Abstract
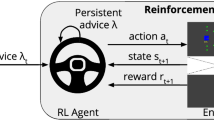
Action advice is an important mechanism to improve the learning speed of multiple agents. To do so, an advisor agent suggests actions to an advisee agent. In the current advising approaches, the advisor’s advice is always applicable based on the assumption that the advisor and advisee have the same objective, and the environment is stable. However, in many real-world applications, the advisor and advisee may have different objectives, and the environment may be dynamic. This would make the advisor’s advice not always applicable. In this paper, we propose an approach where the advisor and advisee jointly determine the applicability of advice by considering the different objectives and dynamic changes in the environment. The proposed approach is evaluated in various robot navigation domains. The evaluation results show that the proposed approach can determine the applicability of advice. The multi-agent learning speed can also be improved benefiting from determined applicable advice.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Amir, O., Kamar, E., Kolobov, A., Grosz, B.J.: Interactive teaching strategies for agent training. In: Proceedings of the 25th International Joint Conferences on Artificial Intelligence, pp. 804–811 (2016)
Busoniu, L., Babuska, R., De Schutter, B.: A comprehensive survey of multiagent reinforcement learning. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cybern. Part C Appl. Rev. 38(2), 156–172 (2008)
De Hauwere, Y.M., Vrancx, P., Nowé, A.: Learning what to observe in multi-agent systems. In: Proceedings of the 20th Belgian-Netherlands Conference on Artificial Intelligence, pp. 83–90. Citeseer (2009)
Maclin, R., Shavlik, J.W.: Creating advice-taking reinforcement learners. Mach. Learn. 22(1–3), 251–281 (1996)
Taylor, M.E., Carboni, N., Fachantidis, A., Vlahavas, I., Torrey, L.: Reinforcement learning agents providing advice in complex video games. Connect. Sci. 26(1), 45–63 (2014)
Taylor, M.E., Stone, P.: Transfer learning for reinforcement learning domains: a survey. J. Mach. Learn. Res. 10, 1633–1685 (2009)
Torrey, L., Taylor, M.: Teaching on a budget: agents advising agents in reinforcement learning. In: Proceedings of the 12th International Conference on Autonomous Agents and Multiagent systems, pp. 1053–1060 (2013)
Yu, C., Zhang, M., Ren, F.: Coordinated learning by exploiting sparse interaction in multiagent systems. Concurrency Comput. Pract. Experience 26(1), 51–70 (2014)
Yu, C., Zhang, M., Ren, F., Tan, G.: Multiagent learning of coordination in loosely coupled multiagent systems. IEEE Trans. Cybern. 45(12), 2853–2867 (2015)
Zhan, Y., Ammar, H.B., Taylor, M.E.: Theoretically-grounded policy advice from multiple teachers in reinforcement learning settings with applications to negative transfer. In: Proceedings of the 25th International Joint Conference on Artificial Intelligence, pp. 2315–2321 (2016)
Zhou, L., Yang, P., Chen, C., Gao, Y.: Multiagent reinforcement learning with sparse interactions by negotiation and knowledge transfer. IEEE Trans. Cybern. 47(5), 1238–1250 (2017)
Zimmer, M., Viappiani, P., Weng, P.: Teacher-student framework: a reinforcement learning approach. In: AAMAS Workshop Autonomous Robots and Multirobot Systems (2014)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2018 Springer International Publishing AG, part of Springer Nature
About this paper
Cite this paper
Wang, Y., Ren, F., Zhang, M. (2018). Determining the Applicability of Advice for Efficient Multi-Agent Reinforcement Learning. In: Geng, X., Kang, BH. (eds) PRICAI 2018: Trends in Artificial Intelligence. PRICAI 2018. Lecture Notes in Computer Science(), vol 11013. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-97310-4_39
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-97310-4_39
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-319-97309-8
Online ISBN: 978-3-319-97310-4
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)