Abstract
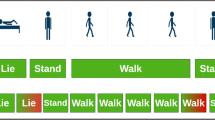
With the growing popularity of the Internet of Things and connected home products, potential healthcare applications in a smart-home context for assisted living are becoming increasingly apparent. However, challenges in performing real-time human activity recognition (HAR) from unlabelled data and adapting to changing user health remain a major barrier to the practicality of such applications. This paper aims to address these issues by proposing a semi-supervised adaptive HAR system which combines offline and online recognition techniques to provide intelligent real-time support for frequently repeated user activities. The viability of this approach is evaluated by pilot testing it on data from the Aruba CASAS dataset, and additional pilot data collected in the Bristol Robotics Lab’s Assisted Living Studio. The results show that 71% of activity instances were discovered, with an F1-score of 0.93 for the repeating “Meal_Prep” activities. Furthermore, real-time recognition on the collected pilot data occurred near the beginning of the activity 64% of the time and at the halfway point in the activity 96% of the time.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Demiris, G., Hensel, B.K.: Technologies for an aging society: a systematic review of “smart home” applications. Yearb Med. Inf. 3, 33–40 (2008)
Kvedar, J., Coye, M.J., Everett, W.: Connected health: a review of technologies and strategies to improve patient care with telemedicine and telehealth. Health Aff. (Millwood) 33, 194–199 (2014)
Shoaib, M., Bosch, S., Incel, O., Scholten, H., Havinga, P.: A survey of online activity recognition using mobile phones. Sensors 15, 2059–2085 (2015)
Ranasinghe, S., Al MacHot, F., Mayr, H.C.: A review on applications of activity recognition systems with regard to performance and evaluation. Int. J. Distrib. Sens. Netw. 12, 1550147716665520 (2016)
CASAS: Smart Home Projects, Washington State University (USA). http://casas.wsu.edu/
Pal, S., Feng, T., Abhayaratne, C.: Real-time recognition of activity levels for ambient assisted living. In: 5th IEEE International Conference Consumer Electronics - Berlin ICCE-Berlin 2015, pp. 485–488 (2016)
Roggen, D., Förster, K., Calatroni, A., Tröster, G.: The adARC pattern analysis architecture for adaptive human activity recognition systems. J. Ambient Intell. Humaniz. Comput. 4, 169–186 (2013)
Cardinaux, F., Bhowmik, D., Abhayaratne, C., Hawley, M.S.: Video based technology for ambient assisted living: A review of the literature. J. Ambient Intell. Smart Environ. 3, 253–269 (2011)
Basu, D., Moretti, G., Sen Gupta, G., Marsland, S.: Wireless sensor network based smart home: Sensor selection, deployment and monitoring. In: 2013 IEEE Sensors Applications Symposium, SAS 2013 – Proceedings, pp. 49–54 (2013)
Rashidi, P., Mihailidis, A.: A survey on ambient-assisted living tools for older adults. IEEE J. Biomed. Heal. Inform. 17, 579–590 (2013)
Boise, L., Wild, K., Mattek, N., Ruhl, M., Dodge, H.H., Kaye, J.: Willingness of older adults to share data and privacy concerns after exposure to unobtrusive home monitoring. Gerontechnology 11, 428–435 (2013)
Kwon, Y., Kang, K., Bae, C.: Unsupervised learning for human activity recognition using smartphone sensors. Expert Syst. Appl. 41, 6067–6074 (2014)
Yala, N., Fergani, B., Fleury, A.: Feature extraction and incremental learning to improve activity recognition on streaming data. In: 2015 IEEE International Conference on Evolving and Adaptive Intelligent Systems EAIS 2015, pp. 1–8 (2015)
Krishnan, N.C., Cook, D.J.: Activity recognition on streaming sensor data. Pervasive Mob. Comput. 10, 138–154 (2014)
Ntalampiras, S., Roveri, M.: An incremental learning mechanism for human activity recognition. In: 2016 IEEE Symposium Series on Computational Intelligence, pp. 1–6 (2016)
Storf, H., Kleinberger, T., Becker, M., Schmitt, M., Bomarius, F., Prueckner, S.: An event-driven approach to activity recognition in ambient assisted living. In: Tscheligi, M., et al. (eds.) AmI 2009. LNCS, vol. 5859, pp. 123–132. Springer, Heidelberg (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-05408-2_16
Cook, D.J.: Learning setting- generalized activity models for smart spaces. IEEE Intell. Syst. 27, 32–38 (2012)
Duda, R.O., Hart, P.E., Stork, D.G.: Pattern Classification, 2nd edn. John Wiley & Sons, Hoboken (2001)
Petitjean, F., Ketterlin, A., Gançarski, P.: A global averaging method for dynamic time warping, with applications to clustering. Pattern Recogn. 44, 678–693 (2011)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2018 Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this paper
Cite this paper
Gupta, P., Caleb-Solly, P. (2018). A Framework for Semi-Supervised Adaptive Learning for Activity Recognition in Healthcare Applications. In: Pimenidis, E., Jayne, C. (eds) Engineering Applications of Neural Networks. EANN 2018. Communications in Computer and Information Science, vol 893. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-98204-5_1
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-98204-5_1
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-319-98203-8
Online ISBN: 978-3-319-98204-5
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)