Abstract
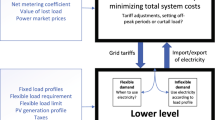
Real-time pricing (RTP) is a financial incentive mechanism designed to encourage demand response (DR) to reduce peak demand in medium and low voltage distribution networks but also impacting the generation and transmission system. Though RTP is believed to be an effective mechanism, challenges exist in implementing RTP for residential consumers wherein manually responding to a changing price is difficult and uncoordinated responses can lead to undesired peak demand at what are normally off-peak times. Previous research has proposed various algorithms to address these challenges, however, they rarely consider algorithms that manage very large numbers of houses and devices with discrete consumption levels. To optimise conflicting objectives under RTP prices in a fast and highly scalable manner is very challenging. We address these issues by proposing a fast and highly scalable algorithm that optimally schedules devices for large numbers of households in a distributed but non-cooperative manner under RTP. The results show that this algorithm minimises the total cost and discomfort for 10,000 households in a second and has a constant computational complexity.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Albadi, M.H., El-Saadany, E.F.: Demand response in electricity markets: an overview, June 2007
Anvari-Moghaddam, A., Monsef, H., Rahimi-Kian, A.: Optimal smart home energy management considering energy saving and a comfortable lifestyle. IEEE Trans. Smart Grid 6(1), 324–332 (2015)
Ausgrid: Appliance usage guide. http://www.ausgrid.com.au/Common/Customer-Services/Homes/Energy-efficiency/Energy-efficiency-at-home-tips/Energy-usage-calculators/~/media/Files/Customer
Barbato, A., Capone, A., Carello, G., Delfanti, M., Merlo, M., Zaminga, A.: House energy demand optimization in single and multi-user scenarios. In: 2011 IEEE International Conference on Smart Grid Communications (SmartGridComm), pp. 345–350, October 2011
Chapman, A.C., Rogers, A., Jennings, N.R., Leslie, D.S.: A unifying framework for iterative approximate best-response algorithms for distributed constraint optimization problems. Knowl. Eng. Rev. 26(4), 411–444 (2011)
Chavali, P., Yang, P., Nehorai, A.: A distributed algorithm of appliance scheduling for home energy management system. IEEE Trans. Smart Grid 5(1), 282–290 (2014)
Chen, L., Li, N., Low, S.H., Doyle, J.C.: Two market models for demand response in power networks. In: 2010 First IEEE International Conference on Smart Grid Communications (SmartGridComm), pp. 397–402, October 2010
Fan, Z.: Distributed demand response and user adaptation in smart grids. In: 12th IFIP/IEEE International Symposium on Integrated Network Management (IM 2011) and Workshops, pp. 726–729, May 2011
Fioretto, F., Yeoh, W., Pontelli, E.: A multiagent system approach to scheduling devices in smart homes. In: Proceedings of the 16th Conference on Autonomous Agents and MultiAgent Systems, AAMAS 2017, pp. 981–989. International Foundation for Autonomous Agents and Multiagent Systems, Richland, SC (2017). http://dl.acm.org/citation.cfm?id=3091125.3091265
Frank, M., Wolfe, P.: An algorithm for quadratic programming. Naval Res. Logist. Q. 3(1–2), 95–110 (1956)
Goudarzi, H., Hatami, S., Pedram, M.: Demand-side load scheduling incentivized by dynamic energy prices. In: 2011 IEEE International Conference on Smart Grid Communications (SmartGridComm), pp. 351–356, October 2011
He, S., Liebman, A., Rendl, A., Wallace, M., Wilson, C.: Modelling RTP-based residential load scheduling for demand response in smart grids. In: Ansotegui, C. (ed.) Proceedings of the Thirteenth International Workshop on Constraint Modelling and Reformulation (ModRef 2014), pp. 36–51. Universitat de Lleida (2014)
Joe-Wong, C., Sen, S., Ha, S., Chiang, M.: Optimized day-ahead pricing for smart grids with device-specific scheduling flexibility. IEEE J. Sel. Areas Commun. 30(6), 1075–1085 (2012)
Kanchev, H., Lu, D., Colas, F., Lazarov, V., Francois, B.: Energy management and operational planning of a microgrid with a PV-based active generator for smart grid applications. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 58(10), 4583–4592 (2011)
Kim, S.J., Giannakis, G.B.: Scalable and robust demand response with mixed-integer constraints. IEEE Trans. Smart Grid 4(4), 2089–2099 (2013)
Kuschel, C., Köstler, H., Rüde, U.: Multi-energy simulation of a smart grid with optimal local demand and supply management. Smart Grid Renew. Energy 06(11), 303–315 (2015)
Li, N., Chen, L., Low, S.H.: Optimal demand response based on utility maximization in power networks. In: 2011 IEEE Power and Energy Society General Meeting, pp. 1–8, July 2011
