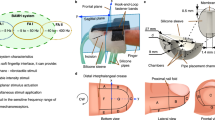
Abstract
This paper presents a novel, wearable, and multi-sensory haptic feedback system intended to support the transmission of large sets of haptic cues that are accurately perceived by the human user. Previous devices have focused on the optimization of haptic cue transmission using a single modality and have typically employed arrays of haptic tactile actuators to maximize information throughput to a user. However, when large cue sets are to be transmitted, perceptual interference between transmitted cues can decrease the efficacy of single-sensory systems. Therefore, we present MISSIVE (Multi-sensory Interface of Stretch, Squeeze, and Integrated Vibration Elements), a wearable system that conveys multi-sensory haptic cues to the user’s upper arm, allowing for increased perceptual accuracy compared to a single-sensory vibrotactile array of a comparable size, conveying the same number of cues. Our multi-sensory haptic cues are comprised of concurrently rendered, yet perceptually distinct elements: radial squeeze, lateral skin stretch, and localized cutaneous vibration. Our experiments demonstrate that our approach can increase perceptual accuracy compared to a single-sensory vibrotactile system of comparable size and that users prefer MISSIVE.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Akhtar, A., Nguyen, M., Wan, L., Boyce, B., Slade, P., Bretl, T.: Passive mechanical skin stretch for multiple degree-of-freedom proprioception in a hand prosthesis. In: Auvray, M., Duriez, C. (eds.) EUROHAPTICS 2014. LNCS, vol. 8619, pp. 120–128. Springer, Heidelberg (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-662-44196-1_16
Alluisi, E.A., Muller Jr., P.F., Fitts, P.M.: An information analysis of verbal and motor responses in a forced-paced serial task. J. Exp. Psychol. 53(3), 153 (1957)
Battaglia, E., Clark, J.P., Bianchi, M., Catalano, M.G., Bicchi, A., O’Malley, M.K.: The rice haptic rocker: skin stretch haptic feedback with the Pisa/IIT softhand. In: IEEE World Haptics Conference, pp. 7–12. IEEE (2017)
Casini, S., Morvidoni, M., Bianchi, M., Catalano, M., Grioli, G., Bicchi, A.: Design and realization of the cuff - clenching upper-limb force feedback wearable device for distributed mechano-tactile stimulation of normal and tangential skin forces. In: IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems, pp. 1186–1193 (2015)
Chinello, F., Pacchierotti, C., Tsagarakis, N.G., Prattichizzo, D.: Design of a wearable skin stretch cutaneous device for the upper limb. In: Haptics Symposium, pp. 14–20. IEEE (2016)
Christiansen, R., Contreras-Vidal, J.L., Gillespie, R.B., Shewokis, P.A., O’Malley, M.K.: Vibrotactile feedback of pose error enhances myoelectric control of a prosthetic hand. In: 2013 World Haptics Conference, pp. 531–536 (2013)
Ernst, M.O.: A bayesian view on multimodal cue integration. In: Human Body Perception from the Inside Out, vol. 131, pp. 105–131 (2006)
Gault, R.H.: Progress in experiments on tactual interpretation of oral speech. J. Abnormal Psychol. Soc. Psychol. 19(2), 155 (1924)
Gopalai, A.A., Senanayake, S.A.A.: A wearable real-time intelligent posture corrective system using vibrotactile feedback. IEEE/ASME Trans. Mechatron. 16(5), 827–834 (2011)
Israr, A., Meckl, P.H., Tan, H.Z.: A two Dof controller for a multi-finger tactual display using a loop-shaping technique. In: Proceedings of the ASME International Mechanical Engineering Congress and Exposition (IMECE 2004), pp. 1083–1089 (2004)
Karam, M., Russo, F.A., Fels, D.I.: Designing the model human cochlea: an ambient crossmodal audio-tactile display. IEEE Trans. Haptics 2(3), 160–169 (2009)
Kim, M., Lee, S., Choi, S.: Saliency-driven real-time video-to-tactile translation. IEEE Trans. Haptics 7(3), 394–404 (2014)
Liang, X., Makatura, C.R., Schubert, M., Solomon, B.H., Walker, J.M., Blank, A.A., O’Malley, M.K.: [D86] skin-stretch proprioceptive feedback for a robotic gripper. In: 2014 IEEE Haptics Symposium, p. 1 (2014)
