Abstract
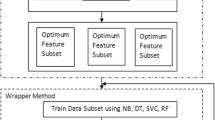
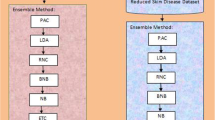
Feature extraction is a kind of dimensionality reduction which refers to the differentiating features of a dataset. In this study, we have worked on ESD_Data Set (33 attributes), composed of clinical and histopathological attributes of erythematous-squamous skin diseases (ESDs) (psoriasis, seborrheic dermatitis, lichen planus, pityriasis rosea, chronic dermatitis, pityriasis rubra pilaris). It’s aimed to obtain distinguishing significant attributes in ESD_Data Set for a successful classification of ESDs. We have focused on three areas: (a) By applying 1-D continuous wavelet coefficient analysis, Principle Component Analysis and Linear Discriminant Analysis to ESD_Data Set; w_ESD Data Set, p_ESD Data Set and l_ESD Data Set were formed. (b) By applying Support Vector Machine kernel algorithms (Linear, Quadratic, Cubic, Gaussian) to these datasets, accuracy rates were obtained. (c) w_ESD Data Set had the highest accuracy. This study seeks to identify deficiencies in literature to determine the distinguishing significant attributes in ESD_Data Set to classify ESDs.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Goldberg, D.E., Holland, J.H.: Genetic algorithms and machine learning. Mach. Learn. 3(2), 95–99 (1988)
Birdal, R.G., Gümüş, E., Sertbaş, A., Birdal, I.S.: Automated lesion detection in panoramic dental radiographs. Oral Radiol. 32(2), 111–118 (2016)
Karaca, Y., Cattani, C., Moonis, M., Bayrak, Ş.: Stroke subtype clustering by multifractal bayesian denoising with Fuzzy C Means and K-means algorithms. Complexity 2018, 1–15 (2018)
Griffiths, W.A.D.: Pityriasis rubra pilaris. Clin. Exp. Dermatol. 5(1), 105–112 (1980)
Kim, G.W., Jung, H.J., Ko, H.C., Kim, M.B., Lee, W.J., Lee, S.J., Kim, D.W., Kim, B.S.: Dermoscopy can be useful in differentiating scalp psoriasis from seborrhoeic dermatitis. Br. J. Dermatol. 164(3), 652–656 (2011)
Elic, R., Durocher, L.P., Kavalec, E.C.: Effect of salicylic acid on the activity of betamethasone-17, 21-dipropionate in the treatment of erythematous squamous dermatoses. J. Int. Med. Res. 11(2), 108–112 (1983)
Krain, L.S.: Dermatomyositis in six patients without initial muscle involvement. Arch. Dermatol. 111(2), 241–245 (1975)
Marzano, A.V., Borghi, A., Stadnicki, A., Crosti, C., Cugno, M.: Cutaneous manifestations in patients with inflammatory bowel diseases: pathophysiology, clinical features, and therapy. Inflamm. Bowel Dis. 20(1), 213–227 (2013)
Ziemer, M., Seyfarth, F., Elsner, P., Hipler, U.C.: Atypical manifestations of tinea corporis. Mycoses 50(s2), 31–35 (2007)
Bonerandi, J.J., Beauvillain, C., Caquant, L., Chassagne, J.F., Chaussade, V., Clavere, P., Desouches, C., Garnier, F., Grolleau, J.L., Grossin, M., Jourdain, A.: Guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma and precursor lesions. J. Eur. Acad. Dermatol. Venereol. 25(s5), 1–51 (2011)
Baxt, W.G.: Use of an artificial neural network for data analysis in clinical decision-making: the diagnosis of acute coronary occlusion. Neural Comput. 2(4), 480–489 (1990)
Ubeyli, E.D., Güler, I.: Automatic detection of erythemato-squamous diseases using adaptive neuro-fuzzy inference systems. Comput. Biol. Med. 35(5), 421–433 (2005)
Polat, K., Güneş, S.: A novel hybrid intelligent method based on C4. 5 decision tree classifier and one-against-all approach for multi-class classification problems. Expert Syst. Appl. 36(2), 1587–1592 (2009)
Guvenir, H.A., Demiröz, G., Ilter, N.: Learning differential diagnosis of erythemato-squamous diseases using voting feature intervals. Artif. Intell. Med. 13(3), 147–165 (1998)
