the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities under Grant ZYGX2016J136.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Amari, S.: Dynamics of pattern formation in lateral-inhibition type neural fields. Biol. Cybern. 27(2), 77–87 (1977)
Yi, Z., Zhang, L., Yu, J., Tan, K.K.: Permitted and forbidden sets in discrete-time linear threshold recurrent neural networks. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. 20, 952–963 (2009)
Yu, J., Yi, Z., Zhang, L.: Representations of continuous attractors of recurrent neural networks. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. 20, 368–372 (2009)
Pouget, A., Dayan, P., Zemel, R.: Information processing with population codes. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 1, 125–132 (2000)
Yu, J., Mao, H., Yi, Z.: Parameter as a switch between dynamical states of a network in population decoding. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst. 28(4), 911–916 (2017)
Seung, H.S.: How the brain keeps the eyes still. Proc. Nat. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 93, 13339–13344 (1996)
Lee, D.D., Reis, B.Y., Seung, H.S., Tank, D.W.: Nonlinear network models of the Oculomotor integrator. In: Bower, J.M. (ed.) Computational Neuroscience. Springer, Boston (1997). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4757-9800-5_60
Zhang, K.C.: Representation of spatial orientation by the intrinsic dynamics of the head-direction cell ensemble: a theory. J. Neurosci. 16, 2112–2126 (1996)
Robinson, D.A.: Integrating with neurons. Ann. Rev. Neurosci. 12, 33–45 (1989)
Koulakov, A., Raghavachari, S., Kepecs, A., Lisman, J.E.: Model for a robust neural integrator. Nat. Neurosci. 5(8), 775–782 (2002)
Stringer, S.M., Trappenberg, T.P., Rolls, E.T., de Araujo, I.E.T.: Self-organizing continuous attractor networks and path integration: one-dimensional models of head direction cells. Netw.: Comput. Neural Syst. 13, 217–242 (2002)
Seung, H.S., Lee, D.D.: The manifold ways of perception. Science 290, 2268–2269 (2000)
Stringer, S.M., Rolls, E.T., Trappenberg, T.P., de Araujo, I.E.T.: Self-organizing continuous attractor networks and motor function. Neural Netw. 16, 161–182 (2003)
Yu, J., Tang, H., Li, H.: Dynamics analysis of a population decoding model. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst. 24(3), 498–503 (2013)
Wimmer, K., Nykamp, D.Q., Constantinidis, C., Compte, A.: Bump attractor dynamics in prefrontal cortex explains behavioral precision in spatial working memory. Nat. Neurosci. 17(3), 431–439 (2014)
Samsonovich, A., McNaughton, B.L.: Path integration and cognitive mapping in a continuous attractor neural network model. J. Neurosci. 17, 5900–5920 (1997)
Miller, P.: Analysis of spike statistics in neuronal systems with continuous attractors or multiple, discrete attractor states. Neural Comput. 18, 1268–1317 (2006)
Yoon, K., Buice, M.A., Barry, C., Hayman, R., Burgess, N., Fiete, I.R.: Specific evidence of low-dimensional continuous attractor dynamics in grid cells. Nat. Neurosci. 16(8), 1077–1084 (2013)
Seung, H.S.: Continouous attractors and oculomotor control. Neural Netw. 11, 1253–1258 (1998)
Skaggs, W.E., Knierim, J.J., Kudrimoti, H.S., Mcnaughton, B.L.: A model of the neural basis of the rat’s sense of direction. Neural Comput. 7(7), 173–180 (1995)
Zhang, W., Wu, S.: Reiprocally coupled local estimator implement bayesian information integration distibutively. In: Advances in Neural Information Processing System, pp. 19–27 (2013)
Wu, S., Wong, K.Y., Fung, C.C., Mi, Y., Zhang, W.: Continuous attractor neural networks: candidate of a canonical model for neural information representation. F1000research 5(16), 209–226 (2016)
Machens, C.K., Brody, C.D.: Design of continuous attractor networks with monotonic tuning using a symmetry principle. Neural Comput. 20, 452–485 (2008)
Hahnloser, H.R., Sarpeshkar, R., Mahowald, M.A., Douglas, R.J., Seung, H.S.: Digital selection and analogue amplication coexist in a cortex-inspired silicon circuit. Nature 405, 947–951 (2000)
Ben-Yishai, R., Bar-Or, R.L., Sompolinsky, H.: Theory of orientation tuning in visual cortex. Proc. Nat. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 92, 3844–3848 (1995)
Zou, L., Tang, H., Tan, K.C., Zhang, W.: Analysis of continuous attractors for 2-D linear threshold neural networks. IEEE Trans. Neural Networks 20, 175–180 (2009)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2018 Springer International Publishing AG, part of Springer Nature
About this paper
Cite this paper
Yu, J., Yi, Z., Liao, Y., Wu, DA., Dai, X. (2018). Continuous Attractors of 3-D Discrete-Time Ring Networks with Circulant Weight Matrix. In: Huang, T., Lv, J., Sun, C., Tuzikov, A. (eds) Advances in Neural Networks – ISNN 2018. ISNN 2018. Lecture Notes in Computer Science(), vol 10878. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-92537-0_45
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-92537-0_45
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-319-92536-3
Online ISBN: 978-3-319-92537-0
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)