Li, Y., Ng, B.L., Trayer, M., Liu, L.: Automated residential demand response: algorithmic implications of pricing models. IEEE Trans. Smart Grid 3(4), 1712–1721 (2012)
Mhanna, S., Chapman, A.C., Verbic, G.: A fast distributed algorithm for large-scale demand response aggregation. CoRR abs/1603.00149 (2016). http://arxiv.org/abs/1603.00149
Mohamed, F.A., Koivo, H.N.: Microgrid online management and balancing using multiobjective optimization. In: 2007 IEEE Lausanne Power Tech, pp. 639–644, July 2007
Mohsenian-Rad, A.H., Leon-Garcia, A.: Optimal residential load control with price prediction in real-time electricity pricing environments. IEEE Trans. Smart Grid 1(2), 120–133 (2010)
Mohsenian-Rad, A.H., Wong, V.W.S., Jatskevich, J., Schober, R., Leon-Garcia, A.: Autonomous demand-side management based on game-theoretic energy consumption scheduling for the future smart grid. IEEE Trans. Smart Grid 1(3), 320–331 (2010)
Ramchurn, S.D., Vytelingum, P., Rogers, A., Jennings, N.: Agent-based control for decentralised demand side management in the smart grid. In: The 10th International Conference on Autonomous Agents and Multiagent Systems, AAMAS 2011, vol. 1, pp. 5–12. International Foundation for Autonomous Agents and Multiagent Systems, Richland (2011). http://dl.acm.org/citation.cfm?id=2030470.2030472
Ren, D., Li, H., Ji, Y.: Home energy management system for the residential load control based on the price prediction. In: 2011 IEEE Online Conference on Green Communications, pp. 1–6, September 2011
Samadi, P., Mohsenian-Rad, A.H., Schober, R., Wong, V.W.S., Jatskevich, J.: Optimal real-time pricing algorithm based on utility maximization for smart grid. In: 2010 First IEEE International Conference on Smart Grid Communications (SmartGridComm), pp. 415–420, October 2010
Sheffi, Y.: Urban Transportation Networks: Equilibrium Analysis with Mathematical Programming Methods. Prentice-Hall, Englewood Cliffs (1985)
Shi, W., Xie, X., Chu, C.C., Gadh, R.: Distributed optimal energy management in microgrids. IEEE Trans. Smart Grid 6(3), 1137–1146 (2015)
Sou, K.C., Weimer, J., Sandberg, H., Johansson, K.H.: Scheduling smart home appliances using mixed integer linear programming. In: 2011 50th IEEE Conference on Decision and Control and European Control Conference, pp. 5144–5149, December 2011
Van Den Briel, M., Scott, P., Thiébaux, S.: Randomized load control: a simple distributed approach for scheduling smart appliances. In: Proceedings of the Twenty-Third International Joint Conference on Artificial Intelligence, IJCAI 2013, pp. 2915–2922. AAAI Press (2013). http://dl.acm.org/citation.cfm?id=2540128.2540548
Veit, A., Xu, Y., Zheng, R., Chakraborty, N., Sycara, K.: Demand side energy management via multiagent coordination in consumer cooperatives. J. Artif. Int. Res. 50(1), 885–922, May 2014. http://dl.acm.org/citation.cfm?id=2693068.2693091
Voice, T.D., Vytelingum, P., Ramchurn, S.D., Rogers, A., Jennings, N.R.: Decentralised control of micro-storage in the smart grid. In: Proceedings of the Twenty-Fifth AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, AAAI 2011, pp. 1421–1427. AAAI Press (2011). http://dl.acm.org/citation.cfm?id=2900423.2900648
Vytelingum, P., Voice, T.D., Ramchurn, S.D., Rogers, A., Jennings, N.R.: Agent-based micro-storage management for the smart grid. In: Proceedings of the 9th International Conference on Autonomous Agents and Multiagent Systems: Volume 1, AAMAS 2010, vol. 1, pp. 39–46. International Foundation for Autonomous Agents and Multiagent Systems, Richland (2010). http://dl.acm.org/citation.cfm?id=1838206.1838212
Wang, Y., Mao, S., Nelms, R.M.: Distributed online algorithm for optimal real-time energy distribution in the smart grid. IEEE Internet Things J. 1(1), 70–80 (2014)
Yu, R., Yang, W., Rahardja, S.: Optimal real-time price based on a statistical demand elasticity model of electricity. In: 2011 IEEE First International Workshop on Smart Grid Modeling and Simulation (SGMS), pp. 90–95, October 2011
Zhang, W., Xu, Y., Liu, W., Zang, C., Yu, H.: Distributed online optimal energy management for smart grids. IEEE Trans. Ind. Inform. 11(3), 717–727 (2015)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2018 Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this paper
Cite this paper
He, S., Wallace, M., Gange, G., Liebman, A., Wilson, C. (2018). A Fast and Scalable Algorithm for Scheduling Large Numbers of Devices Under Real-Time Pricing. In: Hooker, J. (eds) Principles and Practice of Constraint Programming. CP 2018. Lecture Notes in Computer Science(), vol 11008. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-98334-9_42
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-98334-9_42
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-319-98333-2
Online ISBN: 978-3-319-98334-9
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)