Ubeyli, E.D., Doğdu, E.: Automatic detection of erythemato-squamous diseases using k-means clustering. J. Med. Syst. 34(2), 179–184 (2010)
Xie, J., Wang, C.: Using support vector machines with a novel hybrid feature selection method for diagnosis of erythemato-squamous diseases. Expert Syst. Appl. 38(5), 5809–5815 (2011)
Abdi, M.J., Giveki, D.: Automatic detection of erythemato - squamous diseases using PSO - SVM based on association rules. Eng. Appl. Artif. Intell. 26(1), 603–608 (2013)
Polat, K., Güneş, S.: The effect to diagnostic accuracy of decision tree classifier of fuzzy and k-NN based weighted pre-processing methods to diagnosis of erythemato-squamous diseases. Digit. Signal Proc. 16(6), 922–930 (2006)
Ozcift, A., Gulten, A.: Genetic algorithm wrapped Bayesian network feature selection applied to differential diagnosis of erythemato-squamous diseases. Digit. Signal Proc. 23(1), 230–237 (2013)
Asuncion, A., Newman, D.: UCI machine learning repository (2007)
Wickerhauser, M.V.: Adapted Wavelet Analysis from Theory to Software. IEEE Press, New York (1994)
Karaca, Y., Aslan, Z., Cattani, C., Galletta, D., Zhang, Y.: Rank determination of mental functions by 1D wavelets and partial correlation. J. Med. Syst. 41(2), 1–10 (2017)
Flandrin, P.: Wavelet analysis and synthesis of fractional Brownian motion. IEEE Trans. Inf. Theory 38(2), 910–917 (1992)
Jolliffe, I. T.: Principal component analysis and factor analysis. In: Principal Component Analysis, pp. 115–128. Springer (1986)
Wood, F., Esbensen, K., Geladi, P.: Principal component analysis. Chemometr. Intel. Lab. Syst 2(1987), 37–52 (1987)
Izenman, A.J.: Linear discriminant analysis. In: Modern Multivariate Statistical Techniques, pp. 237–280 (2013)
Mika, S., Ratsch, G., Weston, J., Scholkopf, B., Mullers, K.R.: August. Fisher discriminant analysis with kernels. In: Proceedings of the 1999 IEEE Signal Processing Society Workshop Neural Networks for Signal Processing IX, pp. 41–48 (1999)
Altman, E.I., Marco, G., Varetto, F.: Corporate distress diagnosis: comparisons using linear discriminant analysis and neural networks (the Italian experience). J. Bank. Financ. 18(3), 505–529 (1994)
Hearst, M.A., Dumais, S.T., Osuna, E., Platt, J., Scholkopf, B.: Support vector machines. IEEE Intell. Syst. Appl. 13(4), 18–28 (1998)
Karaca, Y., Zhang, Y., Cattani, C., Ayan, U.: The differential diagnosis of multiple sclerosis using convex combination of infinite kernels. CNS Neurol. Disord. Drug Targets (Formerly Current Drug Targets-CNS & Neurological Disorders) 16(1), 36–43 (2017)
Scholkopf, B., Smola, A.J.: Learning with Kernels: Support Vector Machines, Regularization, Optimization, and Beyond. MIT Press, Cambridge (2001)
Karaca, Y., Hayta, Ş.: Application and comparison of ANN and SVM for diagnostic classification for cognitive functioning. Appl. Math. Sci. 10(64), 3187–3199 (2016)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2018 Springer International Publishing AG, part of Springer Nature
About this paper
Cite this paper
Karaca, Y., Sertbaş, A., Bayrak, Ş. (2018). Classification of Erythematous - Squamous Skin Diseases Through SVM Kernels and Identification of Features with 1-D Continuous Wavelet Coefficient. In: Gervasi, O., et al. Computational Science and Its Applications – ICCSA 2018. ICCSA 2018. Lecture Notes in Computer Science(), vol 10961. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-95165-2_8
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-95165-2_8
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-319-95164-5
Online ISBN: 978-3-319-95165-2
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)