Norman, S.L., Doxon, A.J., Gleeson, B.T., Provancher, W.R.: Planar hand motion guidance using fingertip skin-stretch feedback. IEEE Trans. Haptics 7(2), 121–130 (2014)
Novich, S.D., Eagleman, D.M.: Using space and time to encode vibrotactile information: toward an estimate of the skin’s achievable throughput. Exp. Brain Res. 233(10), 2777–2788 (2015)
Pandey, S., Byrne, M.D., Jantscher, W.H., O’Malley, M.K., Agarwal, P.: Toward training surgeons with motion-based feedback: initial validation of smoothness as a measure of motor learning. In: Proceedings of the Human Factors and Ergonomics Society Annual Meeting, vol. 61, no. 1, pp. 1531–1535 (2017)
Reed, C.M., Delhorne, L.A.: Current results of a field study of adult users of tactile aids. In: Seminars in Hearing, vol. 16, pp. 305–315. Thieme Medical Publishers, Inc. (1995)
Reed, C.M., Durlach, N.I., Braida, L.D.: Research on tactile communication of speech: a review. ASHA Monographs 20, 1 (1982)
Stanley, A.A., Kuchenbecker, K.J.: Evaluation of tactile feedback methods for wrist rotation guidance. IEEE Trans. Haptics 5(3), 240–251 (2012)
Suhonen, K., Müller, S., Rantala, J., Väänänen-Vainio-Mattila, K., Raisamo, R., Lantz, V.: Haptically augmented remote speech communication: a study of user practices and experiences. In: Proceedings of the 7th Nordic Conference on Human-Computer Interaction: Making Sense Through Design, pp. 361–369. ACM (2012)
Tan, H., Gray, R., Young, J.J., Taylor, R.: A haptic back display for attentional and directional cueing (2003)
Tan, H.Z., Reed, C.M., Durlach, N.I.: Optimum information transfer rates for communication through haptic and other sensory modalities. IEEE Trans. Haptics 3(2), 98–108 (2010)
Tang, A., McLachlan, P., Lowe, K., Saka, C.R., MacLean, K.: Perceiving ordinal data haptically under workload. In: Proceedings of the 7th International Conference on Multimodal interfaces, pp. 317–324. ACM (2005)
Treadway, E., Gillespie, B., Bolger, D., Blank, A., O’Malley, M.K., Davis, A.: The role of auxiliary and referred haptic feedback in myoelectric control. In: World Haptics Conference, WHC, pp. 13–18. Northwestern University, IEEE (2015)
Walker, J.M., Blank, A.A., Shewokis, P.A., O’Malley, M.K.: Tactile feedback of object slip facilitates virtual object manipulation. IEEE Trans. Haptics 8(4), 454–466 (2015)
Weisenberger, J.M., Broadstone, S.M., Kozma-Spytek, L.: Relative performance of single-channel and multichannel tactile aids for speech perception. J. Rehabil. Res. Dev. 28(2), 45 (1991)
Wheeler, J., Bark, K., Savall, J., Cutkosky, M.: Investigation of rotational skin stretch for proprioceptive feedback with application to myoelectric systems. IEEE Trans. Neural Syst. Rehabil. Eng. 18(1), 58–66 (2010)
Wong, E.Y., Israr, A., O’Malley, M.K.: Discrimination of consonant articulation location by tactile stimulation of the forearm. In: 2010 IEEE Haptics Symposium, pp. 47–54 (2010)
Yuan, H., Reed, C.M., Durlach, N.I.: Tactual display of consonant voicing as a supplement to lipreading. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 118(2), 1003–1015 (2005)
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by Facebook, Inc.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2018 Springer International Publishing AG, part of Springer Nature
About this paper
Cite this paper
Dunkelberger, N. et al. (2018). Improving Perception Accuracy with Multi-sensory Haptic Cue Delivery. In: Prattichizzo, D., Shinoda, H., Tan, H., Ruffaldi, E., Frisoli, A. (eds) Haptics: Science, Technology, and Applications. EuroHaptics 2018. Lecture Notes in Computer Science(), vol 10894. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-93399-3_26
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-93399-3_26
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-319-93398-6
Online ISBN: 978-3-319-93399-3
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)